Abstract
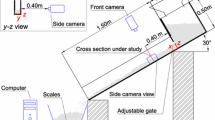
Flows of dry granular materials on a smooth chute are investigated by X-ray radiography. Discontinuities in height, velocity and density, namely jumps, are produced under different incoming steady-flow conditions by varying the mass discharge and the slope angle. This allows to confirm and further reveal the phase-diagram of standing granular jump patterns with diffuse and weakly compressible jumps that move to steep and highly compressible jumps when increasing the slope angle and/or decreasing the mass discharge. A wide range of steady-flow states before and after the jumps are achieved within each of the different experiments over variable input conditions. The flow densities are then measured relatively accurately by the X-ray radiography. This allows to highlight a transition from the supercritical flows before the jump to the subcritical flows after the jump through hysteresis of the depth-averaged effective friction, if incompressible depth-averaged momentum conservation is considered valid for the regions before and after the jump. In addition, the X-ray data of both free-surface and density profiles across the standing granular jumps are successfully used to further validate a recently-established augmented Bélanger equation for the jump height ratio.
Graphic abstract



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennen, C., Sieck, K., Paslaski, J.: Hydraulic jumps in granular material flow. Powder. Technol. 35(1), 31–37 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-5910(83)85023-2. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0032591083850232)
Brodu, N., Richard, P., Delannay, R.: Shallow granular flows down flat frictional channels: steady flows and longitudinal vortices. Phys. Rev. E 87(2), 022202 (2013)
Campbell, C., Brennen, C., Sabersky, R.: Flow regimes in inclined open-channel flows of granular materials. Powder. Technol. 41(1), 77–82 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-5910(85)85077-4. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0032591085850774)
Edwards, A., Gray, J.: Erosion-deposition waves in shallow granular free-surface flows. J. Fluid. Mech. 762, 35–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2014.643
Edwards, A., Russell, A., Johnson, C., Gray, J.: Frictional hysteresis and particle deposition in granular free-surface flows. J. Fluid. Mech. 875, 1058–1095 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2019.517
Faug, T.: Depth-averaged analytic solutions for free-surface granular flows impacting rigid walls down inclines. Phys. Rev. E 92(6), 062310 (2015)
Faug, T.: Impact force of granular flows on walls normal to the bottom: slow versus fast impact dynamics. Can. Geotech. J. 58(1), 114–24 (2021)
Faug, T., Beguin, R., Chanut, B.: Mean steady granular force on a wall overflowed by free-surface gravity-driven dense flows. Phys. Rev. E 80, 021305 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.80.021305. (https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.80.021305)
Faug, T., Childs, P., Wyburn, E., Einav, I.: Standing jumps in shallow granular flows down smooth inclines. Phys. Fluids. 27(7), 073304 (2015)
Gray, J., Tai, Y.C., Noelle, S.: Shock waves, dead zones and particle-free regions in rapid granular free-surface flows. J. Fluid. Mech. 491, 161–181 (2003)
Guillard, F., Marks, B., Einav, I.: Dynamic x-ray radiography reveals particle size and shape orientation fields during granular flow. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 8155 (2017)
Jaworski, A., Dyakowski, T.: (2007) Observations of “granular jump” in the pneumatic conveying system. Exp. Thermal. Fluid. Sci. 31(8), 877–885 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2006.09.003. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0894177706001452)
Jop, P., Forterre, Y., Pouliquen, O.: A constitutive law for dense granular flows. Nature 441(7094), 727–730 (2006)
Josserand, P., Lagrée, P.Y., Lhuillier, D.: Granular pressure and the thickness of a layer jamming on a rough incline. Europhys. Lett. 73(3), 363–369 (2006)
Lu, K., Brodsky, E.E., Kavehpour, H.P.: Shear-weakening of the transitional regime for granular flow. J. Fluid. Mech. 587, 347–372 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112007007331
Méjean, S., Faug, T., Einav, I.: A general relation for standing normal jumps in both hydraulic and dry granular flows. J. Fluid. Mech. 816, 331–351 (2017)
Méjean, S., Guillard, F., Faug, T., Einav, I.: Length of standing jumps along granular flows down smooth inclines. Phys. Rev. Fluids. 5, 034303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.034303. (https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.5.034303)
Morrison, H., Richmond, O.: Application of spencer’s ideal soil model to granular materials flow. J. Appl. Mech. 43(1), 49–53 (1976)
Nakagawa, M., Altobelli, S., Caprihan, A., Fukushima, E., Jeong, E.K.: Non-invasive measurements of granular flows by magnetic resonance imaging. Exp. Fluids. 16, 54–60 (1993)
Pouliquen, O., Forterre, Y.: Friction law for dense granular flows: application to the motion of a mass down a rough inclined plane. J. Fluid. Mech. 453, 133–151 (2002)
Russell, A.S., Johnson, C.G., Edwards, A.N., Viroulet, S., Rocha, F.M., Gray, J.M.N.T.: Retrogressive failure of a static granular layer on an inclined plane. J. Fluid. Mech. 869, 313–340 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2019.215
Samadani, A., Mahadevan, L., Kudrolli, A.: Shocks in sand flowing in a silo. J. Fluid. Mech. 452, 293–301 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112001006991
Sarno, L., Carleo, L., Papa, M.N., Armanini, A.: Optical method for measuring the volume fraction of granular media: application to faced-centered cubic lattices of monodisperse spheres. Phys. Rev. E 101, 022904 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.101.022904. (https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.101.022904)
Savage, S.: Gravity flow of cohesionless granular materials in chutes and channels. J. Fluid. Mech. 92, 53–96 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112079000525
Sheng, L., Kuo, C., Tai, Y., Hsiau, S.: Indirect measurements of streamwise solid fraction variations of granular flows accelerating down a smooth rectangular chute. Exp. Fluids. 51, 1329 (2011)
Smith, G., Rowley, P., Williams, R., Giordano, G., Trolese, M., Silleni, A., Parsons, D., Capon, S.: A bedform phase diagram for dense granular currents. Nat. Commun. 11, 2873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16657-z
Tai, Y., Lin, Y.: A focused view of the behavior of granular flows down a confined inclined chute into the horizontal run-out zone. Phys. Fluids. 20(12), 123302 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3033490
Xiao, H., Hruska, J., Ottino, J., Lueptow, R., Umbanhowar, P.: Unsteady flows and inhomogeneous packing in damp granular heap flows. Phys. Rev. E 98, 032906 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.98.032906. (https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.98.032906)
Zhu, Y., Delannay, R., Valance, A.: High-speed confined granular flows down smooth inclines: scaling and wall friction laws. Granul. Matter. 22, 1–12 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Labex Tec21, which is part of the ANR ”Investissements d’avenir” program for funding. S.M. acknowledges support from both the Idex Graduate School of University of Grenoble Alpes (ANR ”Investissements d’avenir” program) and the Region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes (ExploRa Doc scholarship scheme). T.F. thanks funding by French ministries ”Ministère de l’Europe et des Affaires Etrangères” and ”Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche et de l’Innovation” through the PHC project GrainFlow (FASIC 2017 program). F.G. and I.E. thanks the Australian Research Council for financial support through grant DP190103487. Finally, the authors would like to thank two anonymous referees for their insightful comments and suggestions on this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Méjean, S., Guillard, F., Faug, T. et al. X-ray study of fast and slow granular flows with transition jump in between. Granular Matter 24, 26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01194-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01194-3