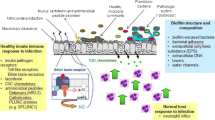
Abstract
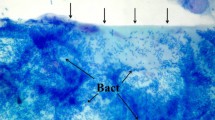
Recurrent respiratory tract infections (RRTIs) are very common in children and a major challenge for pediatricians. In the last few years, bacterial biofilms have been linked to RRTIs and antibiotic resistance, and have raised serious concerns regarding the therapeutic management of recurrent middle ear diseases, chronic rhinosinusitis, and recurrent pharyngotonsillitis. This paper aims to review the new insights into biofilm-related upper respiratory tract infections in children and possible therapeutic strategies. It focuses on the clinical implications for recurrent disease and on studies in pediatric patients. Analysis of the literature showed that the involvement of bacterial biofilm in recurrent upper airway tract infections is an emerging problem that may lead to serious concerns about infection control. Despite the large amount of research within this field, detailed insight into the complex structure of bacterial biofilms and the ultrastructural and biochemical mechanisms responsible for its evasion of the immune system and resistance to treatments is currently lacking. In the future, additional emphasis should be placed on biofilm management as a component of therapeutic strategies. This goal can be attained by finding feasible methods for detecting biofilms in vivo and identifying effective methods for administering treatments that eradicate preexisting bacterial biofilms or hinder bacterial adhesion to respiratory cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Principi N, Esposito S, Cavagna R, Bosis S, Droghetti R, Faelli N, Tosi S, Begliatti E; Snoopy Study Group (2003) Recurrent respiratory tract infections in pediatric age: a population-based survey of the therapeutic role of macrolides. J Chemother 15:53–59
Marchisio P, Bellussi L, Di Mauro G, Doria M, Felisati G, Longhi R, Novelli A, Speciale A, Mansi N, Principi N (2010) Acute otitis media: from diagnosis to prevention. Summary of the Italian guideline. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:1209–1216
Esposito S, Principi N; Italian Society of Pediatrics; Italian Society of Pediatric Infectivology; Italian Society of Pediatric Allergology and Immunology; Italian Society of Pediatric Respiratory Diseases; Italian Society of Preventive and Social Pediatrics; Italian Society of Otorhinolaryngology; Italian Society of Chemotherapy; Italian Society of Microbiology (2008) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and subacute rhinosinusitis in children. J Chemother 20:147–157
Bellussi LM, Marchisio P, Materia E, Passàli FM (2011) Clinical guideline on adenotonsillectomy: the Italian experience. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 72:142–145
Esposito S, Musio A (2013) Immunostimulants and prevention of recurrent respiratory tract infections. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 27:627–636
Esposito S, Marchisio P, Cavagna R, Gironi S, Bosis S, Lambertini L, Droghetti R, Principi N (2003) Effectiveness of influenza vaccination of children with recurrent respiratory tract infections in reducing respiratory-related morbidity within the households. Vaccine 21:3162–3168
de Martino M, Ballotti S (2007) The child with recurrent respiratory infections: normal or not? Pediatr Allergy Immunol 18(Suppl 18):13–18
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Davies D (2003) Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:114–122
Vlastarakos PV, Nikolopoulos TP, Maragoudakis P, Tzagaroulakis A, Ferekidis E (2007) Biofilms in ear, nose, and throat infections: how important are they? Laryngoscope 117:668–673
Pettigrew MM, Gent JF, Revai K, Patel JA, Chonmaitree T (2008) Microbial interactions during upper respiratory tract infections. Emerg Infect Dis 14:1584–1591
Marks LR, Davidson BA, Knight PR, Hakansson AP (2013) Interkingdom signaling induces Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilm dispersion and transition from asymptomatic colonization to disease. MBio 4:e00438-13
McCullers JA (2014) The co-pathogenesis of influenza viruses with bacteria in the lung. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:252–262. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3231. Epub 2014 Mar 3
Liu YC, Post JC (2009) Biofilms in pediatric respiratory and related infections. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 9:449–455
