ABSTRACT
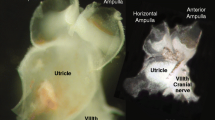
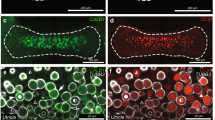
The afferent encoding of vestibular stimuli depends on molecular mechanisms that regulate membrane potential, concentration gradients, and ion and neurotransmitter clearance at both afferent and efferent relays. In many cell types, the Na,K-ATPase (NKA) is essential for establishing hyperpolarized membrane potentials and mediating both primary and secondary active transport required for ion and neurotransmitter clearance. In vestibular sensory epithelia, a calyx nerve ending envelopes each type I hair cell, isolating it over most of its surface from support cells and posing special challenges for ion and neurotransmitter clearance. We used immunofluorescence and high-resolution confocal microscopy to examine the cellular and subcellular patterns of NKAα subunit expression within the sensory epithelia of semicircular canals as well as an otolith organ (the utricle). Results were similar for both kinds of vestibular organ. The neuronal NKAα3 subunit was detected in all afferent endings—both the calyx afferent endings on type I hair cells and bouton afferent endings on type II hair cells—but was not detected in efferent terminals. In contrast to previous results in the cochlea, the NKAα1 subunit was detected in hair cells (both type I and type II) but not in supporting cells. The expression of distinct NKAα subunits by vestibular hair cells and their afferent endings may be needed to support and shape the high rates of glutamatergic neurotransmission and spike initiation at the unusual type I-calyx synapse.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arystarkhova E, Sweadner KJ (1996) Isoform-specific monoclonal antibodies to Na,K-ATPase alpha subunits. Evidence for a tissue-specific post-translational modification of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 271:23407–23417
Beart PM, O’Shea RD (2007) Transporters for L-glutamate: an update on their molecular pharmacology and pathological involvement. Br J Pharmacol 150:5–17
Beisel KW, Rocha-Sanchez SM, Morris KA, Nie L, Feng F, Kachar B, Yamoah EN, Fritzsch B (2005) Differential expression of KCNQ4 in inner hair cells and sensory neurons is the basis of progressive high-frequency hearing loss. J Neurosci 25:9285–9293
Blanco G, Sanchez G, Melton RJ, Tourtellotte WG, Mercer RW (2000) The alpha4 isoform of the Na,K-ATPase is expressed in the germ cells of the testes. J Histochem Cytochem 48:1023–1032
Contini D, Zampini V, Tavazzani E, Magistretti J, Russo G, Prigioni I, Masetto S (2012) Intercellular K(+) accumulation depolarizes type I vestibular hair cells and their associated afferent nerve calyx. Neuroscience 227:232–246
Dalet A, Bonsacquet J, Gaboyard-Niay S, Calin-Jageman I, Chidavaenzi RL, Venteo S, Desmadryl G, Goldberg JM, Lysakowski A, Chabbert C (2012) Glutamate transporters EAAT4 and EAAT5 are expressed in vestibular hair cells and calyx endings. PLoS One 7:e46261
Dememes D, Broca C (1998) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the rat efferent vestibular system during development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 108:59–67
Desai SS, Zeh C, Lysakowski A (2005a) Comparative morphology of rodent vestibular periphery. I. Saccular and utricular maculae. J Neurophysiol 93:251–266
Desai SS, Ali H, Lysakowski A (2005b) Comparative morphology of rodent vestibular periphery. II. Cristae ampullares. J Neurophysiol 93:267–280
Desmadryl G, Dechesne CJ (1992) Calretinin immunoreactivity in chinchilla and guinea pig vestibular end organs characterizes the calyx unit subpopulation. Exp Brain Res 89:105–108
Dobretsov M, Stimers JR (2005) Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci 10:2373–2396
Eatock RA, Songer JE (2011) Vestibular hair cells and afferents: two channels for head motion signals. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:501–534
Favre D, Scarfone E, Di Gioia G, De Camilli P, Dememes D (1986) Presence of synapsin I in afferent and efferent nerve endings of vestibular sensory epithelia. Brain Res 384:379–382
Fernandez C, Baird RA, Goldberg JM (1988) The vestibular nerve of the chinchilla. I. Peripheral innervation patterns in the horizontal and superior semicircular canals. J Neurophysiol 60:167–181
Fernandez C, Goldberg JM, Baird RA (1990) The vestibular nerve of the chinchilla. III. Peripheral innervation patterns in the utricular macula. J Neurophysiol 63:767–780
Fina M, Ryan A (1994) Expression of mRNAs encoding alpha and beta subunit isoforms of Na,K-ATPase in the vestibular labyrinth and endolymphatic sac of the rat. Mol Cell Neurosci 5:604–613
Geering K (2008) Functional roles of Na,K-ATPase subunits. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:526–532
Goldberg JM (1996) Theoretical analysis of intercellular communication between the vestibular type I hair cell and its calyx ending. J Neurophysiol 76:1942–1957
