Abstract
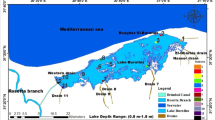
Water clarity in three lakes, Chagan, Xinmiao, and Kuli, in northeast China was evaluated based on Landsat TM data and in situ measurements in this study. The agreement between satellite data and water clarity from field-collected Secchi disk depth (SDD) for individual lakes was strong (0.72 ≤ R 2 ≤ 0.98), and four regression equations were used to estimate SDD values. Lake clarity showed strong geographic patterns: Lake Chagan had low clarity and Lake Xinmiao and Kuli had high clarity. The study indicates that Landsat TM can be effectively applied to estimate water clarity for inland lakes in the area.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allee RJ, Johnson JE (1999) Use of satellite imagery to estimate surface chlorophyll a and Secchi disc depth of Bull Shoals Reservoir, Arkansas, USA. Int J Remote Sens 20:1057–1072. doi:10.1080/014311699212830
Chen Z, Muller-Karger FE, Hu C (2007) Remote sensing of water clarity in Tampa Bay. Remote Sens Environ 109:249–259. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2007.01.002
Dekker AG, Peters SWM (1993) The use of the Thematic Mapper for the analysis of eutrophic lakes: a case study in the Netherlands. Int J Remote Sens 14:799–821. doi:10.1080/01431169308904379
Duan H, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Song K, Wang Z, Liu D, Li F (2008) Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and trophic states for inland lakes in Northeast China from Landsat TM data and field spectral measurements. Int J Remote Sens 29:767–786. doi:10.1080/01431160701355249
Fraser RN (1998a) Hyperspectral remote sensing of turbidity and chlorophyll a among Nebraska Sand Hills lakes. Int J Remote Sens 19:1579–1589. doi:10.1080/014311698215360
Fraser RN (1998b) Multispectral remote sensing of turbidity among Nebraska Sand Hills lakes. Int J Remote Sens 19:3011–3016. doi:10.1080/014311698214406
Ghulam A, Qin Q, Zhu L, Abdrahman P (2004) Satellite remote sensing of groundwater: quantitative modelling and uncertainty reduction using 6S atmospheric simulations. Int J Remote Sens 25:5509–5524. doi:10.1080/01431160410001719821
Giardino C, Pepe M, Brivio PA, Ghezzi P, Zilioli E (2001) Detecting chlorophyll, Secchi disk depth and surface temperature in a sub-alpine lake using Landsat imagery. Sci Total Environ 268:19–29. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00692-6
Harma P, Vepsalainen J, Hannonen T, Pyhalahti T, Kamari J, Kallio K, Eloheimo K, Koponen S (2001) Detection of water quality using simulated satellite data and semi-empirical algorithms in Finland. Sci Total Environ 268:107–121. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00688-4
Heiskary SA, Walker WWJr (1988) Developing phosphorus criteria for Minnesota lakes. Lake Reservoir Manage 4:1–9
Khan FA, Ansari AA (2005) Eutrophication: an ecological vision. Bot Rev 71:449–482. doi:10.1663/0006-8101(2005)071
Kloiber SM, Brezonik PL, Olmanson LG, Bauer ME (2002) A procedure for regional lake water clarity assessment using Landsat multispectral data. Remote Sens Environ 82:38–47. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00022-6
Lathrop RG (1992) Landsat Thematic Mapper monitoring of turbid inland water quality. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 58:465–470
Lathrop RG, Lillesand TM (1986) Use of Thematic Mapper data to assess water quality in Green Bay and Central Lake Michigan. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 52:671–680
Lavery P, Pattiaratchi C, Wyllie A, Hick P (1993) Water quality monitoring in estuarine waters using the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens Environ 46:268–280. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(93)90047-2
Lee T, Kaufman Y (1986) Non-Lambertian effects on remote-sensing of surface reflectance and vegetation index. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 24:699–708. doi:10.1109/TGRS.1986.289617
Lindell T, Pierson D, Premazzi G, Zilioli E (1999) Manual for monitoring European lakes using remote sensing techniques. Report EUR 18665. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Olmanson LG, Bauer ME, Brezonik PL (2008) A 20-year Landsat water clarity census of Minnesota’s 10,000 lakes. Remote Sens Environ 112(11):4086–4097. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2007.12.013
Schneider K, Mauser W (1996) Processing and accuracy of Landsat thematic mapper for lake surface temperature measurement. Int J Remote Sens 11:2027–2041. doi:10.1080/01431169608948757
Wu GF, Leeuw JD, Skidmore AK, Prins HHT, Liu Y (2008) Comparison of MODIS and Landsat TM5 images for mapping tempo-spatial dynamics of Secchi disk depths in Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Int J Remote Sens 29:2183–2198. doi:10.1080/01431160701422254
Yu MR, Shen SD, Zhu MY (1993) The eco-environment changes and the use of protection in Lake Chagan (in Chinese). Jilin Water Resour 5:22–24
Zilioli E, Brivio PA (1997) The satellite derived optical information for the comparative assessment of lacustrine water quality. Sci Total Environ 196:229–245. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(96)05411-3
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Special Prize of President Scholarship for Postgraduate Students of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 07YJ011001), the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. CXNIGLAS200807), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40801137, 40871168) for providing financial support. Thanks are also due to two anonymous reviewers who offered helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, H., Ma, R., Zhang, Y. et al. Remote-sensing assessment of regional inland lake water clarity in northeast China. Limnology 10, 135–141 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-009-0263-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-009-0263-y