Torretta S, Drago L, Marchisio P, Mattina R, Clemente IA, Pignataro L (2011) Diagnostic accuracy of nasopharyngeal swabs in detecting biofilm-producing bacteria in chronic adenoiditis: a preliminary study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144:784–788
Hannig C, Follo M, Hellwig E, Al-Ahmad A (2010) Visualization of adherent micro-organisms using different techniques. J Med Microbiol 59(Pt 1):1–7
Post JC, Stoodley P, Hall-Stoodley L, Ehrlich GD (2004) The role of biofilms in otolaryngologic infections. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:185–190
Post JC, Hiller NL, Nistico L, Stoodley P, Ehrlich GD (2007) The role of biofilms in otolaryngologic infections: update 2007. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15:347–351
Gelardi M, Passalacqua G, Fiorella ML, Mosca A, Quaranta N (2011) Nasal cytology: the “infectious spot”, an expression of a morphological-chromatic biofilm. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30:1105–1109
Hoa M, Tomovic S, Nistico L, Hall-Stoodley L, Stoodley P, Sachdeva L, Berk R, Coticchia JM (2009) Identification of adenoid biofilms with middle ear pathogens in otitis-prone children utilizing SEM and FISH. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1242–1248
Zuliani G, Carlisle M, Duberstein A, Haupert M, Syamal M, Berk R, Du W, Coticchia J (2009) Biofilm density in the pediatric nasopharynx: recurrent acute otitis media versus obstructive sleep apnea. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118:519–524
Hall-Stoodley L, Hu FZ, Gieseke A, Nistico L, Nguyen D, Hayes J, Forbes M, Greenberg DP, Dice B, Burrows A, Wackym PA, Stoodley P, Post JC, Ehrlich GD, Kerschner JE (2006) Direct detection of bacterial biofilms on the middle-ear mucosa of children with chronic otitis media. JAMA 296:202–211
Al-Mazrou KA, Al-Khattaf AS (2008) Adherent biofilms in adenotonsillar diseases in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:20–23
Homøe P, Bjarnsholt T, Wessman M, Sørensen HC, Johansen HK (2009) Morphological evidence of biofilm formation in Greenlanders with chronic suppurative otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:1533–1538
Nistico L, Kreft R, Gieseke A, Coticchia JM, Burrows A, Khampang P, Liu Y, Kerschner JE, Post JC, Lonergan S, Sampath R, Hu FZ, Ehrlich GD, Stoodley P, Hall-Stoodley L (2011) Adenoid reservoir for pathogenic biofilm bacteria. J Clin Microbiol 49:1411–1420
Bakaletz LO (2012) Bacterial biofilms in the upper airway—evidence for role in pathology and implications for treatment of otitis media. Paediatr Respir Rev 13:154–159
Saafan ME, Ibrahim WS, Tomoum MO (2013) Role of adenoid biofilm in chronic otitis media with effusion in children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:2417–2425
Rayner MG, Zhang Y, Gorry MC, Chen Y, Post JC, Ehrlich GD (1998) Evidence of bacterial metabolic activity in culture-negative otitis media with effusion. JAMA 279:296–299
Hoa M, Syamal M, Sachdeva L, Berk R, Coticchia J (2009) Demonstration of nasopharyngeal and middle ear mucosal biofilms in an animal model of acute otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118:292–298
Moriyama S, Hotomi M, Shimada J, Billal DS, Fujihara K, Yamanaka N (2009) Formation of biofilm by Haemophilus influenzae isolated from pediatric intractable otitis media. Auris Nasus Larynx 36:525–531
Yano H, Yamazaki Y, Qin L, Okitsu N, Yahara K, Irimada M, Hirakata Y, Kaku M, Kobayashi T, Watanabe H (2013) Improvement rate of acute otitis media caused by Haemophilus influenzae at 1 week is significantly associated with time to recovery. J Clin Microbiol 51:3542–3546
Mizrahi A, Cohen R, Varon E, Bonacorsi S, Bechet S, Poyart C, Levy C, Raymond J (2014) Non typable-Haemophilus influenzae biofilm formation and acute otitis media. BMC Infect Dis 14:400
García-Cobos S, Moscoso M, Pumarola F, Arroyo M, Lara N, Pérez-Vázquez M, Aracil B, Oteo J, García E, Campos J (2014) Frequent carriage of resistance mechanisms to β-lactams and biofilm formation in Haemophilus influenzae causing treatment failure and recurrent otitis media in young children. J Antimicrob Chemother 69:2394–2399
Torretta S, Marchisio P, Drago L, Baggi E, De Vecchi E, Garavello W, Nazzari E, Pignataro L, Esposito S (2012) Nasopharyngeal biofilm-producing otopathogens in children with nonsevere recurrent acute otitis media. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:991–996
Daniel M, Imtiaz-Umer S, Fergie N, Birchall JP, Bayston R (2012) Bacterial involvement in otitis media with effusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:1416–1422
