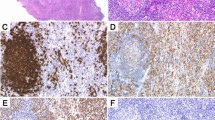
Abstract
A 54-year-old woman with suspected low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type of the eyelids underwent rituximab-containing chemotherapy. She initially responded to the rituximab therapy, but later experienced two recurrences over a 3-year period. Biopsy specimens and a review of her previous histology revealed that she had had immunoglobulin G4-related disease at the initial presentation. Although IgG4-related disease seems to respond well to rituximab therapy, long-term follow up, including disease monitoring, is needed to evaluate disease remission.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–8.
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. Autoimmune pancreatitis: proposal of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:613–25.
Masaki Y, Kurose N, Umehara H. IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J Clin Exp Hematopathol. 2010;51(1):13–20.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(1):1–14.
Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Takahashi H, et al. Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33(6):432–3.
Masaki Y, Sugai S, Umehara H. IgG4-related diseases including Mikulicz’s disease and sclerosing pancreatitis: diagnostic insights. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:1380–5.
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, Kitagawa K, Morikawa Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multi-organ lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1310–5.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Kawano M, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010;78:1016–23.
Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011;15(5):615–26.
Sato Y, Notohara K, Kojima M, Takata K, Masaki Y, Yoshino T, et al. IgG4-related diseases: historical overview and pathology of hematological disorders. Pathol Int. 2010;60:247–58.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30.
Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51.
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, Nishino T, Watanabe H, Kanno A, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009;58:1504–7.
Ghazale A, Chari ST, Zhang L, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Levy MJ, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:706–15.
Topazian M, Witzig TE, Smyrk TC, Pulido JS, Levy MJ, Kamath PS, et al. Rituximab therapy for refractory biliary strictures in immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:364–6.
Zaidan M, Cervera-Pierot P, de Seigneux S, Dahan K, Fabiani B, Callard P, et al. Evidence of follicular T-cell implication in a case of IgG4-related systemic disease with interstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:2047–50.
Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1755–62.
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, Stone JH. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine. 2012;91:57–66.
Khan ML, Colby TV, Viggiano RW, Fonseca R. Treatment with bortezomib of a patient having hyper IgG4 disease. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010;10:217–9.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, J., Matsui, S., Ishizawa, S. et al. Recurrence of IgG4-related disease following treatment with rituximab. Mod Rheumatol 23, 1226–1230 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-012-0738-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-012-0738-2