Abstract
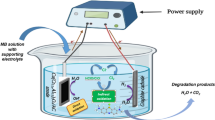
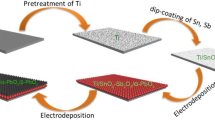
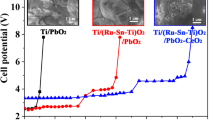
Graphite–lead dioxide electrodes doped with rare earth Cerium (Ce-PbO2/C electrodes) were prepared by electrodeposition. The scanning electron microscope results showed that the microstructure and crystal orientation of electrode surface were changed by Cerium doping. CeO2 was detected from modified electrodes by X-ray diffraction analysis. The cyclic voltammetry spectra indicated that the oxidation peak potential of cerium-doped electrode was smaller than pure PbO2 electrode. Effects of the novel electrode on acid red B degradation were evaluated systematically under different parameters, including applied voltage, initial pH, supporting electrolyte concentration, electrode spacing, and influent concentration. The results indicated that chemical oxygen demand, decolorization, and ammonia nitrogen removal rate of Ce-PbO2/C electrodes reached 90.17, 99.98, and 97.23 %, respectively, after 60-min electrolysis at initial 1000 mg L−1 acid red B concentration. The possible mechanism of acid red B degradation over Ce-PbO2/C electrodes was monitored by gas chromatography-mass spectrometer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou MH, He JJ (2008) Degradation of cationic red X-GRL by electrochemical oxidation on modified PbO2 electrode. J Hazard Mater 153:357–363
Wang J, Jiang Z, Zhang ZH, Xie YP, Wang XF, Xing ZQ, Xu R, Zhang XD (2008) Sonocatalytic degradation of acid red B and rhodamine B catalyzed by nano-sized ZnO powder under ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason Sonochem 15:768–774
Aquino JM, Pereira GF, Rocha-Filho RC, Bocchi N, Biaggio SR (2011) Electrochemical degradation of a real textile effluent using boron-doped diamond or β-PbO2 as anode. J Hazard Mater 192:1275–1282
Körbahti BK, Artut K, Geçgel C, Özer A (2011) Electrochemical decolorization of textile dyes and removal of metal ions from textile dye and metal ion binary mixtures. Chem Eng J 173:677–688
Banat F, AI-Bastaki N (2004) Treating dye wastewater by an integrated process of adsorption using activated carbon and ultrafiltration. Desalination 170:69–75
Gupta VK, Mittal A, Gajbe V (2005) Adsorption and desorption studies of a water soluble dye, Quinoline Yellow, using waste materials. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:89–98
Anouzla A, Abrouki Y, Souabi S, Safi M, Rhbal H (2009) Colour and COD removal of disperse dye solution by a novel coagulant: application of statistical design for the optimization and regression analysis. J Hazard Mater 166:1302–1306
Alaton IA, Insel G, Eremektar G, Babuna FG, Orhon D (2006) Effect of textile auxiliaries on the biodegradation of dyehouse effluent in activated sludge. Chemosphere 62:1549–1557
Zhu XP, Ni JR, Wei JJ, Xing X, Li HN (2011) Destination of organic pollutants during electrochemical oxidation of biologically-pretreated dye wastewater using boron-doped diamond anode. J Hazard Mater 189:127–133
Kariyajjanavar P, Jogttappa N, Nayaka YA (2011) Studies on degradation of reactive textile dyes solution by electrochemical method. J Hazard Mater 190:952–961
Sanroma’n MA, Pazos M, Cameselle C (2004) Optimisation of electrochemical decolourisation process of an azo dye, Methyl Orange. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:1349–1353
Duan XY, Ma F, Yuan ZX, Chang LM, Jin XT (2013) Electrochemical degradation of phenol in aqueous solution using PbO2 anode. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44:95–102
Velichenko AB, Devilliers D (2007) Electrodeposition of fluorine-doped lead dioxide. J Fluor Chem 128:269–276
Andrade LS, Ruotolo LAM, Rocha-Filho RC, Bocchi N, Biaggio SR, Iniesta J, García-Garcia V, Montiel V (2007) On the performance of Fe and Fe, F doped Ti–Pt/PbO2 electrodes in the electrooxidation of the Blue Reactive 19 dye in simulated textile wastewater. Chemosphere 66:2035–2043
Velichenko AB, Amadelli R, Baranova EA, Girenko DV, Danilov FI (2002) Electrodeposition of Co-doped lead dioxide and its physicochemical properties. J Electroanal Chem 527:56–64
Borrás C, Laredo T, Mostany J, Scharifker BR (2004) Study of the oxidation of solutions of p-chlorophenol and p-nitrophenol on Bi-doped PbO2 electrodes by UV-Vis and FTIR in situ spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 49:641–648
Liu Y, Liu HL (2008) Comparative studies on the electrocatalytic properties of modified PbO2 anodes. Electrochim Acta 53:5077–5083
