Abstract
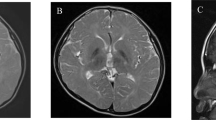
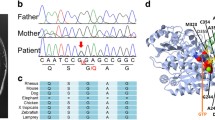
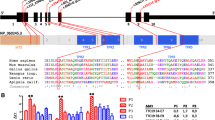
Mutations in the TUBB4A gene have been identified so far in two neurodegenerative disorders with extremely different clinical features and course: whispering dysphonia, also known as dystonia type 4 (DYT4), and hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC). We describe a patient with slowly progressive spastic paraparesis, segmental dystonia, intellectual disability, behavioral problems, and evidence of permanent, incomplete myelination associated with progressive cerebellar atrophy. Whole exome sequencing revealed a novel E410K de novo heterozygous mutation in the TUBB4A gene. The clinical and radiological picture of our patient is different from the classic phenotype; thus, it expands the phenotypic variation of TUBB4A-gene-related disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hersheson J, Mencacci NE, Davis M, Macdonald N, Trabzuni D, Ryten M, Pittman A, Paudel R, Kara E, Fawcett K, Plagnol V, Bhatia KP, Medlar AJ, Stanescu HC, Hardy J, Kleta R, Wood NW, Houlden H (2013) Mutations in the autoregulatory domain of β-tubulin 4a cause hereditary dystonia. Ann Neurol 73:546–553
Lohmann K, Wilcox RA, Winkler S, Ramirez A, Rakovic A, Park JS, Arns B, Lohnau T, Groen J, Kasten M, Brüggemann N, Hagenah J, Schmidt A, Kaiser FJ, Kumar KR, Zschiedrich K, Alvarez-Fischer D, Altenmüller E, Ferbert A, Lang AE, Münchau A, Kostic V, Simonyan K, Agzarian M, Ozelius LJ, Langeveld AP, Sue CM, Tijssen MA, Klein C (2013) Whispering dysphonia (DYT4 dystonia) is caused by a mutation in the TUBB4 gene. Ann Neurol 73:537–545
Simons C, Wolf NI, McNeil N, Caldovic L, Devaney JM, Takanohashi A, Crawford J, Ru K, Grimmond SM, Miller D, Tonduti D, Schmidt JL, Chudnow RS, van Coster R, Lagae L, Kisler J, Sperner J, van der Knaap MS, Schiffmann R, Taft RJ, Vanderver A (2013) A de novo mutation in the β-tubulin gene TUBB4A results in the leukoencephalopathy hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum. Am J Hum Genet 92:767–773
van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Pouwels PJ, Bonavita S, van Coster R, Lagae L, Sperner J, Surtees R, Schiffmann R, Valk J (2002) New syndrome characterized by hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1466–1474
Redeker V, Melki R, Promé D, Le Caer JP, Rossier J (1992) Structure of tubulin C-terminal domain obtained by subtilisin treatment. The major alpha and beta tubulin isotypes from pig brain are glutamylated. FEBS Lett 313:185–192
Lefèvre J, Chernov KG, Joshi V, Delga S, Toma F, Pastré D, Curmi PA, Savarin P (2011) The C terminus of tubulin, a versatile partner for cationic molecules: binding of Tau, polyamines, and calcium. J Biol Chem 286:3065–3078
Cushion TD, Dobyns WB, Mullins JG, Stoodley N, Chung SK, Fry AE, Hehr U, Gunny R, Aylsworth AS, Prabhakar P, Uyanik G, Rankin J, Rees MI, Pilz DT (2013) Overlapping cortical malformations and mutations in TUBB2B and TUBA1A. Brain 136:536–548
Wilcox RA, Winkler S, Lohmann K, Klein C (2011) Whispering dysphonia in an Australian family (DYT4): a clinical and genetic reappraisal. Mov Disord 26:2404–2408
van der Knaap M, Linnankivi T, Paetau A, Feigenbaum A, Wakusawa K, Haginoya K, Ko¨hler W, Henneke M, Dinopoulos A, Grattan-Smith P, Brockmann K, Schiffmann R, Blaser S (2007) Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum: follow-up and pathology. Neurology 69:166–171
Breuss M, Heng JI, Poirier K, Tian G, Jaglin XH, Qu Z, Braun A, Gstrein T, Ngo L, Haas M, Bahi-Buisson N, Moutard ML, Passemard S, Verloes A, Gressens P, Xie Y, Robson KJ, Rani DS, Thangaraj K, Clausen T, Chelly J, Cowan NJ, Keays DA (2012) Mutations in the β-tubulin gene TUBB5 cause microcephaly with structural brain abnormalities. Cell Rep 2:1554–1562
Sasaki M, Takanashi J, Tada H, Sakuma H, Furushima W, Sato N (2009) Diffuse cerebral hypomyelination with cerebellar atrophy and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. Brain Dev 31:582–587
Grattagliano I, Bonfrate L, Ruggiero V, Scaccianoce G, Palasciano G, Portincasa P (2013) Novel therapeutics for the treatment of familial mediterranean fever: from colchicine to biologics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. online 18 Jul 2013
Parker N (1985) Hereditary whispering dysphonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:218–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lubov Blumkin, Ayelet Halevy, and Esther Leshinsky-Silver contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blumkin, L., Halevy, A., Ben-Ami-Raichman, D. et al. Expansion of the spectrum of TUBB4A-related disorders: a new phenotype associated with a novel mutation in the TUBB4A gene. Neurogenetics 15, 107–113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-014-0392-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-014-0392-2