Abstract
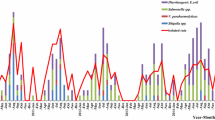
In this study, we hoped to provide valuable clinical information on yersiniosis for clinicians. Two thousand six hundred stool samples were collected from in- and outpatients with diarrhea, which were tested with both culture method and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). In total, 188 positive samples were detected by RT-PCR (178) and culture method (160), while the incidence was about 7.23%. The detection rate of RT-PCR was significantly higher than culture method and a higher incidence in autumn-winter was also noticeably identified than in spring-summer. Infection sources mostly focused on unboiled foods (101) and pets (45), while clinical manifestation mainly presented as gastroenteritis (156), pseudoappendicitis (32), and extraintestinal complications (46). The morbidity of extraintestinal complications in adults was significantly higher than in children and it was the same for high-risk patients between adults over the age of 60 years (4.7%) and children under the age of 3 years (1.4%), whereas the constituent ratio of children versus adults with yersiniosis in different systems was not significant. Of 160 isolates tested for antimicrobial susceptibility, the majority were susceptible to third-generation cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, whereas only a small portion was susceptible to the first-generation cephalosporins and penicillins. During autumn-winter months, clinicians should pay more attention to clinical manifestation, early diagnosis, and treatment with susceptible antibiotics of yersiniosis and its complications, targeting high-risk patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottone EJ (1997) Yersinia enterocolitica: the charisma continues. Clin Microbiol Rev 10:257–276
Feng P, Weagant SD (1994) Yersinia. In: Hui YH, Gorham JR, Murrell KD, Cliver DO (eds) Food-borne diseases handbook: diseases caused by bacteria. Dekker, New York, pp 427–460
Rabson AR, Hallett AF, Koornhof HJ (1975) Generalized Yersinia enterocolitica infection. J Infect Dis 131:447–451
Portnoy D, Martinez LA (1979) Yersinia enterocolitica septicemia with pneumonia. Can Med Assoc J 120:61–62
Taylor BG, Zafarzai MZ, Humphreys DW, Manfredi F (1977) Nodular pulmonary infiltrates and septic arthritis associated with Yersinia enterocolitica bacteremia. Am Rev Respir Dis 116:525–529
Sonnenwirth AC (1970) Bacteremia with and without meningitis due to Yersinia enterocolitica, Edwardsiella tarda, Comamonas terrigena, and Pseudomonas maltophilia. Ann NY Acad Sci 174:488–502
Clarridge J, Roberts C, Peters J, Musher D (1983) Sepsis and empyema caused by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol 17:936–938
Urbano-Márquez A, Estruch R, Agustí A, Jimenez De Anta MT, Ribalta T, Grau JM, Rozman C (1983) Infectious endocarditis due to Yersinia enterocolitica. J Infect Dis 148:940
Yang SH, Fang H (2003) Yersinia enterocolitica. In: Pathogen and bacteriology for animal and people (in Chinese). Shijiazhuang, Hebei Scientific and Technological Publishing House, pp 558–592
Bassler HA, Flood SA, Livak KJ, Mawmaro J, Knorr R, Batt CA (1995) Use of a fluorogenic probe in a PCR-based assay for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3724–3728
Feng P, Keasler SP, Hill WE (1992) Direct identification of Yersinia enterocolitica in blood by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Transfusion 32:850–854
Gibello A, Blanco MM, Moreno MA, Cutuli MT, Domenech A, Domínguez L, Fernández-Garayzábal JF (1999) Development of a PCR assay for detection of Yersinia ruckeri in tissues of inoculated and naturally infected trout. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:346–350
Ibrahim A, Liesack W, Griffiths MW, Robins-Browne RM (1997) Development of a highly specific assay for rapid identification of pathogenic strains of Yersinia enterocolitica based on PCR amplification of the Yersinia heat-stable enterotoxin gene (yst). J Clin Microbiol 35:1636–1638
Weynants V, Jadot V, Denoel PA, Tibor A, Letesson JJ (1996) Detection of Yersinia enterocolitica serogroup O:3 by a PCR method. J Clin Microbiol 34:1224–1227
Bowman AS, Glendening C, Wittum TE, LeJeune JT, Stich RW, Funk JA (2007) Prevalence of Yersinia enterocolitica in different phases of production on swine farms. J Food Prot 70:11–16