Saylam G, Tatar EC, Tatar I, Ozdek A, Korkmaz H (2010) Association of adenoid surface biofilm formation and chronic otitis media with effusion. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:550–555
Torretta S, Drago L, Marchisio P, Gaffuri M, Clemente IA, Pignataro L (2013) Topographic distribution of biofilm-producing bacteria in adenoid subsites of children with chronic or recurrent middle ear infections. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 122:109–113
Chole RA, Faddis BT (2003) Anatomical evidence of microbial biofilms in tonsillar tissues: a possible mechanism to explain chronicity. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:634–636
Galli J, Calò L, Ardito F, Imperiali M, Bassotti E, Fadda G, Paludetti G (2007) Biofilm formation by Haemophilus influenzae isolated from adeno-tonsil tissue samples, and its role in recurrent adenotonsillitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 27:134–138
Stoodley P, Debeer D, Longwell M, Nistico L, Hall-Stoodley L, Wenig B, Krespi YP (2009) Tonsillolith: not just a stone but a living biofilm. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141:316–321
Marks LR, Mashburn-Warren L, Federle MJ, Hakansson AP (2014) Streptococcus pyogenes biofilm growth in vitro and in vivo and its role in colonization, virulence, and genetic exchange. J Infect Dis 210:25–34
Roberts AL, Connolly KL, Kirse DJ, Evans AK, Poehling KA, Peters TR, Reid SD (2012) Detection of group A Streptococcus in tonsils from pediatric patients reveals high rate of asymptomatic streptococcal carriage. BMC Pediatr 12:3
Ogawa T, Terao Y, Okuni H, Ninomiya K, Sakata H, Ikebe K, Maeda Y, Kawabata S (2011) Biofilm formation or internalization into epithelial cells enable Streptococcus pyogenes to evade antibiotic eradication in patients with pharyngitis. Microb Pathog 51:58–68
Brodsky L, Adler E, Stanievich JF (1989) Naso- and oropharyngeal dimensions in children with obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 17:1–11
Torretta S, Drago L, Marchisio P, Cappadona M, Rinaldi V, Nazzari E, Pignataro L (2013) Recurrences in chronic tonsillitis substained by tonsillar biofilm-producing bacteria in children. Relationship with the grade of tonsillar hyperplasy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 77:200–204
Starner TD, Zhang N, Kim G, Apicella MA, McCray PB Jr (2006) Haemophilus influenzae forms biofilms on airway epithelia: implications in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:213–220
Kasperska-Zajac A, Czecior E, Namyslowski G (2010) Effect of tonsillectomy on the level of exhaled nitric oxide (NO) in patients with recurrent tonsillitis. Respir Med 104:1757–1759
Torretta S, Marchisio P, Esposito S, Garavello W, Cappadona M, Clemente IA, Pignataro L (2011) Exhaled nitric oxide levels in children with chronic adenotonsillar disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:471–480
Schreiber F, Beutler M, Enning D, Lamprecht-Grandio M, Zafra O, González-Pastor JE, de Beer D (2011) The role of nitric-oxide-synthase-derived nitric oxide in multicellular traits of Bacillus subtilis 3610: biofilm formation, swarming, and dispersal. BMC Microbiol 11:111
Barraud N, Schleheck D, Klebensberger J, Webb JS, Hassett DJ, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2009) Nitric oxide signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms mediates phosphodiesterase activity, decreased cyclic di-GMP levels, and enhanced dispersal. J Bacteriol 191:7333–7342
Falsetta ML, McEwan AG, Jennings MP, Apicella MA (2010) Anaerobic metabolism occurs in the substratum of gonococcal biofilms and may be sustained in part by nitric oxide. Infect Immun 78:2320–2328
Jardeleza C, Foreman A, Baker L, Paramasivan S, Field J, Tan LW, Wormald PJ (2011) The effects of nitric oxide on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm growth and its implications in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 1:438–444
Sudhamsu J, Crane BR (2009) Bacterial nitric oxide synthases: what are they good for? Trends Microbiol 17:212–218
Esposito S, Marchisio P, Tenconi R, Tagliaferri L, Albertario G, Patria MF, Principi N (2012) Diagnosis of acute rhinosinusitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 23(Suppl 22):17–19
Chow AW, Benninger MS, Brook I, Brozek JL, Goldstein EJ, Hicks LA, Pankey GA, Seleznick M, Volturo G, Wald ER, File TM Jr; Infectious Diseases Society of America (2012) IDSA clinical practice guideline for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis in children and adults. Clin Infect Dis 54:1041–1045
Silviu-Dan F (2011) Pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis: the old, the new, and the reasonable. Pediatr Ann 40:213–220
Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, Schleimer RP, Ledford D (2013) Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131:1479–1490
Perloff JR, Palmer JN (2005) Evidence of bacterial biofilms in a rabbit model of sinusitis. Am J Rhinol 19:1–6
Sanclement JA, Webster P, Thomas J, Ramadan HH (2005) Bacterial biofilms in surgical specimens of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 115:578–582
Hunsaker DH, Leid JG (2008) The relationship of biofilms to chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:237–241
Ramadan HH, Sanclement JA, Thomas JG (2005) Chronic rhinosinusitis and biofilms. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:414–417
Tatar EÇ, Tatar I, Ocal B, Korkmaz H, Saylam G, Ozdek A, Celik HH (2012) Prevalence of biofilms and their response to medical treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis without polyps. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:669–675
Chen HH, Liu X, Ni C, Lu YP, Xiong GY, Lu YY, Wang SQ (2012) Bacterial biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis and their relationship with inflammation severity. Auris Nasus Larynx 39:169–174
Ragab A, Essa N, El-Raghy N, Zahran W, El Borolsy A (2012) Evaluation of bacterial adherence and biofilm arrangements as new targets in treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:537–544
Foreman A, Boase S, Psaltis A, Wormald PJ (2012) Role of bacterial and fungal biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 12:127–135
Sanderson AR, Leid JG, Hunsaker D (2006) Bacterial biofilms on the sinus mucosa of human subjects with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 116:1121–1126
Healy DY, Leid JG, Sanderson AR, Hunsaker DH (2008) Biofilms with fungi in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138:641–647
Mladina R, Skitarelić N, Musić S, Ristić M (2010) A biofilm exists on healthy mucosa of the paranasal sinuses: a prospectively performed, blinded, scanning electron microscope study. Clin Otolaryngol 35:104–110
Li H, Wang D, Sun X, Hu L, Yu H, Wang J (2012) Relationship between bacterial biofilm and clinical features of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:155–163
Bendouah Z, Barbeau J, Hamad WA, Desrosiers M (2006) Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with an unfavorable evolution after surgery for chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:991–996
Singhal D, Psaltis AJ, Foreman A, Wormald PJ (2010) The impact of biofilms on outcomes after endoscopic sinus surgery. Am J Rhinol Allergy 24:169–174
Psaltis AJ, Ha KR, Beule AG, Tan LW, Wormald PJ (2007) Confocal scanning laser microscopy evidence of biofilms in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 117:1302–1306
Prince AA, Steiger JD, Khalid AN, Dogrhamji L, Reger C, Eau Claire S, Chiu AG, Kennedy DW, Palmer JN, Cohen NA (2008) Prevalence of biofilm-forming bacteria in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol 22:239–245
Coticchia J, Zuliani G, Coleman C, Carron M, Gurrola J 2nd, Haupert M, Berk R (2007) Biofilm surface area in the pediatric nasopharynx: chronic rhinosinusitis vs obstructive sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:110–114
Zuliani G, Carron M, Gurrola J, Coleman C, Haupert M, Berk R, Coticchia J (2006) Identification of adenoid biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70:1613–1617
Sanchez CJ, Kumar N, Lizcano A, Shivshankar P, Dunning Hotopp JC, Jorgensen JH, Tettelin H, Orihuela CJ (2011) Streptococcus pneumoniae in biofilms are unable to cause invasive disease due to altered virulence determinant production. PLoS One 6:e28738
Weimer KE, Armbruster CE, Juneau RA, Hong W, Pang B, Swords WE (2010) Coinfection with Haemophilus influenzae promotes pneumococcal biofilm formation during experimental otitis media and impedes the progression of pneumococcal disease. J Infect Dis 202:1068–1075
Ferguson BJ, Stolz DB (2005) Demonstration of biofilm in human bacterial chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol 19:452–457
Al-Mutairi D, Kilty SJ (2011) Bacterial biofilms and the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 11:18–23
Karosi T, Sziklai I, Csomor P (2013) Low-frequency ultrasound for biofilm disruption in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis: in vitro pilot study. Laryngoscope 123:17–23
Drago L, De Vecchi E, Torretta S, Mattina R, Marchisio P, Pignataro L (2012) Biofilm formation by bacteria isolated from upper respiratory tract before and after adenotonsillectomy. APMIS 120:410–416