Hasson T, Gillespie PG, Garcia JA, MacDonald RB, Zhao Y, Yee AG, Mooseker MS, Corey DP (1997) Unconventional myosins in inner-ear sensory epithelia. J Cell Biol 137:1287–1307
Hurley KM, Gaboyard S, Zhong M, Price SD, Wooltorton JR, Lysakowski A, Eatock RA (2006) M-like K + currents in type I hair cells and calyx afferent endings of the developing rat utricle. J Neurosci 26:10253–10269
Ichimiya I, Adams JC, Kimura RS (1994) Immunolocalization of Na+, K(+)-ATPase, Ca(++)-ATPase, calcium-binding proteins, and carbonic anhydrase in the guinea pig inner ear. Acta Otolaryngol 114:167–176
Leonard RB, Kevetter GA (2002) Molecular probes of the vestibular nerve. I. Peripheral termination patterns of calretinin, calbindin and peripherin containing fibers. Brain Res 928:8–17
Lim R, Kindig AE, Donne SW, Callister RJ, Brichta AM (2011) Potassium accumulation between type I hair cells and calyx terminals in mouse crista. Exp Brain Res 210:607–621
Lysakowski A, Gaboyard-Niay S, Calin-Jageman I, Chatlani S, Price SD, Eatock RA (2011) Molecular microdomains in a sensory terminal, the vestibular calyx ending. J Neurosci 31:10101–10114
McGuirt JP, Schulte BA (1994) Distribution of immunoreactive alpha- and beta-subunit isoforms of Na,K-ATPase in the gerbil inner ear. J Histochem Cytochem 42:843–853
McLean WJ, Smith KA, Glowatzki E, Pyott SJ (2009) Distribution of the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit in the rat spiral ganglion and organ of corti. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 10:37–49
Meza G, Acuna D, Gutierrez A, Merchan JM, Rueda J (1996) Development of vestibular function: biochemical, morphological and electronystagmographical assessment in the rat. Int J Dev Neurosci 14:507–513
Perry B, Jensen-Smith HC, Luduena RF, Hallworth R (2003) Selective expression of beta tubulin isotypes in gerbil vestibular sensory epithelia and neurons. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 4:329–338
Pressley TA (1992) Phylogenetic conservation of isoform-specific regions within alpha-subunit of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. Am J Physiol 262:C743–751
Rocha-Sanchez SM, Morris KA, Kachar B, Nichols D, Fritzsch B, Beisel KW (2007) Developmental expression of Kcnq4 in vestibular neurons and neurosensory epithelia. Brain Res 1139:117–125
Rose EM, Koo JC, Antflick JE, Ahmed SM, Angers S, Hampson DR (2009) Glutamate transporter coupling to Na,K-ATPase. J Neurosci 29:8143–8155
Rüsch A, Lysakowski A, Eatock RA (1998) Postnatal development of type I and type II hair cells in the mouse utricle: acquisition of voltage-gated conductances and differentiated morphology. J Neurosci 18:7487–7501
Scarfone E, Dememes D, Jahn R, De Camilli P, Sans A (1988) Secretory function of the vestibular nerve calyx suggested by presence of vesicles, synapsin I, and synaptophysin. J Neurosci 8:4640–4645
Schulte BA, Steel KP (1994) Expression of alpha and beta subunit isoforms of Na,K-ATPase in the mouse inner ear and changes with mutations at the Wv or Sld loci. Hear Res 78:65–76
Sheean RK, Lau CL, Shin YS, O’Shea RD, Beart PM (2013) Links between l-glutamate transporters, Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase and cytoskeleton in astrocytes: evidence following inhibition with Rottlerin. Neuroscience 254:335–346
Songer JE, Eatock RA (2013) Tuning and timing in mammalian type I hair cells and calyceal synapses. J Neurosci 33:3706–3724
Spicer SS, Schulte BA, Adams JC (1990) Immunolocalization of Na+, K(+)-ATPase and carbonic anhydrase in the gerbil’s vestibular system. Hear Res 43:205–217
Spitzmaul G, Tolosa L, Winkelman BH, Heidenreich M, Frens MA, Chabbert C, de Zeeuw CI, Jentsch TJ (2013) Vestibular role of KCNQ4 and KCNQ5 K+ channels revealed by mouse models. J Biol Chem 288:9334–9344
ten Cate WJ, Curtis LM, Rarey KE (1994) Na,K-ATPase alpha and beta subunit isoform distribution in the rat cochlear and vestibular tissues. Hear Res 75:151–160
Wangemann P (2002) K+ cycling and the endocochlear potential. Hear Res 165:1–9
Zerangue N, Kavanaugh MP (1996) Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 383:634–637
Zhang D, Hou Q, Wang M, Lin A, Jarzylo L, Navis A, Raissi A, Liu F, Man HY (2009) Na,K-ATPase activity regulates AMPA receptor turnover through proteasome-mediated proteolysis. J Neurosci 29:4498–4511
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Dwayne Simmons for the original suggestion to compare profile and cross-sectional views of the vestibular sensory epithelia. We gratefully acknowledge funds from UNC Wilmington to O. S. and S. J. P. and from NIDCD R01 DC0002290 and DC0012347 to R. A. E.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuth, O., McLean, W.J., Eatock, R.A. et al. Distribution of Na,K-ATPase α Subunits in Rat Vestibular Sensory Epithelia. JARO 15, 739–754 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-014-0479-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-014-0479-3