Abstract
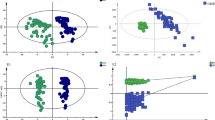
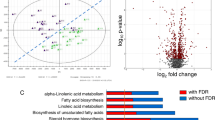
Metabolomics has been applied to explore altered metabolite profiles in disease and identify unique metabolic signatures in recent years. We aim to characterize the metabolic profile of rheumatoid arthritis patients and explore its underlying pathological processes using metabolomics approach. Serum samples from 30 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, 30 primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) patients, and 32 healthy controls (HC) were collected. The sample was analyzed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC-HRMS). Potential biomarkers were screened from orthogonal projection to latent structure discriminate analysis (OPLS-DA) and further evaluated by receiver operating characteristic analysis (ROC). Compared with HC and pSS patients, the RA patients had increased serum levels of 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid, glutamic acid, L-leucine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan, L-proline, glyceraldehyde, fumaric acid, and cholesterol as well as decreased capric acid, argininosuccinic acid, and billirubin. A total of eight potential biomarkers were screened and tentatively identified for RA. A panel of three metabolites (4-methoxyphenylacetic acid, L-phenylalanine, and L-leucine) was identified as specific biomarkers of RA. ROC analysis showed that the panel had a sensitivity of 93.30% with a specificity of 95.20% in discrimination RA from other groups. UPLC-HRMS-based quantification of circulating metabolites was a useful tool for identifying RA patients from pSS patients and healthy controls. The potential biomarkers indicated that the RA metabolic disturbance might be associated with inflammation injury, amino acid metabolism, oxidative stress, and phospholipid metabolism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Jaarsveld CH, Jacobs JW, Schrijvers AJ, Heurkens AH, Haanen HC, Bijlsma JW (1998) Direct cost of rheumatoid arthritis during the first six years: a cost-of-illness study. Br J Rheumatol 37(8):837–847. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/37.8.837
Albers JM, Kuper HH, van Riel PL, Prevoo ML, van 't Hof MA, van Gestel AM, Severens JL (1999) Socio-economic consequences of rheumatoid arthritis in the first years of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38(5):423–430. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/38.5.423
Goldring MB (2006) Update on the biology of the chondrocyte and new approaches to treating cartilage diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(5):1003–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2006.06.003
van der Kooij SM, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Guler-Yuksel M, Zwinderman AH, Kerstens PJ, van der Lubbe PA, de Beus WM, Grillet BA, Ronday HK, Huizinga TW, Breedveld FC, Dijkmans BA, Allaart CF (2009) Drug-free remission, functioning and radiographic damage after 4 years of response-driven treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):914–921. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.092254
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310302
Lauridsen MB, Bliddal H, Christensen R, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bennett R, Keun H, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Dorff MH, Jaroszewski JW, Hansen SH, Cornett C (2010) 1H NMR spectroscopy-based interventional metabolic phenotyping: a cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Proteome Res 9(9):4545–4553. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr1002774
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC (2008) Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 455(7216):1054–1056. https://doi.org/10.1038/4551054a
Scrivo R, Casadei L, Valerio M, Priori R, Valesini G, Manetti C (2014) Metabolomics approach in allergic and rheumatic diseases. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 14(6):445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-014-0445-5
Kim S, Hwang J, Xuan J, Jung YH, Cha HS, Kim KH (2014) Global metabolite profiling of synovial fluid for the specific diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis from other inflammatory arthritis. PLoS One 9(6):e97501. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097501
Qi Y, Pi Z, Liu S, Song F, Lin N, Liu Z (2014) A metabonomic study of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Mol BioSyst 10(10):2617–2625. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00131a
Zhou J, Chen J, Hu C, Xie Z, Li H, Wei S, Wang D, Wen C, Xu G (2016) Exploration of the serum metabolite signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 127:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.02.004
Jandera P (2013) Advances in the development of organic polymer monolithic columns and their applications in food analysis--a review. J Chromatogr A 1313:37–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.08.010
Choi JY, Yoon YJ, Choi HJ, Park SH, Kim CD, Kim IS, Kwon TH, Do JY, Kim SH, Ryu DH, Hwang GS, Kim YL (2011) Dialysis modality-dependent changes in serum metabolites: accumulation of inosine and hypoxanthine in patients on haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(4):1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq554
Zhao YY, Zhang L, Long FY, Cheng XL, Bai X, Wei F, Lin RC (2013) UPLC-Q-TOF/HSMS/MS(E)-based metabonomics for adenine-induced changes in metabolic profiles of rat faeces and intervention effects of ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one. Chem Biol Interact 201(1–3):31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2012.12.002
Dauphinee M, Tovar Z, Talal N (1988) B cells expressing CD5 are increased in Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 31(5):642–647. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310509
Murota A, Suzuki K, Kassai Y, Miyazaki T, Morita R, Kondo Y, Takeshita M, Niki Y, Yoshimura A, Takeuchi T (2016) Serum proteomic analysis identifies interleukin 16 as a biomarker for clinical response during early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 78:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2015.12.002
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH, European Study Group on Classification Criteria for Sjogren's S (2002) Classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European consensus group. Ann Rheum Dis 61(6):554–558
