Abstract
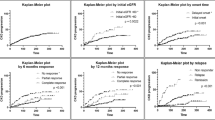
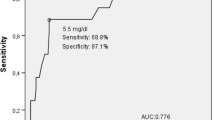
The objective is to investigate the accrual rate and risk factors of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in an inception cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) followed at a single tertiary center. A prospectively collected database of 256 consecutive patients with SLE followed over a 25-year period was systematically interrogated for demographic, disease manifestations, co-morbidities, and outcome. Standardized SLE activity and damage scores were determined for the first and last study visits, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; MDRD formula) was calculated at the time of diagnosis and at each year of the follow-up. CKD was defined as eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2. Results were analyzed with univariate and multivariate models and Kaplan-Meier curves, as appropriate. The cohort was predominantly female (90 %) and Jewish (91.1 %). Mean age at diagnosis was 38 ± 15.5 years, mean SLE activity score 6.4 ± 3.8, mean disease duration 8.8 ± 6.6 years, and mean damage score 0.2 ± 0.6. Seventy-five patients (30.8 %) were diagnosed with American College of Rheumatology (ACR)-defined lupus renal disease during the study period. There was a progressive decrease in eGFR over time. The prevalence of CKD was 46.7 % in patients with ACR-defined renal lupus disease and 16.4 % in those without. The hazards ratio for CKD was significantly higher in patients with lupus nephritis (LN) than without (p < 0.001). Earlier CKD was positively associated with hypertension (p = 0.01), older age at diagnosis (p = 0.01), and LN (p < 0.001), and negatively associated with hydroxychloroquine treatment (p < 0.001). The prevalence of CKD increases cumulatively in patients with SLE, also in those without overt lupus renal disease. Lupus renal disease poses a significant hazard for earlier development of CKD, and hypertension is a major risk factor for patients with and without nephritis. Antimalarial treatment is associated with renal preservation only in patients with lupus nephritis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group (2013) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 3:1–150
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351:1296–1305
Culleton BF, Larson MG, Wilson PW, Evans JC, Parfrey PS, Levy D (1999) Cardiovascular disease and mortality in a community-based cohort with mild renal insufficiency. Kidney Int 56:2214–2219
Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention et al (2003) Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation 108:2154–2169
Goicoechea M, de Vinuesa SG, Gómez-Campderá F, Luño J (2005) Predictive cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int Suppl 93:S35–S38
D’Cruz DP, Khamashta M, Hughes GR (2007) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 369:587–596
Seshan SV, Jennette JC (2009) Renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus with emphasis on classification of lupus glomerulonephritis. Advances and implications. Arch Pathol Lab Med 133:233–248
Zhang W, Agheh E, Reich HN et al (2011) Glomerular filtration rate predicts arterial events in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 50:799–805
Croca SC, Rodrigues T, Isenberg D (2011) Assessment of a lupus nephritis cohort over a 30-year period. Rheumatology 50:1424–1430
Faurschou M, Dreyer L, Kamper AL, Starklint H, Jacobsen S (2010) Long-term mortality and renal outcome in a cohort of 100 patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res 62:873–880
Baranowska-Daca E, Choi YJ, Barrios R, Nassar G, Suki WN, Truong LD (2001) Nonlupus nephritides in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Hum Pathol 32:1125–1135
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Nirel N, Rosen B, Sharon A, Blondheim O, Sherf M, Samuel H, Cohen AD (2010) The impact of an integrated hospital-community medical information system on quality and service utilization in hospital departments. Int J Med Inform 79:649–657
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Goldsmith CH et al (1997) The reliability of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:809–813
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D, Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtrating rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Leung YY, Lo KM, Szeto CC, Li EK, Kun EW (2006) Estimation of glomerular filtration rate in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 15:276–281
Austin HA, Muenz LR, Joyce KM et al (1983) Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am J Med 75:382–391
Ward MM (1999) Premature morbidity from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 42:338–346
McMahon M, Hahn BH, Skaggs BJ (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: prediction and potential for therapeutic intervention. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 7:227–241
Mok CC (2005) Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Lupus 14:39–44
