Abstract
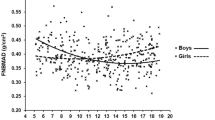
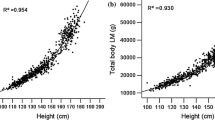
The clinical utility of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measurement requires appropriate normative values, designed to be diverse with respect to age, gender and ethnic background. The purpose of this study was to generate age-related trends for bone density in Chinese children and adolescents, and to establish a gender-specific reference database. A total of 1,541 Chinese children and adolescents aged from 5 to 19-years were recruited from southern China. Bone mineral density (BMD), bone mineral content (BMC), and bone area (BA) were measured for the total body (TB) and total body less head (TBLH). The height-for-age, height-for-BA, and BMC-for-BA percentile curves were developed using the least mean square method. TB BMD and TBLH BMD were highly correlated. After 18 years, TB BMD was significantly higher in boys than girls. For TB BMC and TBLH BMC, gender differences were found in age groups 12 years and 16–19 years; however, the TBLH BMD was significantly different between genders >16 years. The head region accounted for 13–52 and 16–49 % of the TB BMC in boys and girls, respectively. Furthermore, the percentages were negatively correlated with age and height. This study describes a gender-specific reference database for Chinese children and adolescents aged 5–19 years. These normative values could be used for clinical assessment in this population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogunovic L, Doyle SM, Vogiatzi MG (2009) Measurement of bone density in the pediatric population. Curr Opin Pediatr 21:77–82
Gordon CM (2005) Evaluation of bone density in children. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes 12:444–451
Bachrach LK (2005) Osteoporosis and measurement of bone mass in children and adolescents. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 34:521–535
Khan AA, Bachrach L, Brown JP, Hanley DA, Josse RG, Kendler DL, Leib ES, Lentle BC, Leslie WD, Lewiecki EM, Miller PD, Nicholson RL, O’Brien C, Olszynski WP, Theriault MY, Watts NB, Canadian Panel of the International Society of Clinical Densitometry (2004) Standards and guidelines for performing central dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in premenopausal women, men, and children. J Clin Densitom 7:51–64
Ekbote VH, Khadilkar AV, Chiplonkar SA, Khadilkar VV (2011) Determinants of bone mineral content and bone area in Indian preschool children. J Bone Miner Metab 29:334–341
Baim S, Leonard MB, Bianchi ML, Hans DB, Kalkwarf HJ, Langman CB, Rauch F (2008) Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and executive summary of the 2007 ISCD Pediatric Position Development Conference. J Clin Densitom 11:6–21
Gordon CM, Bachrach LK, Carpenter TO, Crabtree N, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Kutilek S, Lorenc RS, Tosi LL, Ward KA, Ward LM, Kalkwarf HJ (2008) Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry interpretation and reporting in children and adolescents: the 2007 ISCD Pediatric Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 11:43–58
Xu H, Chen JX, Gong J, Zhang TM, Wu QL, Yuan ZM, Wang JP (2008) Normal reference for bone density in healthy Chinese children. J Clin Densitom 10:266–275
Li H, Ji CY, Zong XN, Zhang YQ (2009) Height and weight standardized growth charts for Chinese children and adolescents aged 0 to 18 years. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 47:487–492
Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (2007) Report on the physical fitness and health surveillance of Chinese school students. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Cole TJ, Green PJ (1992) Smoothing reference centile curves: the LMS method and penalized likelihood. Stat Med 11:1305–1319
Boot AM, de Ridder MA, Pols HA, Krenning EP, de Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM (1997) Bone mineral density in children and adolescents: relation to puberty, calcium intake, and physical activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:57–62
Nelson DA, Simpson PM, Johnson CC, Barondess DA, Kleerekoper M (1997) The accumulation of whole body skeletal mass in third- and fourth-grade children: effects of age, gender, ethnicity, and body composition. Bone 20:73–78
Crabtree NJ, Oldroyd B, Truscott JG, Fordham JN, Kibirige M, Fewtrell M, Gordon I, Shaw NJ (2005) UK paediatric DXA reference data (GE Lunar Prodigy): effects of ethnicity, gender, and pubertal status. Bone 36:S42
Wang MC, Aguirre M, Bhudhikanok GS, Kendall CG, Kirsch S, Marcus R, Bachrach LK (1997) Bone mass and hip axis length in healthy Asian, black, Hispanic, and white American youths. J Bone Miner Res 12:1922–1935