Stewart PS (2014) Biophysics of biofilm infection. Pathog Dis 70:212–218
Macià MD, Rojo-Molinero E, Oliver A (2014) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin Microbiol Infect. Epub 2014 Apr 26
Smith A, Buchinsky FJ, Post JC (2011) Eradicating chronic ear, nose, and throat infections: a systematically conducted literature review of advances in biofilm treatment. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 144:338–347
Desrosiers M, Bendouah Z, Barbeau J (2007) Effectiveness of topical antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vitro. Am J Rhinol 21:149–153
Solares CA, Batra PS, Hall GS, Citardi MJ (2006) Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis exacerbations due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with mupirocin irrigations. Am J Otolaryngol 27:161–165
Oxley KS, Thomas JG, Ramadan HH (2007) Effect of ototopical medications on tympanostomy tube biofilms. Laryngoscope 117:1819–1824
Wang JC, Hamood AN, Saadeh C, Cunningham MJ, Yim MT, Cordero J (2014) Strategies to prevent biofilm-based tympanostomy tube infections. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 78:1433–1438
Kim SG, Yoon YH, Choi JW, Rha KS, Park YH (2012) Effect of furanone on experimentally induced Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation: in vitro study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:1575–1578
Steel HC, Theron AJ, Cockeran R, Anderson R, Feldman C (2012) Pathogen- and host-directed anti-inflammatory activities of macrolide antibiotics. Mediators Inflamm 2012:584262
Singhal D, Jekle A, Debabov D, Wang L, Khosrovi B, Anderson M, Foreman A, Wormald PJ (2012) Efficacy of NVC-422 against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in a sheep biofilm model of sinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2:309–315
Korkmaz H, Ocal B, Tatar EC, Tatar I, Ozdek A, Saylam G, Celik HH (2014) Biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps: is eradication possible? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:2695–2702
Chen K, Wu X, Jiang G, Du J, Jiang H (2013) Low dose macrolide administration for long term is effective for otitis media with effusion in children. Auris Nasus Larynx 40:46–50
Kilty SJ, Duval M, Chan FT, Ferris W, Slinger R (2011) Methylglyoxal: (active agent of manuka honey) in vitro activity against bacterial biofilms. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 1:348–350
Drago L, Cappelletti L, De Vecchi E, Pignataro L, Torretta S, Mattina R (2014) Antiadhesive and antibiofilm activity of hyaluronic acid against bacteria responsible for respiratory tract infections. APMIS 122:1013–1019
Riise GC, Qvarfordt I, Larsson S, Eliasson V, Andersson BA (2000) Inhibitory effect of N-acetylcysteine on adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae to human oropharyngeal epithelial cells in vitro. Respiration 67:552–558
Zhao T, Liu Y (2010) N-acetylcysteine inhibit biofilms produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol 10:140
Pintucci JP, Corno S, Garotta M (2010) Biofilms and infections of the upper respiratory tract. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14:683–690
Marchese A, Debbia EA, Tonoli E, Gualco L, Schito AM (2002) In vitro activity of thiamphenicol against multiresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus in Italy. J Chemother 14:554–561
Macchi A, Ardito F, Marchese A, Schito GC, Fadda G (2006) Efficacy of N-acetyl-cysteine in combination with thiamphenicol in sequential (intramuscular/aerosol) therapy of upper respiratory tract infections even when sustained by bacterial biofilms. J Chemother 18:507–513
Macchi A, Castelnuovo P (2009) Aerosol antibiotic therapy in children with chronic upper airway infections: a potential alternative to surgery. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 22:303–310
Varricchio A, Capasso M, Di Gioacchino M, Ciprandi G (2008) Inhaled thiamphenicol and acetylcysteine in children with acute bacterial rhinopharyngitis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 21:625–629
Acknowledgments
The authors are financially supported by Bando Giovani Ricercatori 2009 (Italian Ministry of Health).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazzari, E., Torretta, S., Pignataro, L. et al. Role of biofilm in children with recurrent upper respiratory tract infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34, 421–429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2261-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2261-1