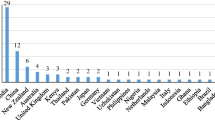
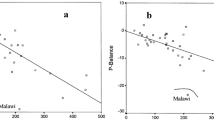
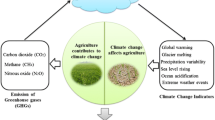
Abstract
One of the targets of the United Nations ‘Millennium Development Goals’ adopted in 2000 is to cut in half the number of people who are suffering from hunger between 1990 and 2015. However, crop yield growth has slowed down in much of the world because of declining investments in agricultural research, irrigation, and rural infrastructure and increasing water scarcity. New challenges to food security are posed by accelerated climatic change. Considerable uncertainties remain as to when, where and how climate change will affect agricultural production. Even less is known about how climate change might influence other aspects that determine food security, such as accessibility of food for various societal groups and the stability of food supply. This paper presents the likely impacts of thermal and hydrological stresses as a consequence of projected climate change in the future potential agriculture productivity in South Asia based on the crop simulation studies with a view to identify critical climate thresholds for sustained food productivity in the region. The study suggests that, on an aggregate level, there might not be a significant impact of global warming on food production of South Asia in the short term (<2°C; until 2020s), provided water for irrigation is available and agricultural pests could be kept under control. The increasing frequency of droughts and floods would, however, continue to seriously disrupt food supplies on year to year basis. In long term (2050s and beyond), productivity of Kharif crops would decline due to increased climate variability and pest incidence and virulence. Production of Rabi crops is likely to be more seriously threatened in response to 2°C warming. The net cereal production in South Asia is projected to decline at least between 4 and 10% under the most conservative climate change projections (a regional warming of 3°C) by the end of this century. In terms of the reference to UNFCCC Article 2 on dangerous anthropogenic (human-induced) interference with the climate system, the critical threshold for sustained food productivity in South Asia appears to be a rise in surface air temperature of ~2°C and a marginal decline in water availability for irrigation or decrease in rainfall during the cropping season.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal PK, Mall RK (2002) Climate change and rice yields in diverse agro-environments of India. II. Effect of uncertainties in scenarios and crop models on impact assessment. Clim Change 52(3):331–343
Aggarwal PK, Joshi PK, Ingram JSI, Gupta RK (2004) Adapting food systems of the Indo-Gangetic plains to global environmental change: key information needs to improve policy formulation. Environ Sci Policy 7(6):487–498
Alocilja EC, Ritchie RT (1988) Rice simulation and its use in multicriteria optimization. IBSNAT Research Report Series 01 IBSNAT Project, Hawaii
Ashrit R, Douville H, Rupa Kumar K (2003) Response of the Indian monsoon and ENSO-monsoon teleconnection to enhanced greenhouse effect in the CNRM coupled model. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 81(4):779–803
Auffhammer M, Ramanathan V, Vincent JR (2006) Integrated model shows that atmospheric brown clouds and greenhouse gases have reduced rice harvests in India. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103(52):19668–19672. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609584104
Bhalla GS, Hazell P, Kerr J (1999) Prospects for India’s cereal supply and demand for 2020. Food, Agriculture and the Environment Discussion Paper 29. IFFRI, Washington
Broca SS (2002) Food Insecurity, Poverty and Agriculture: A Concept Paper. ESA Working Paper. Agriculture and Development Economics Division of the Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, Italy
Brown L, Kane H (1994) Full house: reassessing the Earth’s population carrying capacity. Worldwatch environmental alert series. Norton, New York
Bruinsma J (ed) (2003) World agriculture: towards 2015/2030—An FAO perspective. Earthscan Publications Ltd, London
Cenderelli DA, Wohl EE (2003) Flow hydraulics and geomorphic effects of glacial-lake outburst floods in the Mount Everest region, Nepal. Earth Surf Proc Land 28(4):385–407
