Abstract
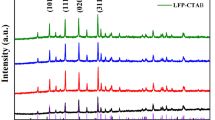
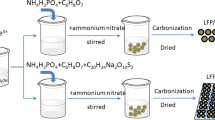
Nanospherical LiFePO4 particle with a uniform carbon coating layer (core-shell structure expressed as LiFePO4/C) in the presence of both low-cost FeOOH as iron resource and polyoxyethylene sorbitan monopalmitate (Tween 40) as surfactant is synthesized via a solid–liquid reaction milling method consisting of high-energy milling and pyrolysis steps. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are used for structure, morphology, and composition characterization. Both XRD and FTIR results confirm the existence of interactions between surfactant molecules and precursor, which can benefit the formation of the core-shell structure with an average particle size of about 200 nm and a high tap density of 1.7 g cm−3. The electrochemical properties of as-prepared LiFePO4/C as cathode material are investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), charge–discharge, and cycling tests. The results show that the LiFePO4/C can achieve high discharge capacities of 163.6 and 131.3 mAh g−1 under 0.1 °C at room temperature (25 °C) and sub-zero temperature (−20 °C), respectively, due to its improved conductivity. In addition, the material also shows an excellent cycling performance with capacity retention of 98.8 % (0.1 °C) after 120 cycles at 25 °C and 102.9 mAh g−1 at the ends of the 200th cycle corresponding to a fading of 0.01 % per cycle.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dimesso L, Forster C, Jaegermann W, Khanderi JP, Tempel H, Popp A, Engstler J, Schneider JJ, Sarapulova A, Mikhailova D, Schmitt LA, Oswald S, Ehrenberg H (2012) Chem Soc Rev 41:5068–5080
Cheng FY, Liang J, Tao ZL, Chen J (2011) Adv Mater 23:1695–1715
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:1609–1613
Chung SY, Chiang YM (2003) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 6:A278–A281
Prosini PP, Lisi M, Zane D, Pasquali M (2002) Solid State Ionics 148:45–51
Herle PS, Ellis B, Coombs N, Nazar LF (2004) Nat Mater 3:147–152
Kobayashi G, Nishimura SI, Park MS, Kanno R, Yashima M, Ida T, Yamada A (2009) Adv Funct Mater 19:395–403
Lv DP, Wen W, Huang XK, Bai JY, Mi JX, Wu SQ, Yang Y (2011) J Mater Chem 21:9506–9512
Liivat A, Thomas JO (2010) Comput Mater Sci 50:191–197
Li HQ, Zhou HS (2012) Chem Commun 48:1201–1207
Zheng ZM, Wang Y, Zhang A, Zhang TR, Cheng FY, Tao ZL, Chen J (2012) J Power Sources 198:229–235
Kang B, Ceder G (2009) Nature 458:190–193
Wang JJ, Sun XL (2012) Energy Environ Sci 5:5163–5185
Wang J, Yang J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Tang Y, Banis MN, Li X, Liang G, Li R, Sun X (2013) Adv Funct Mater 23:806–814
He X, Li J, Cai Y, Ying JR (2005) J Power Sources 150:216–222
Benoit C, Bourbon C, Berthet P, Franger S (2006) J Phys Chem Solids 67:1265–1269
Ying JR, Wan CR, Jiang CY (2001) J Power Sources 99:78–84
Cho TH, Chung HT (2004) J Power Sources 133:272–276
Liao XZ, Ma ZF, Wang L, Zhang XM, Jiang Y, He YS (2004) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 7:A522–A525
Ait-Salah A, Zaghib K, Mauger A, Gendron F, Julien CM (2006) Phys Status Solidi 203:R1–R3
Gaberscek M, Dominko R, Jamnik J (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:2778–2783
Zhu YM, Tang SZ, Shi HH, Hu HL (2014) Ceram Int 40:2685–2690
Liu H, Xie JY, Wang K (2008) J Alloy Compd 459:521–525
Sun CS, Zhou Z, Xu ZG, Wang DG, Wei JP, Bian XK, Yan J (2009) J Power Sources 193:841–845
Lin ZJ, Hu XB, Huai YJ, Liu L, Deng ZH, Suo JS (2010) Solid State Ionics 181:412–415
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (21063003, 51064004 and 51364004), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2011GXNSFA018016), Guangxi Experiment Center of Science and Technology (LGZXKF201105), and Program for Excellent Talents in Guangxi Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HQ., Zhang, XH., Zheng, FH. et al. Surfactant effect on synthesis of core-shell LiFePO4/C cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 19, 187–194 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2598-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2598-5