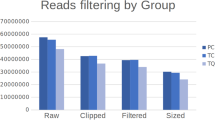
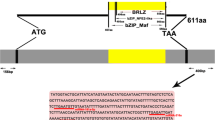
Abstract
The Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi) is one of the most commercially important carnivorous fish species in aquaculture with its large-scale culture in China. Increasing evidence suggests that microRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in muscle cell proliferation and differentiation. However, the knowledge of the identity of myogenic miRNAs and the effect of nutrient status on miRNA expression in teleost remains limited. In the present study, among the 21 miRNAs identified with high abundance in the fast muscle of adult Chinese perch, 19 miRNAs were differentially expressed in the adults and juveniles. The postprandial changes in the transcript abundance were determined for the 21 miRNAs following a single satiating meal in the juveniles after fasting for 1 week. The results showed that the seven miRNAs (miR-10c, miR-107a, miR-133a-3p, miR-140-3p, miR-181a-5p, miR-206, and miR-214) were sharply upregulated or downregulated within 1 h after refeeding. These miRNAs may be the promising candidate miRNAs involved in a fast-response signaling system that regulates fish skeletal muscle growth. Target prediction and expressional analysis suggested that four miRNAs (miR-10c, miR-107a, miR-140-3p, and miR-181a-5p) might play a role in regulating the translation of target gene transcripts such as myostatin following acute anabolic stimuli.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amthor H, Macharia R, Navarrete R, Schuelke M, Brown SC, Otto A, Voit T, Muntoni F, Vrbova G, Partridge T, Zammit P, Bunger L, Patel K (2007) Lack of myostatin results in excessive muscle growth but impaired force generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1835–1840
Ballantyne JS (2001) Amino acid metabolism. In: Wright PA, Anderson AJ (eds) Nitrogen excretion, vol 20, Fish physiology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 77–107
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bower NI, Johnston IA (2010) Discovery and characterization of nutritionally regulated genes associated with muscle growth in Atlantic salmon. Physiol Genomics 42A:114–130
Bower NI, Li X, Taylor R, Johnston IA (2008) Switching to fast growth: the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in skeletal muscle of Atlantic salmon. J Exp Biol 211:3859–3870
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622
Carter C, Houlihan D, Kiessling A, Médale F, Jobling M (2001) Physiological effects of feeding. In Food intake in fish. Ed. by D.Houlihan., T. Boujard. and M.Jobling. Blackwell Science, UK. vol. 1, pp 297–331
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q, Callis TE, Hammond SM, Conlon FL, Wang DZ (2006) The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet 38:228–233
Chu WY, Fu GH, Chen J, Chen DG, Meng T, Zhou RX, Xj X, Zhang JS (2010) Gene expression profiles of the muscle tissues of the commercial important teleost, Siniperca chuatsi L. Aquacult Int 18:667–678
Chu WY, Liu LS, Li YL, Chen L, Wang KZ, Li HH, Du SJ, Zhang JS (2013) Systematic identification and differential expression profiling of microRNAs from white and red muscles of Siniperca chuatsi. Curr Mol Med 13:1397–1407
Drummond MJ, Glynn EL, Fry CS, Dhanani V, Shaheen E, Asmussen BB (2009) Essential amino acids increase microRNA-499, -208b, and -23a and downregulate myostatin and myocyte enhancer factor 2C mRNA expression in human skeletal muscle. J Nutr 139:2279–2284
Eisenberg I, Alexander MS, Kunkel LM (2009) miRNAs in normal and diseased skeletal muscle. J Cell Mol Med 13:2–11
Fauconneau B, Paboeuf G (2000) Effect of fasting and refeeding on in vitro muscle cell proliferation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cell Tissue Res 301:459–463
Flynt AS, Li N, Thatcher EJ, Solnica-Krezel L, Patton JG (2007) Zebrafish miR-214 modulates Hedgehog signaling to specify muscle cell fate. Nat Genet 39:259–263
Fu YS, Shi ZY, Wu ML, Zhang JL, Jia L, Chen XW (2011) Identification and differential expression of microRNAs during metamorphosis of the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). PLoS One 6:e22957
Fuentes EN, Ruiz P, Valdes JA, Molina A (2012) Catabolic signaling pathways, atrogenes, and ubiquitinated proteins are regulated by the nutritional status in the muscle of the fine flounder. PLoS One 7:e44256
Huang CW, Li YH, Hu SY, Chi JR, Lin GH, Lin CC, Gong HY, Chen JY, Chen RH, Chang SJ, Liu FG, Wu JL (2012) Differential expression patterns of growth-related microRNAs in the skeletal muscle of Nile tilapia(Oreochromis niloticus). J Anim Sci 90:4266–4279
Jiao Y, Zheng Z, Du X, Wang Q, Huang R, Deng Y, Shi S, Zhao X (2014) Identification and characterization of microRNAs in pearl oyster Pinctada martensii by Solexa deep sequencing. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 16:54–62