Challinor AJ, Slingo JM, Wheeler TR, Craufurd PQ, Grimes DIF (2003) Toward a combined seasonal weather and crop productivity forecasting system: determination of the working spatial scale. J Appl Meteorol 42(2):175–192
Challinor AJ, Wheeler TR, Craufurd PQ, Ferro CAT, Stephenson DB (2007) Adaptation of crops to climate change through genotypic responses to mean and extreme temperatures. Agric Ecosyst Environ 119(1-2):190–204
Chandrapala L (1996) Long term trends of rainfall and temperature in Sri Lanka. In: Abrol YP, Gadgil S, Pant GB (eds) Climate variability and agriculture. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 153–162
Christensen JH, Hewitson B, Busuioc A, Chen A, Gao X, Held I, Jones R, Kolli RK, Kwon W-T, Laprise R, Magaña Rueda V, Mearns L, Menéndez CG, Räisänen J, Rinke A, Sarr A, Whetton P (2007) Regional climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M et al (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, p 996
Chung CE, Ramanathan V (2006) Weakening of North Indian SST gradients and the monsoon rainfall in India and the Sahel. J Clim 19(10):2036–2045
Collins M (2000) The El Niño-Southern Oscillation in the second Hadley Centre coupled model and its response to greenhouse warming. J Clim 13(7):1299–1312
CWC (2001) Water and related statistics, Report of the Ministry of Water Resources. Central Water Commission, New Delhi, India
de Fraiture C, Cai X, Amarasinghe U, Rosegrant M, Molden D (2004) Does international cereal trade save water? The impact of virtual water trade on global water use. Comprehensive Assessment Research Report 4. International Water Management Institute (IWMI), Comprehensive Assessment Secretariat, Colombo, Srilanka
De US, Mukhopadhyay RK (1998) Severe heat wave over the Indian subcontinent in 1998 in perspective of global climate. Curr Sci 75(12):1308–1315
De US, Khole M, Dandekar MM (2004) Meteorological Office, Pune-411 005. Nat Hazards 31(2):487–497
De US, Dube RK, Prakasa Rao GS (2005) Extreme weather events over India in the last 100 years. J Indian Geophys Union 9(3):173–187
DES (2003) Agricultural statistics at a glance. Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Government of India. http://agricoop.nic.in/Agristatistics.htm
Droogers P (2004) Adaptation to climate change to enhance food security and preserve environmental quality: example for southern Sri Lanka. Agric Water Manage 66(1):15–33
Dyson T (1999) World food trends and prospects to 2025. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96(11):5929–5936
Dyurgerov MB, Meier MF (2005) Glaciers and the changing earth system: a 2004 snapshot. Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research Occasional Paper, vol 58. University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, USA
Easterling WE, Aggarwal PK, Batima P, Brander KM, Erda L, Howden SM, Kirilenko A, Morton J, Soussana J-F, Schmidhuber J, Tubiello FN (2007) Food, fibre and forest products. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 273–313
Emanuel K (2005) Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 436(7051):686–688
Faisal IM, Parveen S (2004) Food security in the face of climate change, population growth, and resource constraints: implications for Bangladesh. Environ Manage 34(4):487–498
FAO (2001) The state of food insecurity in the world 2001. State of food insecurity in the world. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
FAO (2002) Crops and drops: making the best use of water for agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
FAO (2005a) Food outlook no. 3, September. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
FAO (2005b) The state of food and agriculture. Agricultural trade and poverty—can trade work for the poor?. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
FAO (2005c) The state of food insecurity in the world 2005. Eradicating world hunger—key to achieving the millennium development goals. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Farooq AB, Khan AH (2004) Climate change perspective in Pakistan in. In: Capacity building APN workshop on global change research, Islamabad, Pakistan, June 8–10. pp 39–46
