Abstract
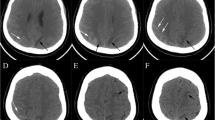
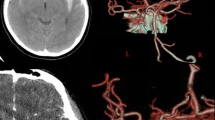
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes (RCVS) comprise a group of disorders characterized by prolonged, but reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries, usually associated with acute-onset, severe, recurrent headaches, with or without additional neurological signs and symptoms. Various complications of this condition have been observed, such as cortical subarachnoid hemorrhages (cSAH), intracerebral hemorrhages, reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy, ischaemic strokes and transient ischaemic attacks. It is important to include RCVS in thunderclap headache differential diagnosis and among non-aneurismatic subarachnoid hemorrhage causes. In the past years, thanks to the major diffusion of new diagnostic tools such as magnetic resonance, computed tomography and digital subtraction angiography, RCVS have been demonstrated to be more frequent than previously thought. We report an illustrative case of a woman affected by a small cSAH, associated to RCVS, after elective triplet cesarean delivery. To our knowledge, this is the first case of cSAH associated to RCVS after a triplet pregnancy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calabrese LH, Dodick DW, Schwedt TJ, Singhal AB (2007) Narrative review: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Intern Med 146(1):34–44
Call GK, Fleming MC, Sealfon S, Levine H, Kistler JP, Fisher CM (1988) Reversible cerebral segmental vasoconstriction. Stroke 19(9):1159–1170
Hajj-Ali RA, Furlan A, Abou-Chebel A, Calabrese LH (2002) Benign angiopathy of the central nervous system: cohort of 16 patients with clinical course and long-term follow-up. Arthritis Rheum 47(6):662–669
Bogousslavsky J, Despland PA, Regli F, Dubuis PY (1989) Postpartum cerebral angiopathy: reversible vasoconstriction assessed by transcranial Doppler ultrasounds. Eur Neurol 29(2):102–105
Day JW, Raskin NH (1986) Thunderclap headache: symptom of unruptured cerebral aneurysm. Lancet 2(8518):1247–1248
Slivka A, Philbrook B (1995) Clinical and angiographic features of thunderclap headache. Headache 35(1):1–6
Dodick DW, Brown RD Jr, Britton JW, Huston J 3rd (1999) Nonaneurysmal thunderclap headache with diffuse, multifocal, segmental, and reversible vasospasm. Cephalalgia 19(2):118–123
Serdaru M, Chiras J, Cujas M, Lhermitte F (1984) Isolated benign cerebral vasculitis or migrainous vasospasm? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47(1):73–76
Solomon S, Lipton RB, Harris PY (1990) Arterial stenosis in migraine: spasm or arteriopathy? Headache 30(2):52–61
Gomez CR, Gomez SM, Puricelli MS, Malik MM (1991) Transcranial Doppler in reversible migrainous vasospasm causing cerebellar infarction: report of a case. Angiology 42(2):152–156
Jackson M, Lennox G, Jaspan T, Jefferson D (1993) Migraine angiitis precipitated by sex headache and leading to watershed infarction. Cephalalgia 13(6):427–430
Henry PY, Larre P, Aupy M, Lafforgue JL, Orgogozo JM (1984) Reversible cerebral arteriopathy associated with the administration of ergot derivatives. Cephalalgia 4(3):171–178
Le Coz P, Woimant F, Rougemont D, Sanson M, Laplane D, Haguenau M, Pépin B (1988) Benign cerebral angiopathies and phenylpropanolamine. Rev Neurol (Paris) 144(4):295–300
Raroque HG Jr, Tesfa G, Purdy P (1993) Postpartum cerebral angiopathy. Is there a role for sympathomimetic drugs? Stroke 24(12):2108–2110
Singhal AB, Bernstein RA (2005) Postpartum angiopathy and other cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Neurocrit Care 3(1):91–97
Singhal AB (2004) Postpartum angiopathy with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy. Arch Neurol 61(3):411–416
Singhal AB, Kimberly WT, Schaefer PW, Hedley-Whyte ET (2009) Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 8-2009. A 36-year-old woman with headache, hypertension, and seizure 2 weeks post partum. N Engl J Med 360(11):1126–1137
Ducros A, Boukobza M, Porcher R, Sarov M, Valade D, Bousser MG (2007) The clinical and radiological spectrum of reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. A prospective series of 67 patients. Brain 130(Pt 12):3091–4101
Dodick DW (2003) Reversible segmental cerebral vasoconstriction (Call-Fleming syndrome): the role of calcium antagonists. Cephalalgia 23(3):163–165
Lu SR, Liao YC, Fuh JL, Lirng JF, Wang SJ (2004) Nimodipine for treatment of primary thunderclap headache. Neurology 62(8):1414–1416
Bouchard M, Verreault S, Gariépy JL, Dupré N (2009) Intra-arterial milrinone for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Headache 49(1):142–145
Singhal AB, Caviness VS, Begleiter AF, Mark EJ, Rordorf G, Koroshetz WJ (2002) Cerebral vasoconstriction and stroke after use of serotonergic drugs. Neurology 58(1):130–133
Sibai B, Dekker G, Kupferminc M (2005) Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 365(9461):785–799
Lindegaard KF, Nornes H, Bakke SJ, Sorteberg W, Nakstad P (1989) Cerebral vasospasm diagnosis by means of angiography and blood velocity measurements. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 100(1–2):12–24
Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM (1980) Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6(1):1–9
Saito I, Ueda Y, Sano K (1977) Significance of vasospasm in the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 47(3):412–429
Gerretsen P, Kern RZ (2007) Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome or primary angiitis of the central nervous system? Can J Neurol Sci 34(4):467–477
Chen SP, Fuh JL, Chang FC, Lirng JF, Shia BC, Wang SJ (2008) Transcranial color Doppler study for reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndromes. Ann Neurol 63(6):751–757
Ursell MR, Marras CL, Farb R, Rowed DW, Black SE, Perry JR (1998) Recurrent intracranial hemorrhage due to postpartum cerebral angiopathy: implications for management. Stroke 29(9):1995–1998
Sances G, Granella F, Nappi RE, Fignon A, Ghiotto N, Polatti F, Nappi G (2003) Course of migraine during pregnancy and pospartum: a prospective study. Cephalalgia 23:197–205
Zacur HA (2006) Hormonal changes throughout life in women. Headache 46:S49–S54
Stella CL, Jodicke CD, How HY, Harkness UF, Sibai BM (2007) Postpartum headache: is your work complete? Am J Obstet Gynecol 197:318e1–318e7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albano, B., Del Sette, M., Roccatagliata, L. et al. Cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage associated with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome after elective triplet cesarean delivery. Neurol Sci 32, 497–501 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0505-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0505-8