Bachrach LK, Hastie T, Wang MC, Narasimhan B, Marcus R (1999) Bone mineral acquisition in healthy Asian, Hispanic, black, and Caucasian youth: a longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:4702–4712
Kalkwarf HJ, Zemel BS, Gilsanz V, Lappe JM, Horlick M, Oberfield S, Mahboubi S, Fan B, Frederick MM, Winer K, Shepherd JA (2007) The bone mineral density in childhood study: bone mineral content and density according to age, sex, and race. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2087–2099
Pludowski P, Matusik H, Olszaniecka M, Lebiedowski M, Lorenc RS (2005) Reference values for the indicators of skeletal and muscular status of healthy Polish children. J Clin Densitom 8:164–177
Khadilkar AV, Sanwalka NJ, Chiplonkar SA, Khadilkar VV, Mughal MZ (2011) Normative data and percentile curves for Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in healthy Indian girls and boys aged 5–17 years. Bone 4:810–819
Ward KA, Ashby RL, Roberts SA, Adams JE, Zulf Mughal M (1997) UK reference data for the Hologic QDR Discovery dual-energy x ray absorptiometry scanner in healthy children and young adults aged 6–17 years. Arch Dis Child 92:53–59
Molgaard C, Thomsen BL, Michaelsen KF (1999) Whole body bone mineral accretion in healthy children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child 81:10–15
Zanchetta JR, Plotkin H, Alvarez FML (1995) Bone mass in children: normative values for the 2–20-year-old population. Bone 16:S393–S399
Arabi A, Nabulsi M, Maalouf J, Choucair M, Khalifé H, Vieth R, El-Hajj Fuleihan G (2004) Bone mineral density by age, gender, pubertal stages, and socioeconomic status in healthy Lebanese children and adolescents. Bone 35:1169–1179
Faulkner RA, Bailey DA, Drinkwater DT, McKay HA, Arnold C, Wilkinson AA (1996) Bone densitometry in Canadian children 8–17 years of age. Calcif Tissue Int 59:344–351
Goksen D, Darcan S, Coker M, Kose T (2006) Bone mineral density of healthy Turkish children and adolescents. J Clin Densitom 9:84–90
Binkley TL, Specker BL, Wittig TA (2002) Centile curves for bone densitometry measurements in healthy males and females ages 5–22 yr. J Clin Densitom 5:343–353
Lazcano-Ponce E, Tamayo J, Cruz-Valdez A, Díaz R, Hernández B, Del Cueto R, Hernández-Avila M (2003) Peak bone mineral area density and determinants among females aged 9 to 24 years in Mexico. Osteoporos Int 14:539–547
Maynard LM, Guo SS, Chumlea WC, Roche AF, Wisemandle WA, Zeller CM, Towne B, Siervogel RM (1998) Total-body and regional bone mineral content and areal bone mineral density in children aged 8–18 y: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Am J Clin Nutr 68:1111–1117
Willing MC, Torner JC, Burns TL, Janz KF, Marshall TA, Gilmore J, Warren JJ, Levy SM (2005) Percentile distributions of bone measurements in Iowa children: the Iowa Bone Development Study. J Clin Densitom 8:39–47
Taylor A, Konrad PT, Norman ME, Harcke HT (1997) Total body bone mineral density in young children: influence of head bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 12:652–655
Fewtrell MS, British Paediatric & Adolescent Bone Group (2003) Bone densitometry in children assessed by dual x ray absorptiometry: uses and pitfalls. Arch Dis Child 88:795–798
Mølgaard C, Thomsen BL, Prentice A, Cole TJ, Michaelsen KF (1997) Whole body bone mineral content in healthy children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child 76:9–15
Laskey MA, Prentice A (1999) Comparison of adult and paediatric spine and whole body software for the Lunar dual energy X-ray absorptiometer. Br J Radiol 72:967–976
Tothill P, Hannan WJ (2002) Bone mineral and soft tissue measurements by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry during growth. Bone 31:492–496
Tothill P, Avenell A, Love J, Reid DM (1994) Comparisons between Hologic, Lunar and Norland dual-energy X-ray absorptiometers and other techniques used for whole-body soft tissue measurements. Eur J Clin Nutr 48:781–794
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all participating children and their parents. We are grateful to Dr Qi Zhou, GE Healthcare Shanghai and Dr Jing Xiang, First Hospital of Jiaxing for their useful comments and suggestions. We also thank the staff members of the Department of Nuclear Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University for excellent technical support.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any personal or financial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Xu, Y., Gong, J. et al. Age trends of bone mineral density and percentile curves in healthy Chinese children and adolescents. J Bone Miner Metab 31, 304–314 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0401-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0401-1