Faruque HSM, Ali ML (2005) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden, pp 231–254
Fischer G, Shah MM, Velthuizen HTv (2002) Climate change and agricultural vulnerability a special report on “Climate Change and Agricultural Vulnerability”, contribution to the world summit on sustainable development, Johannesburg 2002. IIASA and FAO
Fushimi H (1999) Recent changes in Glacier phenomena in the Nepalese Himalayas. IUCN Report on Climate Change and Biodiversity. International Union for Conservation of Nature, Gland, Switzerland
Giorgi F (2006) Climate change hot-spots. Geophys Res Lett 33:L08707. doi:10.1029/2006GL025734
Giorgi F, Hewitson B (2001) Regional climate information—evaluation and projections. In: Houghton JT, Ding Y, Griggs DJ et al (eds) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of working group I to the third assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 583–638
Givati A, Rosenfeld D (2004) Quantifying precipitation suppression due to air pollution. J Appl Meteorol 43(7):1038–1056
Godwin D, Ritchie JT, Singh U, Hunt L (1989) A user’s guide to CERES-Wheat—V2.10. International Fertilizer Development Center, Muscle Shoals
Goswami BN, Xavier PK (2005) ENSO control on the south Asian monsoon through the length of the rainy season. Geophys Res Lett 32:L18717
Gupta SK, Deshpande RD (2004) Water for India in 2050: first-order assessment of available options. Curr Sci 86(9):1216–1224
GWP (2000) Integrated water resources management. Tac Background Paper No. 4. Global Water Partnership, Stockholm, Sweden
Hansen J, Nazarenko L (2004) Soot climate forcing via snow and ice albedos. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101(2):423–428
Hasnain SI (2002) Himalayan glaciers meltdown: impacts on South Asian rivers. In: Lanen HAJv, Demuth S (eds) Regional hydrology: bridging the gap between research and practice. IAHS series of proceedings and reports, vol IAHS Publication No. 274. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, pp 417–425
IMD (2000–3) Disastrous Weather Events (DWE) Annual Reports, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003. India Meteorological Department
IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.L. Miller, Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
Kahlown MA, Ashraf M, Raoof A, Haq Zu (2003) Determination of crop water requirement of major crops under shallow water table conditions. Research Report-2 2003. Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources
Kalsi SR, Pareek RS (2001) Hottest April of the 20th century over northwest and central India. Curr Sci 80(7):867–873
Kataki PK, Hobbs P, Adhikary B (2001) The rice–wheat cropping system of South Asia: trends, constraints. productivity and policy. Haworth Press, Binghampton
Kiehl JT, Schneider TL, Portmann RW, Solomon S (1999) Climate forcing due to tropospheric and stratospheric ozone. J Geophys Res 104(D24):31239–31254
Knutson TR, Manabe S (1998) Model assessment of decadal variability and trends in the tropical Pacific Ocean. J Clim 11(9):2273–2296
Knutson TR, Tuleya RE (2004) Impact of CO2-induced warming on simulated hurricane intensity and precipitation: Sensitivity to the choice of climate model and convective parameterization. J Clim 17(18):3477–3495
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS (2001) El Niño Southern Oscillation, Eurasian snow cover and the Indian monsoon rainfall. In: Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Science 67A:361–368
Kripalani RH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS, Khandekar ML (2003) Indian monsoon variability in a global warming scenario. Nat Hazards 29(2):189–206
Krishnamurthy V, Goswami BN (2000) Indian monsoon-ENSO relationship on interdecadal timescale. J Clim 13:579–595
Krishnan R, Ramanathan V (2002) Evidence of surface cooling from absorbing aerosols. Geophys Res Lett 29:54–56
Kumar KS, Parikh J (1998) Climate change impacts on Indian agriculture: results from a crop modeling approach. In: Dinar A, Mendelsohn R, Evenson R et al (eds) Measuring the impacts of climate change on Indian agriculture. World Bank Technical Paper No. 402. World Bank, Washington, DC
Lal M (2003) Global climate change: India’s monsoon and its variability. J Environ Stud Policy 6(1):1–34