Donadio JV Jr, Hart GM, Bergstralh EJ, Holley KE (1995) Prognostic determinants in lupus nephritis: a long-term clinicopathologic study. Lupus 4:109–115
Mok CC, Wong RW, Lau CS (1999) Lupus nephritis in southern Chinese patients: clinicopathologic findings and long-term outcome. Am J Kidney Dis 34:315–323
Korbet SM, Lewis EJ, Schwartz MM, Reichlin M, Evans J, Rohde RD, Lupus Nephritis Collaborative Study Group (2000) Factors predictive of outcome in severe lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 35:904–914
Austin HA III, Boumpas DT, Vaughan EM, Balow JE (1995) High-risk features of lupus nephritis: importance of race and clinical and histological factors in 166 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10:1620–1628
Esdaile JM, Federgreen W, Quintal H, Suissa S, Hayslett JP, Kashgarian M (1991) Predictors of one year outcome in lupus nephritis: the importance of renal biopsy. Q J Med 81:907–918
Reich HN, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB et al (2011) Persistent proteinuria and dyslipidemia increase the risk of progressive chronic kidney disease in lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int 79:914–920
Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS (2007) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298(17):2038–2047
Hallan SI, Coresh J, Astor BC, Asberg A, Powe NR, Romundstad S, Hallan HA, Lydersen S, Holmen J (2006) International comparison of the relationship of chronic kidney disease prevalence and ESRD risk. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(8):2275–2284
Zhang L, Zhang P, Wang F, Zuo L, Zhou Y, Shi Y, Li G, Jiao S, Liu Z, Liang W, Wang H (2008) Prevalence and factors associated with CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 51(3):373–384
Al-Herz A, Ensworth S, Shojania K, Esdaile JM (2003) Cardiovascular risk factor screening in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30:493–496
Budman DR, Steinberg AD (1976) Hypertension and renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med 136:1003–1007
Ryan MJ (2009) The pathophysiology of hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1258–R1267
Molad Y, Gorshttein A, Wysenbeek AJ et al (2002) Protective effect of hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus. Prospective long-term study of an Israeli cohort. Lupus 11:356–361
Esdaile J (1991) For the Canadian Hydroxychloroquine Study Group. A randomized study of the effect of withdrawing hydroxychloroquine sulfate in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 324:150–154
Fessler BJ, Alarcón GS, McGwin G Jr, LUMINA Study Group et al (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XVI. Association of hydroxychloroquine use with reduced risk of damage accrual. Arthritis Rheum 52:1473–1480
Alarcon GS, McGwin G, Bertoli AM, LUMINA Study Group et al (2007) Effect of hydroxychloroquine on the survival of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: data from LUMINA, a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA L). Ann Rheum Dis 66:1168–1172
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA (2008) Hydroxychloroquine: the cornerstone of lupus therapy. Lupus 17:271–273
Pons-Estel GJ, Alarcón GS, McGwin G Jr, Lumina Study Group (2009) Protective effect of hydroxychloroquine on renal damage in patients with lupus nephritis. LXV. Data from a multiethnic US cohort. Arthritis Rheum 61:830–839
Kasitanon N, Fine DM, Haas M, Magder LS, Peti M (2006) Hydroxychloroquine use predicts complete renal remission within 12 months among patients treated with mycophenolate mofetil therapy for membranous lupus nephritis. Lupus 15:366–370
Sisó A, Ramos-Casals M, Bové A et al (2008) Previous antimalarial therapy in patients diagnosed with lupus nephritis: influence on outcomes and survival. Lupus 17:281–288
Sisó A, Ramos-Casals M, Bové A et al (2010) Outcomes in biopsy-proven lupus nephritis: evaluation of 190 white patients from a single center. Medicine (Baltimore) 89:300–307
Kuznik A, Bencina M, Svajger U, Jeras M, Rozman B, Jerala R (2011) Mechanism of endosomal TLR inhibition by antimalarial drugs and imidazoquinolines. J Immunol 186:4794–4804
Papadimitraki ED, Tzardi M, Bertsias G, Sotsiou E, Boumpas DT (2009) Glomerular expression of toll-like receptor-9 in lupus nephritis but not in normal kidneys: implications for the amplification of the inflammatory response. Lupus 18:831–835
Frieri M, Samih MA, Dzhindzhikhashvili M, Liu H, Balsam L, Rubinstein S (2012) Toll-like receptor 9 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in human kidneys from lupus nephritis patients. J Nephrol 25:1041–1046
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pokroy-Shapira, E., Gelernter, I. & Molad, Y. Evolution of chronic kidney disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus over a long-period follow-up: a single-center inception cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 33, 649–657 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2527-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2527-0