Abstract
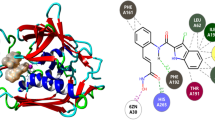
Amoebiasis, a worldwide explosive epidemic, caused by the gastrointestinal anaerobic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica, infects the large intestine and, in advance stages, liver, kidney, brain and lung. Metronidazole (MNZ)—the first line medicament against amoebiasis—is potentially carcinogenic to humans and shows significant side-effects. Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine compounds have been reported to demonstrate antiamoebic activity. In silico molecular docking simulations on nine pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine molecules without linkers (molecules 1–9) and nine pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine molecules with a trimethylene linker (molecules 10–18) along with the reference drug metronidazole (MNZ) were conducted using the modules of the programs Glide-SP, Glide-XP and Autodock with O-acetyl-l-serine sulfhydrylase (OASS) enzyme—a promising target for inhibiting the growth of Entamoeba histolytica. Docking simulations using Glide-SP demonstrate good agreement with reported biological activities of molecules 1–9 and indicate that molecules 2 and 4 may act as potential high affinity inhibitors. Trimethylene linker molecules show improved binding affinities among which molecules 15 and 16 supersede. MD simulations on the best docked poses of molecules 2, 4, 15, 16 and MNZ were carried out for 20 ns using DESMOND. It was observed that the docking complexes of molecules 4, 15 and MNZ remain stable in aqueous conditions and do not undergo noticeable fluctuations during the course of the dynamics. Relative binding free energy calculations of the ligands with the enzyme were executed on the best docked poses using the molecular mechanics generalized Born surface area (MM-GBSA) approach, which show good agreement with the reported biological activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lejeune M, Rybicka JM, Chadee K (2009) Recent discoveries in the pathogenesis and immense response towards Entamoeba histolytica. Future Microbiol 4:105–118
Salles JM, Moraes LA, Salles MC (2003) Hepatic amebiasis. Braz J Infect Dis 7:96–100
Takeuchi T, Weinbach EC, Gottlieb M, Diamond LS (1979) Mechanism of l-serine oxidation in Entamoeba histolytica. Comp Biochem Physiol B 62:281–285
Kumar S, Raj I, Nagpal I, Subbarao N, Gourinath S (2011) Structural and biochemical studies of serine acetyltransferase reveal why the parasite Entamoeba histolytica cannot form a cysteine synthase complex. J Biol Chem 286:12533–12541
Chinthalapudi K, Kumar M, Kumar S, Jain S, Alam N (2008) Crystal structure of native O-acetyl-serine sulfhydrylase from Entamoeba histolytica and its complex with cysteine: structural evidence for cysteine binding and lack of interactions with serine acetyl transferase. Proteins 72:1222–1232
Bendesky A, Menendez D, Ostosky-Wegman P (2002) Is metonidazole carcinogenic? Mutat Res 511:134–144
Becker S, Hoffman P, Houpt ER (2011) Efficiency of antiamoebic drugs in a mouse model. Am J Trop Med Hyg 84:581–586
Nagpal I, Raj I, Subbarao N, Gourinath S (2012) Virtual screening, identification and in vitro testing of novel inhibitors of O-acetyl-l-serine sulfhydrylase of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS ONE 7(2):e30305. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030305
Bekhit AA, Abdel-Azeim T (2004) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of some pyrazole derivatives as anti-inflammatory-antimicrobial agents. Bioorg Med Chem 12:1935–1945
Yadava U, Singh M, Roychoudhury M (2013) Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as inhibitor of anti-coagulation and inflammation activities of phospholipase A2: insight from molecular docking studies. J Biol Phys 39:419–438
Elion GB, Callahan SW, Nathan H, Bieber S, Rundles RW, Hilching GH (1963) Pontetiation by inhibition of drug degradation:6-substituted purines and xanthine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol 12:85–93
Schenone S, Brullo C, Musumeci F, Botta M (2010) Novel dual Src/Abl inhibitors for hematologic and solid malignancies. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:931–945
Indovina P, Giorgi F, Rizzo V, Khadang B, Schenone S, Marzo D, Forte IM, Tomei V, Mattioli E, Urso VD, Grilli B, Botta M, Giordano A, Pentimalli F (2012) New pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidiine SRC inhibitors induce apoptosis in mesothelioma cell lines through p 27 nuclear nuclear stabilization. Oncogenes 31:929–938