Lal R (2004) Soil and water resources of south Asia in an uncertain climate. In: Lal R, Hobbs PR, Uphoff N, Hansen DO (eds) Sustainable agriculture and the international rice–wheat system. Marcel Dekker Publishers (Taylor & Francis Group), New York, USA, pp 19–36
Lal M (2005) Climate change—implications for India’s water resources. In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. A.A. Balkema Publishers (Taylor & Francis Group), UK, pp 15–193
Lal M (2007) Implications of climate change in South Asia on interlinking project of Indian rivers. In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmed AU, Ahmad QK (eds) Interlinking rivers in India—issues and concerns. Taylor & Francis Publishers, New York, USA, pp 187–217
Lal M, Bhaskaran B, Singh SK (1998a) Indian summer monsoon variability as simulated by regional model nested in a global climate model. Chin J Atmos Sci 22(1):93–102
Lal M, Singh KK, Rathore LS, Srinivasan G, Saseendran SA (1998b) Vulnerability of rice and wheat yields in NW India to future changes in climate. Agric For Meteorol 89(2):101–114
Lal M, Meehl GA, Arblaster JM (2000) Simulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall and its intraseasonal variability in the NCAR climate system model. Reg Environ Change 1(3–4):163–179
Lal M, Harasawa H, Murdiyarso D (2001a) Asia. In: McCarthy JJ, Canziani OF, Leary NA, Dokken DJ, White KS (eds) Climate change 2001: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Contribution of working group II to the third assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 533–590
Lal M, Nozawa T, Emori S, Harasawa H, Takahashi K, Kimoto M, Abe-Ouchi A, Nakajima T, Takemura T, Numaguti A (2001b) Future climate change: implications for Indian summer monsoon and its variability. Curr Sci 81(9):1196–1207
Long SP, Ainsworth EA, Leakey ADB, Morgan PB (2005) Global food insecurity. Treatment of major food crops with elevated carbon dioxide or ozone under large-scale fully open-air conditions suggests recent models may have overestimated future yields. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360(1463):2011–2020
Malthus TR (2003) An essay on the principle of population. Norton, New York
May W (2004) Simulation of the variability and extremes of daily rainfall during the Indian summer monsoon for present and future times in a global time-slice experiment. Clim Dyn 22(2–3):183–204
Meehl GA, Arblaster JM (2003) Mechanisms for projected future changes in south Asian monsoon precipitation. Clim Dyn 21(7–8):659–675
Meehl GA, Washington WM (1996) El Niño-like climate change in a model with increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Nature 382(6586):56–60
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A (2007) Global climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M et al (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 747–846
Meier M (1998) Land ice on Earth: a beginning of a global synthesis, Unpublished transcript of the 1998 Walter B. Langbein memorial lecture, Geophysical union spring meeting—26 May 1998, Boston, MA
Mirza MMQ (2002) Global warming and changes in the probability of occurrence of floods in Bangladesh and implications. Glob Environ Change Hum Policy Dimens 12(2):127–138
Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) (2005) Climate change and water resources in south Asia. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden
Mirza MQ, Dixit A (1997) Climate change and water management in the GBM Basins. Water Nepal 5:71–100
Mirza MMQ, Warrick RA, Erickson NJ, Kenny GJ (2005) Are floods getting worse in the GBM Basins? In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden, p 322
MOA (1996) Agricultural statistics at a glance. Ministry of Agriculture, New Delhi
Molden D, de Fraiture C (2004) Investing in water for food, ecosystems and livelihoods. Blue Paper Discussion Draft. Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture, Stockholm, Sweden
Mool PK, Bajracharya SR, Joshi SP (2001) Inventory of glaciers, glacial lakes and glacial lake outburst floods in Nepal. ICIMOD, Kathmandu
Moshabbir PM, Khan S (1994) Management of groundwater resources in Pakistan. In: Water lifting devices and groundwater management for irrigation. Expert consultation of the Asian network on water lifting devices for irrigation. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 197–202
