Abstract
Background
Naturally occurring regulatory T cells (Treg) are essential for the prevention of autoimmunity and overshooting immune responses to pathogens; however, the involvement of Treg in mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis, a major cause of chronic kidney disease, remains unclear. Superagonistic CD28-specific monoclonal antibodies (CD28SA) are highly effective activators of Treg in rats.
Method
To confirm our hypothesis that CD28SA reduces the severity of experimental glomerulonephritis, anti-Thy1 nephritis model rats were treated with CD28SA or saline.
Results
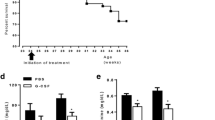
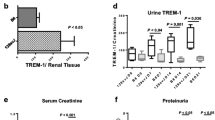
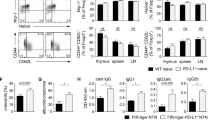
CD28SA significantly suppressed the increase in proteinuria and serum creatinine levels. CD28SA-treated nephritic rats exhibited an increase in the infiltration of Treg in the glomeruli accompanied by infiltration of CD163-positive macrophages (“alternatively activated” macrophages). In addition, CD28SA significantly induced interleukin-10 mRNA expression in glomeruli, thereby ameliorating mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix expansion.
Conclusion
We established a new therapeutic approach to suppressing progressive glomerulonephritis. The therapeutic value of this approach warrants further attention and preclinical studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers CE, Hudkins KL, Gown AM, Johnson RJ. Enhanced expression of “muscle-specific” actin in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1992;41:1134–42.
Striker LJ, Peten EP, Elliot SJ, Doi T, Striker GE. Mesangial cell turnover: effect of heparin and peptide growth factors. Lab Invest. 1991;64:446–56.
Mukai K, Shibata T, Kato K, Sugisaki T. Adjuvant-induced macrophage-dominant nephrotoxic serum nephritis in rats. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2005;9:15–23.
Huang XR, Tipping PG, Shuo L, Holdsworth SR. Th1 responsiveness to nephritogenic antigens determines susceptibility to crescentic glomerulonephritis in mice. Kidney Int. 1997;51:94–103.
El-Shemi AG, Fujinaka H, Matsuki A, Kamiie J, Kovalenko P, Qu Z, et al. Suppression of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis by interleukin-10 gene transfer. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1280–9.
Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nature Immunol. 2005;6:345–52.
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H, Hori S, Fehervari Z, et al. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:8–27.
Beyersdorf N, Gaupp S, Balbach K, Schmidt J, Toyka KV, Lin CH, et al. Selective targeting of regulatory T cells with CD28 superagonists allows effective therapy of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 2005;202:445–55.
Luhder F, Huang Y, Dennehy KM, Guntermann C, Muller I, Winkler E, et al. Topological requirements and signaling properties of T cell-activating, anti-CD28 antibody superagonists. J Exp Med. 2003;197:955–66.
Tacke M, Clark GJ, Dallman MJ, Hunig T. Cellular distribution and costimulatory function of rat CD28. Regulated expression during thymocyte maturation and induction of cyclosporin A sensitivity of costimulated T cell responses by phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1995;154:5121–7.
Lin CH, Hunig T. Efficient expansion of regulatory T cells in vitro and in vivo with a CD28 superagonist. Eur J Immunol. 2003;33:626–38.
Kawachi H, Orikasa M, Matsui K, Iwanaga T, Toyabe S, Oite T, et al. Epitope-specific induction of mesangial lesions with proteinuria by a MoAb against mesangial cell surface antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992;88:399–404.
Yamamoto T, Wilson CB. Complement dependence of antibody-induced mesangial cell injury in the rat. J Immunol. 1987;138:3758–65.
Takabatake Y, Isaka Y, Mizui M, Kawachi H, Shimizu F, Ito T, et al. Exploring RNA interference as a therapeutic strategy for renal disease. Gene Ther. 2005;12:965–73.
Azuma H, Isaka Y, Li X, Hunig T, Sakamoto T, Nohmi H, et al. Superagonistic CD28 antibody induces donor-specific tolerance in rat renal allografts. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:2004–14.
Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:958–69.
Mosser DM. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:209–12.
Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Roncarolo MG. Rapamycin selectively expands CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Blood. 2005;105:4743–8.
Mahajan D, Wang Y, Qin X, Zheng G, Wang YM, Alexander SI, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells protect against injury in an innate murine model of chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2731–41.
Wang YM, Zhang GY, Wang Y, Hu M, Wu H, Watson D, et al. Foxp3-transduced polyclonal regulatory T cells protect against chronic renal injury from adriamycin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:697–706.
Wolf D, Hochegger K, Wolf AM, Rumpold HF, Gastl G, Tilg H, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells inhibit experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis in mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1360–70.
Tiemessen MM, Jagger AL, Evans HG, van Herwijnen MJ, John S, Taams LS. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:19446–51.
Miyara M, Sakaguchi S. Natural regulatory T cells: mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:108–16.
Vignali DA, Collison LW, Workman CJ. How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:523–32.
Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, Brett SJ, Castello-Cortes A, Brunner MD, et al. Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1018–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Miyasato, K., Takabatake, Y., Kaimori, J. et al. CD28 superagonist-induced regulatory T cell expansion ameliorates mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis in rats. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 50–57 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0370-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0370-4