Juan AH, Kumar RM, Marx JG, Young RA, Sartorelli V (2009) Mir-214-dependent regulation of the polycomb protein Ezh2 in skeletal muscle and embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 36:61–74
Kim HK, Lee YS, Sivaprasad U, Malhotra A, Dutta A (2006) Muscle specific microRNA miR-206 promotes muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol 174:677–687
Liu J (2008) Control of protein synthesis and mRNA degradation by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:214–221
Liu J, Luo XJ, Xiong AW, Zhang ZD, Yue S, Zhu MS, Cheng SY (2010) MicroRNA-214 promotes myogenic differentiation by facilitating exit from mitosis via down-regulation of proto-oncogene N-ras. J Biol Chem 285:26599–26607
Liu L, Li C, Su B, Beck BH, Peatman E (2013) Short-term feed deprivation alters immune status of surface mucosa in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). PLoS One 8:e74581
Livak KJ, Thomas DS (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408
McCarthy JJ, Esser KA (2007) MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-133a expression are decreased during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 102:306–313
Mennigen JA, Pansera TS, Larquier M, Plagnes-Juan E, Medale F (2012) Postprandial regulation of hepatic microRNAs predicted to target the insulin pathway in rainbow trout. PLoS One 7:e38604
Nihei Y, Kobiyama A, Ikeda D, Ono Y, Ohara S, Cole NJ, Johnston IA, Watabe S (2006) Molecular cloning and mRNA expression analysis of carp embryonic, slow and cardiac myosin heavy chain isoforms. J Exp Biol 209:188–198
Panserat S, Kaushik SJ (2010) Regulation of gene expression by nutritional factors in fish. Aquacult Res 41:751–762
Peragón J, Barroso JB, García-Salguero L, Aranda F, de la Higuera M, Lupiáñez JA (1999) Selective changes in the protein-turnover rates and nature of growth induced in trout liver by long-term starvation followed by re-feeding. Mol Cell Biochem 201:1–10
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W (2007) Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol 17:118–126
Salem M, Xiao C, Womack J, Rexroad CE 3rd, Yao J (2010) A microRNA repertoire for functional genome research in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 12:410–429
Škugor A, Slanchev K, Torgersen JS, Tveiten H, Andersen Ø (2014) Conserved mechanisms for germ cell-specific localization of nanos3 transcripts in teleost species with aquaculture significance. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 16:256–264
Steinbacher P, Haslett JR, Six M, Gollmann HP, Sänger AM, Stoiber W (2006) Phases of myogenic cell activation and possible role of dermomyotome cells in teleost muscle formation. Dev Dyn 235:3132–3143
Valente LM, Bower NI, Johnston IA (2012) Postprandial expression of growth related genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) juveniles fasted for 1 week and fed a single meal to satiation. Br J Nutr 108:2148–2157
Watanabe T, Sato T, Amano T, Kawamura Y, Kawamura N, Kawaguchi H, Yamashita N, Kurihara H, Nakaoka T (2008) Dnm3os, a non-coding RNA, is required for normal growth and skeletal development in mice. Dev Dyn 237:3738–3748
Wilfred BR, Wang WX, Nelson PT (2007) Energizing miRNA research: a review of the role of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, with a prediction that miR-103/107 regulates human metabolic pathways. Mol Genet Metab 91:209–217
Xie X, Lu J, Kulbokas EJ (2005) Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3′UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature 434:338–345
Yan B, Guo JT, Zhao LH, Zhao JL (2012a) MicroRNA expression signature in skeletal muscle of Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 364–365:240–246
Yan XC, Ding L, Li YC, Zhang XF, Liang Y, Sun XW, Teng CB (2012b) Identification and profiling of microRNAs from skeletal muscle of the common carp. PloS One 7:e30925
Zhang JS, Fu GH, Chu WY, Chen J, Liu Z, Liu F, Lu SQ, Liang P (2009) cDNA cloning and expression analysis of myosin heavy chain gene (MHC) of the Mandarin fish, Sniperca kneri. Aquac Res 40:412–418
Zhang QG, Chu WY, Hu SN, Meng T, Pan LL, Zhou RX, Liu Z, Zhang JS (2011) Identification and analysis of muscle-related protein isoforms expressed in the white muscle of the mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi). Mar Biotechnol (NY) 13:151–162
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31230076; 31340054) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (14JJ2135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Chen, D., Hu, Y. et al. The microRNA Signature in Response to Nutrient Restriction and Refeeding in Skeletal Muscle of Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Mar Biotechnol 17, 180–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-014-9606-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-014-9606-8