Carlomagno F, Vitagliano D, Guida T, Basolo F, Castellone MD, Melillo RM, Fusco A, Santro M (2003) Efficient inhibition of RET/papillary thyroid carcinoma oncogenic kinases by 4-amino-5-(4-chloro-phenyl)-7-(t-Butyl)Pyrazolo[3,4-d]Pyrimidine (PP2). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:1897–1902
Hayat F, Salahudin A, Ummar S, Azam A (2010) Synthesis charasterization, antiamoebic activity and cytotoxicity of novel series of pyrazoline derivatives bearing quinoline tail. Eur J Med Chem 45:4669–4675
Budakoti A, Abid M, Azam A (2007) Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antiamoebic activity of new Pd(II) complexes with 1-N-substituted thiocarbonyl1-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyrazoline derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 42:544–551
Parveen H, Hayat F, Mukhtar S, Salahudin A, Khan A, Islam F, Azam A (2011) Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of novel 2,4, 6 trisubstituted bis-pyrimidine derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 46:4669–4675
Siddiqui SM, Salahudin A, Azam A (2013) Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine analogues: synthesis, characterization and their in-vitro antiamoebic activity. Med Chem Res 22:775–781
Yadava U, Singh M, Roychoudhury M (2011) Gas-phase conformational and intramolecular π-π interaction studies on some pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Comput Theo Chem 977:134–139
(2012) Glide: version 5.2 Schrödinger. LLC, New York
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Kliclic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK, Shaw DE, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid accurate docking and scoring, method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery JA, Vreven JT, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2003) GAUSSIAN 03, revision B.04. Gaussian, Inc, Pittsburgh
Jorgenson WL, Maxwell DS, Tirado-Rives J (1996) Development and testing of the OPLS all atom force field on conformational energetic and properties of organic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 118:11225–11236
(2012) Prime, version 3.1. Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) Autodock 4 and Autodock Tools 4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791
(2012) DESMOND molecular dynamics system, version 3.1. Shaw, New York
Bowers KJ, Chow E, Xu H, Dror RO, Eastwood MP, Gregersen BA, Klepeis JL, Kolossvary I, Moraes MA, Sacerdoti FD, Salmon JK, Shan Y and Shaw DE (2006) Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. Proc ACM/IEEE Conf Supercomp (SC06), Tampa, FL
Verlet L (1967) Computer “Experiments” on classical fluids I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard–Jones molecules. Phys Rev 159:98–103
Swegat W, Schlitter JR, Kruger P, Wollmer A (2003) MD simulation of protein-ligand interaction: formation and dissociation of an insulin-phenol complex. Biophys J 84:1493–1506
Tripathi SK, Muttineni R, Singh SK (2013) Extra precision docking, free energy calculation and molecular dynamics simulation studies of CDK2 inhibitors. J Theor Biol 334:87–100
Kennedy T (1997) Managing the discovery/development interface. Drug Discov Today 2:436–444
DiMassi JA (1995) Success rates for new drugs entering clinical testing in the Unites States. Clin Pharmacol Ther 58:1–14
(2012) QikProp: version 3.5. Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Lipinski CA (2000) Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 44:235–249
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (1997) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 23:3–25
Krishna C, Jain R, Kashav T, Wadhwa D, Alam N (2007) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of cysteine synthase from Entamoeba histolytica. Acta Crystallogr F63:512–515
Kawatkar S, Wang H, Czerminski R, Joseph-McCarthy D (2009) Virtual fragment screening: an exploration of various docking and scoring protocols for fragments using glide. J Comput Aided Mol Des 23:527–539
Acknowledgments
U. Y. is thankful to DST, New Delhi, India for financial support through SERC Fast Track Young Scientist scheme(SR/FT/CS-78/2010) and UGC, New Delhi, India for the award of a Raman Fellowship for postdoctoral studies in the United States [F.No. 5-1/2013(IC)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 6430 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadava, U., Shukla, B.K., Roychoudhury, M. et al. Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines as novel inhibitors of O-acetyl-l-serine sulfhydrylase of Entamoeba histolytica: an in silico study. J Mol Model 21, 96 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-015-2631-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-015-2631-3