Vuckovic D (2012) Current trends and challenges in sample preparation for global metabolomics using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(6):1523–1548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6039-y
Blasco H, Corcia P, Pradat PF, Bocca C, Gordon PH, Veyrat-Durebex C, Mavel S, Nadal-Desbarats L, Moreau C, Devos D, Andres CR, Emond P (2013) Metabolomics in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an untargeted approach via high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 12(8):3746–3754. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr400376e
Xia J, Mandal R, Sinelnikov IV, Broadhurst D, Wishart DS (2012) MetaboAnalyst 2.0--a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic acids res 40 (web server issue):W127-133. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks374
Smolenska Z, Smolenski RT, Zdrojewski Z (2016) Plasma concentrations of amino acid and nicotinamide metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis--potential biomarkers of disease activity and drug treatment. Biomarkers 21(3):218–224. https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2015.1130746
Surowiec I, Arlestig L, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Trygg J (2016) Metabolite and lipid profiling of biobank plasma samples collected prior to onset of rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 11(10):e0164196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164196
Toms TE, Symmons DP, Kitas GD (2010) Dyslipidaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of inflammation, drugs, lifestyle and genetic factors. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 8(3):301–326. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016110791112269
Steiner G, Urowitz MB (2009) Lipid profiles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and the impact of treatment. Semin Arthritis Rheum 38(5):372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.01.015
Tall AR, Yvan-Charvet L (2015) Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 15(2):104–116. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3793
Zhai G, Wang-Sattler R, Hart DJ, Arden NK, Hakim AJ, Illig T, Spector TD (2010) Serum branched-chain amino acid to histidine ratio: a novel metabolomic biomarker of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):1227–1231. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.120857
Gao P, Lu C, Zhang F, Sang P, Yang D, Li X, Kong H, Yin P, Tian J, Lu X, Lu A, Xu G (2008) Integrated GC-MS and LC-MS plasma metabonomics analysis of ankylosing spondylitis. Analyst 133(9):1214–1220. https://doi.org/10.1039/b807369d
Mero A (1999) Leucine supplementation and intensive training. Sports Med 27(6):347–358. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-199927060-00001
Du Y, Meng Q, Zhang Q, Guo F (2012) Isoleucine or valine deprivation stimulates fat loss via increasing energy expenditure and regulating lipid metabolism in WAT. Amino Acids 43(2):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1123-8
Yue R, Zhao L, Hu Y, Jiang P, Wang S, Xiang L, Liu W, Shan L, Zhang W, Liu R (2013) Metabolomic study of collagen-induced arthritis in rats and the interventional effects of huang-lian-jie-du-tang, a traditional chinese medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:439690. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/439690
McNearney T, Speegle D, Lawand N, Lisse J, Westlund KN (2000) Excitatory amino acid profiles of synovial fluid from patients with arthritis. J Rheumatol 27(3):739–745
Mason DJ (2004) The role of glutamate transporters in bone cell signalling. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 4(2):128–131
Straub RH, Kalden JR (2009) Stress of different types increases the proinflammatory load in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11(3):114. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2712
Isogai H, Hirayama N (2013) A possible molecular mechanism of immunomodulatory activity of bilirubin. Int J Med Chem 2013:467383. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/467383
Rosillo MA, Alcaraz MJ, Sanchez-Hidalgo M, Fernandez-Bolanos JG, Alarcon-de-la-Lastra C, Ferrandiz ML (2014) Anti-inflammatory and joint protective effects of extra-virgin olive-oil polyphenol extract in experimental arthritis. J Nutr Biochem 25(12):1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.07.006
Park EJ, Kim SA, Choi YM, Kwon HK, Shim W, Lee G, Choi S (2011) Capric acid inhibits NO production and STAT3 activation during LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis. PLoS One 6(11):e27739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027739
Soreide K (2009) Receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis in diagnostic, prognostic and predictive biomarker research. J Clin Pathol 62(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2008.061010
Acknowledgments
We thank minjian Chen, from Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Toxicology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
Author′s contributions
Study concept and design: Miaojia Zhang, Wenfeng Tan, Nan Che, and Ju Li. Recruit patients: Miaojia Zhang, Wenfeng Tan, Nan Che, Lingxiao Xu, Qian Zhang, Qi Wang, and Ju Li. Acquisition of data: Ju Li. Analysis and interpretation of the data: Miaojia Zhang, Wenfeng Tan, and Ju Li. Write the paper: Miaojia Zhang, Wenfeng Tan, and Ju Li. All authors reviewed the manuscript before submission.
Funding
This research was supported by the Special Project of Clinical Medicine from Jiangsu Province (BL2013034), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81671615) and exchange visiting scholarships from Huai’an First People’s Hospital in Swedish Karolinska Medical School.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
The investigation protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board and the Ethic committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Consent forms were obtained from all study participants.
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Che, N., Xu, L. et al. LC-MS-based serum metabolomics reveals a distinctive signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 37, 1493–1502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4021-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4021-6