Bhaduri S, Wesley I (2006) Isolation and characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica from swine feces recovered during the National Animal Health Monitoring System Swine 2000 study. J Food Prot 69:2107–2112
Bhaduri S, Wesley IV, Bush EJ (2005) Prevalence of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica strains in pigs in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7117–7121
Zheng HX, Zhang MJ, Sun Y, Jiang B (2006) Detection of Yersinia enterocolitica in diarrhea stool by real-time PCR (in Chinese). Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86:2281–2284
Zheng H, Wang J, Sun Y, Jiang B (2007) Clinical isolation and characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica in China using real-time PCR and culture method. Digestion 75:199–204
Wauters G, Kandolo K, Janssens M (1987) Revised biogrouping scheme of Yersinia enterocolitica. Contrib Microbiol Immunol 9:14–21
Sanchez-Vizcaino JM, Cambro-Alvarez M (1987) Execution of the ELISA technique. In: Enzyme immunoassay techniques in animal and plant disease, 2nd edn. Office International des Epizooties, Paris, pp 23–24
Chen S, Yee A, Griffiths M, Larkin C, Yamashiro CT, Behari R, Paszko-Kolva C, Rahn K, de Grandis SA (1997) The evaluation of a fluorogenic polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Salmonella species in food commodities. Int J Food Microbiol 35:239–250
Xu XQ, Chen XJ, Cheng YZ, Ceng YS (2004) Comparison of three culture methods of Yersinia enterocolitica. Lab Med 19:451–454
Bhaduri S (2001) Pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica. In: Labbe RH, Garcia-Alvarado JS (eds) Guide to foodborne pathogens. Wiley, New York, pp 245–255
Thibodeau V, Frost E, Chénier H, Quessy S (1999) Presence of Yersinia enterocolitica in tissues of orally-inoculated pigs and the tonsils and feces of pigs at slaughter. Can J Vet Res 63:96–100
Ray SM, Ahuja SD, Blake PA, Farley MM, Samuel M, Fiorentino T, Swanson E, Cassidy M, Lay JC, Van Gilder T; Emerging Infections Program FoodNet Working Group (2004) Population-based surveillance for Yersinia enterocolitica infections in FoodNet Sites, 1996–1999: higher risk of disease in infants and minority populations. Clin Infect Dis 38(Suppl 3):S181–S189
Burnens AP, Frey A, Nicolet J (1996) Association between clinical presentation, biogroups and virulence attributes of Yersinia enterocolitica strains in human diarrhoeal disease. Epidemiol Infect 116:27–34
Grant T, Bennett-Wood V, Robins-Browne RM (1998) Identification of virulence-associated characteristics in clinical isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica lacking classical virulence markers. Infect Immun 66:1113–1120
Lee TS, Lee SW, Seok WS, Yoo MY, Yoon JW, Park BK, Moon KD, Oh DH (2004) Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility, and virulence factors of Yersinia enterocolitica and related species from ready-to-eat vegetables available in Korea. J Food Prot 67:1123–1127
Fredriksson-Ahomaa M, Stolle A, Korkeala H (2006) Molecular epidemiology of Yersinia enterocolitica infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 47(3):315–329
Abdel-Haq NM, Asmar BI, Abuhammour WM, Brown WJ (2000) Yersinia enterocolitica infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19(10):954–958
Blei F, Puder DR (1993) Yersinia enterocolitica bacteremia in a chronically transfused patient with sickle cell anemia. Case report and review of the literature. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 15:430–434
Saebo A, Vik E, Lange OJ, Matuszkiewicz L (2005) Inflammatory bowel disease associated with Yersinia enterocolitica O:3 infection. Eur J Intern Med 16(3):176–182
Lamps LW, Madhusudhan KT, Havens JM, Greenson JK, Bronner MP, Chiles MC, Dean PJ, Scott MA (2003) Pathogenic Yersinia DNA is detected in bowel and mesenteric lymph nodes from patients with Crohn’s disease. Am J Surg Pathol 27(2):220–227
Persson S, Danielsson D, Kjellander J, Wallensten S (1976) Studies on Crohn’s disease. 1. The relationship between Yersinia enterocolitica infection and terminal ileitis. Acta Chir Scand 142:84–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Sun, Y., Lin, S. et al. Yersinia enterocolitica infection in diarrheal patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 27, 741–752 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-008-0562-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-008-0562-y