Naithani AK, Nainwal HV, Sati KK, Prasad C (2001) Geomorphological evidences of retreat of the Gangotri glacier and its characteristics. Curr Sci 80(1):87–94
Pai DS, Thapliyal V, Kokate PD (2004) Decadal variation in the heat and cold waves over India during 1971–2000. Mausam 55(2):281–292
Pandey S, Bhandari H, Sharan R, Naik D, Taunk SK, Sastri A (2005) Economic costs of drought and rainfed rice farmers’ coping mechanisms in eastern India. Final project report. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines
Parker DE (2004) Climate: large-scale warming is not urban. Nature 432(7015):290
Parry M, Rosenzweig C, Iglesias A, Fischer G, Livermore M (1999) Climate change and world food security: a new assessment. Glob Environ Change 9(1001):51–67(17)
Parry ML, Rosenzweig C, Iglesias A, Livermore M, Fischer G (2004) Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob Environ Change Hum Policy Dimens 14(1):53–67
Peng S, Ingram KT, Neue HU, Ziska LH (1995) Climate change and rice. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and Springer, Manila, Philippines and Berlin, Germany
Planning Commission (2001) Report of the Working Group on Agriculture Statistics for the formulation of Tenth Five Year Plan. TFYP Working Group Series. No. 13/2001. Government of India, New Delhi
Qureshi AS (2005) Climate change and water resources management in Pakistan. In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden, pp 197–230
Ramanathan V, Crutzen PJ, Kiehl JT, Rosenfeld D (2001) Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 294(5549):2119–2124
Regmi AP, Ladha JK, Pathak H, Pasuquin E, Bueno C, Dawe D, Hobbs PR, Joshy D, Maskey SL, Pandey SP (2002) Yield and soil fertility trends in a 20-year rice–rice–wheat experiment in Nepal. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66(3):857–867
Rosegrant MW, Cline SA (2003) Global food security: challenges and policies. Science 302(5652):1917–1919
Royal Society (2005) Food crops in a changing climate: Report of a Royal Society Discussion Meeting held in April 2005. Policy Document 10/05
Ruosteenoja K, Carter TR, Jylhä K, Tuomenvirta H (2003) Future climate in world regions: an intercomparison of model-based projections for the new IPCC emissions scenarios. The Finnish Environment 644. Finnish Environment Institute
Sarkar S, Singh RP, Kafatos M (2004) Further evidences for the weakening relationship of Indian rainfall and ENSO over India. Geophys Res Lett 31:L13209
Seckler D, Seckler DW (1996) The new era of water resources management: from “dry” to “wet” water savings. Research Report 1. International Water Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Seckler D, Amarasinghe U, Molden D, Silva Rd, Barker R (1997) World water demand and supply, 1990 to 2025: scenarios and issues. Research Report 19. International Water Management Institute, Colombo, Sri Lanka
Selvaraju R (2003) Impact of El Niño-southern oscillation on Indian foodgrain production. Int J Climatol 23(2):187–206
Sen Roy S, Balling RC Jr (2004) Trends in extreme daily precipitation indices in India. Int J Climatol 24(4):457–466
Sen Roy S, Balling RC Jr (2005) Analysis of trends in maximum and minimum temperature, diurnal temperature range, and cloud cover over India. Geophys Res Lett 32:L12702
Shah T, Molden D, Sakthivadivel R, Seckler D (2000) The global groundwater situation: overview of opportunities and challenges. International Water Management Institute, Colombo
Shaman J, Tziperman E (2005) The effect of ENSO on Tibetan Plateau snow depth: a stationary wave teleconnection mechanism and implications for the South Asian Monsoons. J Clim 18(12):2067–2079
Shiklomanov A. I (1997) On the effect on anthropogenic change in the global climate on river runoff in the Yenisei basin. In: Runoff Computations for Water Projects. Proceedings of the St. Petersburg Symposium, 30 Oct–03 Nov 1995. IHP-V UNESCO Technical Documents in Hydrology, N9, pp 113–119
Shrestha AB (2004) Climate change in Nepal and its impact on Himalayan glaciers. In: Paper presented at the in European climate forum symposium on key vulnerable regions and climate change: identifying thresholds for impacts and adaptation in relation to Article 2 of the UNFCCC, Beijing, 27–30 October