Dai QZ, Shen H, Xia YJ, Chen JM (2012) Typical rare earth doped lead dioxide electrode: preparation and application. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:10054–10062
Wang Y, Shen ZY, Li Y, Niu JF (2010) Electrochemical properties of the erbium–chitosan–fluorine–modified PbO2 electrode for the degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 79:987–996
Kong JT, Shi SY, Kong LC, Zhu XP, Ni JR (2007) Preparation and characterization of PbO2 electrodes doped with different rare earth oxides. Electrochim Acta 53:2048–2054
Ai SY, Gao MN, Zhang W, Wang QJ, Xie YF, Jin LT (2004) Preparation of Ce-PbO2 modified electrode and its application in detection of anilines. Talanta 62:445–450
Petersson I, Ahlberg E, Berghult B (1998) Parameters influencing the ratio between electrochemically formed α-and β-PbO2. J Power Sources 76:98–105
Liu HL, Liu Y, Zhang C, Shen RS (2008) Electrocatalytic oxidation of nitrophenols in aqueous solution using modified PbO2 electrodes. J Appl Electrochem 38:101–108
Koehne JE, Marsh M, Boakye A, Douglas B, Kim IY, Chang S, Jang D, Bennet KE, Kimble C, Andrews R, Meyyappan M, Lee KH (2011) Carbon nanofiber electrode array for electrochemical detection of dopamine using fast scan cyclic voltammetry. Analyst 136:1802–1805
Masek A, Zaborski M, Chrzescijanska E (2011) Electrooxidation of flavonoids at platinum electrode studied by cyclic voltammetry. Food Chem 127:699–704
Santos DMF, Sequeira CAC (2010) Cyclic voltammetry investigation of borohydride oxidation at a gold electrode. Electrochim Acta 55:6775–6781
Kariyajjanavar P, Narayana J, Nayaka YA, Umanaik M (2010) Electrochemical degradation and cyclic voltammetric studies of textile reactive azo dye cibacron navy WB. Port Electrochim Acta 28:265–277
Yu NF, Gao LJ, Zhao SH, Wang ZD (2009) Electrodeposited PbO2 thin film as positive electrode in PbO2/AC hybrid capacitor. Electrochim Acta 54:3835–3841
Tong SP, Ma CA, Feng H (2008) A novel PbO2 electrode preparation and its application in organic degradation. Electrochim Acta 53:3002–3006
Alaton IA, Balcioglu IA, Bahnemann DW (2002) Advanced oxidation of a reactive dye bath effluent: comparison of O3, H2O2/UV-C and TiO2 /UV-A processes. Water Res 36:1143–1154
Mascia M, Vacca A, Polcaro AM, Palmas S, Ruiz JR, Pozzo AD (2010) Electrochemical treatment of phenolic waters in presence of chloride with boron-doped diamond (BDD) anodes: experimental study and mathematical model. J Hazard Mater 174:314–322
Mukimin A, Wijaya K, Kuncaka A (2012) Oxidation of removal brilliant blue R (RB.19) with in situ electro-generated active chlorine using Ti/PbO2 electrode. Sep Purif Technol 95:1–9
Rajkumar D, Song BJ, Kim JG (2007) Electrochemical degradation of Reactive Blue 19 in chloride medium for the treatment of textile dyeing wastewater with identification of intermediate compounds. Dyes Pigments 72:1–7
Shen ZM, Wu D, Yang J, Yuan T, Wang WH, Jia JP (2006) Methods to improve electrochemical treatment effect of dye wastewater. J Hazard Mater 131:90–97
Wang YQ, Gu B, Xu WL (2009) Electro-catalytic degradation of phenol on several metal-oxide anodes. J Hazard Mater 162:1159–1164
Song S, Fan JQ, He ZQ, Zhan LY, Liu ZW, Chen JM, Xu XH (2010) Electrochemical degradation of azo dye C.I. Reactive Red 195 by anodic oxidation on Ti/SnO2–Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim Acta 55:3606–3613
Zhao HZ, Sun Y, Xu LN, Ni JR (2010) Removal of Acid Orange 7 in simulated wastewater using a three-dimensional electrode reactor: removal mechanisms and dye degradation pathway. Chemosphere 78:46–51
Zhao WR, Shi HX, Wang DH (2003) Kinetics of the react ion between ozone and cat ionic red X-GRL. Chin J Chem Eng 11:388–394
Martins MAM, Lima N, Silvestre AJD, Queiroz MJ (2003) Comparative studies of fungal degradation of single or mixed bioaccessible reactive azo dyes. Chemosphere 52:967–973
Siddique M, Farooq R, Khan ZM, Khan Z, Shaukat SF (2011) Enhanced decomposition of reactive blue 19 dye in ultrasound assisted electrochemical reactor. Ultrason Sonochem 18:190–196
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (Project No. 2011BAE07B09-2) for financial support. Additionally, the analytical work was supported by the Water Pollution Control Laboratory of Beijing University of Chemical Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Yu, Y. & Yang, L. Electrocatalytic activity of Ce-PbO2/C anode for acid red B reduction in aqueous solution. J Solid State Electrochem 19, 1599–1609 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-2781-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-2781-3