Abstract
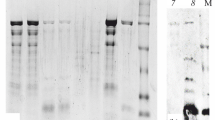
Tropomyosin represents a major allergen of decapod crustaceans such as shrimps and crabs, and its highly conserved amino acid sequence (>90% identity) is a molecular basis of the immunoglobulin E (IgE) cross-reactivity among decapods. At present, however, little information is available about allergens in edible crustaceans other than decapods. In this study, the major allergen in two species of edible crustaceans, Antarctic krill Euphausia superba and mantis shrimp Oratosquilla oratoria that are taxonomically distinct from decapods, was demonstrated to be tropomyosin by IgE-immunoblotting using patient sera. The cross-reactivity of the tropomyosins from both species with decapod tropomyosins was also confirmed by inhibition IgE immunoblotting. Sequences of the tropomyosins from both species were determined by complementary deoxyribonucleic acid cloning. The mantis shrimp tropomyosin has high sequence identity (>90% identity) with decapod tropomyosins, especially with fast-type tropomyosins. On the other hand, the Antarctic krill tropomyosin is characterized by diverse alterations in region 13–42, the amino acid sequence of which is highly conserved for decapod tropomyosins, and hence, it shares somewhat lower sequence identity (82.4–89.8% identity) with decapod tropomyosins than the mantis shrimp tropomyosin. Quantification by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay revealed that Antarctic krill contains tropomyosin at almost the same level as decapods, suggesting that its allergenicity is equivalent to decapods. However, mantis shrimp was assumed to be substantially not allergenic because of the extremely low content of tropomyosin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayuso R, Lehrer SB, Reese G (200a) Identification of continuous, allergenic regions of the major shrimp allergen Pen a 1 (tropomyosin). Int Arch Allergy Immunol 127:27–37
Ayuso R, Reese G, Leong-Kee S, Plante M, Lehrer SB (2002b) Molecular basis of arthropod cross-reactivity: IgE-binding cross-reactive epitopes of shrimp, house dust mite and cockroach tropomyosins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 129:38–48
Bousquet J, Björkstén B, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Huggett A, Ortolani C, Warner JO, Smith M (1998) Scientific criteria and the selection of allergenic foods for product labelling. Allergy 53(47 Suppl):3–21
Cummins P, Perry SV (1973) The subunits and biological activity of polymorphic forms of tropomyosin. Biochem 133:765–777
Daul CB, Slattery M, Reese G, Lehrer SB (1994) Identification of the major brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) allergen as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 105:49–55
Greaser ML, Gergely J (1971) Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem 246:4226–4233
Higgins D, Thompson J, Gibson T, Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Jansen JJ, Kardinaal AF, Huijbers G, Vlieg-Boerstra BJ, Martens BP, Ockhuizen T (1994) Prevalence of food allergy and intolerance in the adult Dutch population. J Allergy Clin Immunol 93:446–456
Keet CA, Wood RA (2007) Food allergy and anaphylaxis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 27:193–212
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lehrer SB, Ayuso R, Reese G (2003) Seafood allergy and allergens: a review. Mar Biotechnol 5:339–348
Leung PSC, Chu KH, Chow WK, Ansari A, Bandea CI, Kwan HS, Nagy SM, Gershwin ME (1994) Cloning, expression, and primary structure of Metapenaeus ensis tropomyosin, the major heat-stable shrimp allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94:882–890
Leung PSC, Chen YS, Mykles DL, Chow WK, Li CP, Chu KH (1998a) Molecular identification of the lobster muscle protein tropomyosin, as a seafood allergen. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 7:12–20
Leung PSC, Chen YS, Gershwin ME, Wong SH, Kwan HS, Chu KH (1998b) Identification and molecular characterization of Charybdis feriatus tropomyosin, the major crab allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:847–852
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu Y, Ohshima T, Ushio H, Hamada Y, Shiomi K (2007) Immunological characteristics of monoclonal antibodies against shellfish major allergen tropomyosin. Food Chem 100:1093–1099
Motoyama K, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2006) Cephalopod tropomyosins: identification as major allergens and molecular cloning. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1997–2002
Motoyama K, Suma Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2007) Molecular cloning of tropomyosins identified as allergens in six species of crustaceans. J Agric Food Chem 55:985–991
Nakano S, Yoshinuma T, Yamada T (2008) Reactivity of shrimp allergy-related IgE antibodies to krill tropomyosin. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 145:175–181
Reese G, Ayuso R, Lehrer SB (1999) Tropomyosin: an invertebrate pan-allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 119:247–258
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shanti KN, Martin BM, Nagpal S, Metcalfe DD, Subba Rao PV (1993) Identification of tropomyosin as the major shrimp allergen and characterization of its IgE-binding epitopes. J Immunol 151:5354–5363
Suma Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Lu Y, Ushio H, Shiomi K (2007) Comparative analysis of barnacle tropomyosin: divergence from decapod tropomyosins and role as a potential allergen. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 147:230–236
Wild LG, Lehrer SB (2005) Fish and shellfish allergy. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 5:74–79
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professors T. Ishimaru and Y. Koike and the crew of Umitaka-Maru, Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology, for collecting Antarctic krill samples and to Drs. N. Shimojo and Y. Kohno, Department of Pediatrics, Chiba University, Drs. R. Shibata and S. Nishima, National Minami-Fukuoka Chest Hospital, and Drs. H. Ohsuna and Z. Ikezawa, Department of Dermatology, Yokohama City University, for providing patient sera. This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan and a Grant-in-Aid for Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motoyama, K., Suma, Y., Ishizaki, S. et al. Identification of Tropomyosins as Major Allergens in Antarctic Krill and Mantis Shrimp and Their Amino Acid Sequence Characteristics. Mar Biotechnol 10, 709–718 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-008-9109-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-008-9109-6