Shrestha AB, Wake CP, Dibb JE, Mayewski PA (2000) Precipitation fluctuations in the Nepal Himalaya and its vicinity and relationship with some large scale climatological parameters. Int J Climatol 20(3):317–327
Siddiqui KM, Mohammad I, Ayaz M (1999) Forest ecosystem climate change impact assessment and adaptation strategies for Pakistan. Clim Res 12:195–203
Simon JL (1998) The ultimate resource 2. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Singh P, Bengtsson L (2004) Hydrological sensitivity of a large Himalayan basin to climate change. Hydrol Process 18(13):2363–2385
Singh P, Kumar N (1997) Impact assessment of climate change on the hydrological response of a snow and glacier melt runoff dominated Himalayan river. J Hydrol 193:316–350
Sinha SK (1997) Global change scenario: current and future with reference to land cover changes and sustainable agriculture—south and south-east Asian context. Curr Sci 72(11):846–854
Sinha SK, Swaminathan MS (1991) Deforestation, climate change and sustainable nutrition security—a case-study of India. Clim Change 19(1–2):201–209
Sinha SK, Singh GB, Rai M (1998) Decline in crop productivity in Haryana and Punjab: myth or reality. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Slingo JM, Challinor AJ, Hoskins BJ, Wheeler TR (2005) Introduction: food crops in a changing climate. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360(1463):1983–1989
Sridharan S, Muthuchami A (2002) Some salient features of the Bay of Bengal super cyclonic storm of October. Mausam 53(2):237–251
Swaminathan MS (2003) Count down from 2007. The Hindu Magazine
TF–ILR (2003) Interbasin water transfer proposals, task force on interlinking of rivers. Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, New Delhi
Timmermann A, Oberhuber J, Bacher A, Esch M, Latif M, Roeckner E (1999) Increased El Niño frequency in a climate model forced by future greenhouse warming. Nature 398(6729):694–697
Timsina J, Connor DJ (2001) Productivity and management of rice-wheat cropping systems: issues and challenges. Field Crops Res 69(2):93–132
Trenberth K (2005) Uncertainty in hurricanes and global warming. Science 308(5729):1753–1754
Tuong TP, Bouman BAM (2003) Rice production in water-scarce environments. In: Kijne JW, Barker R, Molden D (eds) Water productivity in agriculture: limits and opportunities for improvement. CAB International, United Kingdom, pp 53–67
UNEP (1999) Global environmental outlook 2000. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi
Vecchi GA, Soden BJ, Wittenberg AT, Held IM, Leetmaa A, Harrison MJ (2006) Weakening of tropical Pacific atmospheric circulation due to anthropogenic forcing. Nature 441(7089):73–76
Walsh K (2004) Tropical cyclones and climate change: unresolved issues. Clim Res 27(1):77–83
Wheeler TR, Craufurd PQ, Ellis RH, Porter JR, Prasad PVV (2000) Temperature variability and the yield of annual crops. Agric Ecosyst Environ 82(1-3):159–167
WMO (1999) The 1997–1998 El Niño event: a scientific and technical retrospective: a contribution to the United Nations Task Force on El Niño for implementation of United Nations General Assembly Resolutions 52/200 and 53/185. World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
World Bank (2003) Millennium development goals: about the goals
Yohe G, Strzepek K (2005) Climate change and water resources assessment in south Asia: addressing uncertainties. In: Mirza MMQ, Ahmad QK (eds) Climate change and water resources in South Asia. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Leiden, p 322
Zickfeld K, Knopf B, Petoukhov V, Schellnhuber HJ (2005) Is the Indian summer monsoon stable against global change? Geophys Res Lett 32:L15707
Zimmer D, Renault D (2004) Virtual water in food production and global trade: a review of methodological issues and preliminary results. http://www.worldwatercouncil.org/fileadmin/wwc/Programs/Virtual_Water/VirtualWater_article_DZDR.pdf. Accessed May 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lal, M. Implications of climate change in sustained agricultural productivity in South Asia. Reg Environ Change 11 (Suppl 1), 79–94 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-010-0166-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-010-0166-9