Abstract
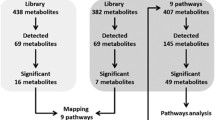
A high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet has been regarded as a dietary intervention for weight loss in the obese population. We integrated metabolomics profiles and correlation-based network analysis to reveal the difference in metabolism under diets with different protein:carbohydrate ratios. Rats were fed a control diet (moderate-protein moderate-carbohydrate: MPMC; 20 % protein, 56 % carbohydrate) or HPLC diet (high-protein low-carbohydrate: 45 % protein, 30 % carbohydrate) for 6 weeks. The fat content was equal for both diets. HPLC feeding induced weight loss and reduced adipose weight and plasma triglyceride. Compared to the MPMC diet, HPLC significantly increased plasma α-tocopherol, pyruvate, 2-oxoisocaproate, and β-hydroxybutyrate, and reduced linoleate, palmitate, α-glycerophosphate and pyroglutamic acid. The HPLC-associated urinary metabolite profile was signified with an increase in palmitate and stearate and a reduction of citrate, 2-ketoglutarate, malate, and pantothenate. Pathway analysis implicated a significant alteration of the TCA cycle in urine. Biomarker screening demonstrated that individual metabolites, including plasma urea, pyruvate, and urinary citrate, robustly distinguished the HPLC group from the MPMC group. Correlation-based network analysis enabled to demonstrate that the correlation of plasma metabolite was strengthened after the HPLC diet, while the energy-metabolism relatives 2-ketoglutarate and fumarate correlated positively with phenylalanine, methionine, and serine. The correlation network between plasma–urinary metabolites revealed a negative correlation of plasma valine with urinary β-hydroxybutyrate in MPMC rats. In HPLC rats, plasma 2-oxoisocaproate negatively correlated with urinary pyruvate and glycine. This study using metabolomics analysis revealed the systemic metabolism in response to diet treatment and identified the significantly distinct profiles associated with a HPLC diet.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A J, Trygg J, Gullberg J, Johansson AI, Jonsson P, Antti H, Marklund SL, Moritz T (2005) Extraction and GC/MS analysis of the human blood plasma metabolome. Anal Chem 77:8086–8094
A J, Huang Q, Wang G, Zha W, Yan B, Ren H, Gu S, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Shao F, Sheng L, Sun J (2008) Global analysis of metabolites in rat and human urine based on gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 379:20–26
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. ICWSM 8:361–362
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate—a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc B Met 57:289–300
Blouet C, Mariotti F, Azzout-Marniche D, Bos C, Mathe V, Tome D, Huneau JF (2006) The reduced energy intake of rats fed a high-protein low-carbohydrate diet explains the lower fat deposition, but macronutrient substitution accounts for the improved glycemic control. J Nutr 136:1849–1854
Camacho D, de la Fuente A, Mendes P (2005) The origin of correlations in metabolomics data. Metabolomics 1:53–63
Carroll JJ, Coburn H, Douglass R, Babson AL (1971) A simplified alkaline phosphotungstate assay for uric acid in serum. Clin Chem 17:158–160
Chevalier L, Bos C, Azzout-Marniche D, Fromentin G, Mosoni L, Hafnaoui N, Piedcoq J, Tome D, Gaudichon C (2013) Energy restriction only slightly influences protein metabolism in obese rats, whatever the level of protein and its source in the diet. Int J Obes 37:263–271
Clifton P (2012) Effects of a high protein diet on body weight and comorbidities associated with obesity. Brit J Nutr 108:S122–S129
Deng P, Jones JC, Swanson KS (2014) Effects of dietary macronutrient composition on the fasted plasma metabolome of healthy adult cats. Metabolomics 10:638–650
Eriksson L, Trygg J, Wold S (2008) CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS® models. J Chemom 22:594–600
Folin O (1914) On the determination of creatinine and creatine in urine. J Biol Chem 17:469–473
Gannon MC, Nuttall FQ, Saeed A, Jordan K, Hoover H (2003) An increase in dietary protein improves the blood glucose response in persons with type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 78:734–741
Gu C, Shi Y, Le G (2008) Effect of dietary protein level and origin on the redox status in the digestive tract of mice. Int J Mol Sci 9:464–475
Halton TL, Hu FB (2004) The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review. J Am Coll Nutr 23:373–385
Huang Y, Zhou M, Sun H, Wang Y (2011) Branched-chain amino acid metabolism in heart disease: an epiphenomenon or a real culprit? Cardiovasc Res 90:220–223
Jarrett SG, Milder JB, Liang LP, Patel M (2008) The ketogenic diet increases mitochondrial glutathione levels. J Neurochem 106:1044–1051
Jean C, Rome S, Mathe V, Huneau JF, Aattouri N, Fromentin G, Achagiotis CL, Tome D (2001) Metabolic evidence for adaptation to a high protein diet in rats. J Nutr 131:91–98
Johnstone AM, Horgan GW, Murison SD, Bremner DM, Lobley GE (2008) Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum. Am J Clin Nutr 87:44–55
Lacroix M, Gaudichon C, Martin A, Morens C, Mathe V, Tome D, Huneau JF (2004) A long-term high-protein diet markedly reduces adipose tissue without major side effects in Wistar male rats. Am J Physiol-Reg I 287:R934–R942
Layman DK, Clifton P, Gannon MC, Krauss RM, Nuttall FQ (2008) Protein in optimal health: heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1571s–1575s
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA (1999) Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing—comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 22:1462–1470
Matthews D, Hosker J, Rudenski A, Naylor B, Treacher D, Turner R (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Menni C, Fauman E, Erte I, Perry JRB, Kastenmuller G, Shin SY, Petersen AK, Hyde C, Psatha M, Ward KJ, Yuan W, Milburn M, Palmer CNA, Frayling TM, Trimmer J, Bell JT, Gieger C, Mohney RP, Brosnan MJ, Suhre K, Soranzo N, Spector TD (2013) Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose using a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes 62:4270–4276
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross JM, Darzi AW, Takats Z, Lindon JC (2012) Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature 491:384–392
Noguchi Y, Shikata N, Furuhata Y, Kimura T, Takahashi M (2008) Characterization of dietary protein-dependent amino acid metabolism by linking free amino acids with transcriptional profiles through analysis of correlation. Physiol Genomics 34:315–326
Obuchowski NA, Lieber ML, Wians FH (2004) ROC curves in clinical chemistry: uses, misuses, and possible solutions. Clin Chem 50:1118–1125
Qi Y, Li P, Zhang YY, Cui LL, Guo Z, Xie GX, Su MM, Li X, Zheng XJ, Qiu YP, Liu YM, Zhao AH, Jia WP, Jia W (2012) Urinary metabolite markers of precocious puberty. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(1):M111.011072
Rasmussen LG, Winning H, Savorani F, Toft H, Larsen TM, Dragsted LO, Astrup A, Engelsen SB (2012) Assessment of the effect of high or low protein diet on the human urine metabolome as measured by NMR. Nutrients 4:112–131
Reimer RA, Maurer AD, Eller LK, Hallam MC, Shaykhutdinov R, Vogel HJ, Weljie AM (2012) Satiety hormone and metabolomic response to an intermittent high energy diet differs in rats consuming long-term diets high in protein or prebiotic fiber. J Proteome Res 11:4065–4074
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase and serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase. Am J Clin Path 28:56–62
Roberts LD, Koulman A, Griffin JL (2014) Towards metabolic biomarkers of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: progress from the metabolome. Lancet Diabetes Endo 2:65–75
Ross AB, Pere-Trepat E, Montoliu I, Martin FPJ, Collino S, Moco S, Godin JP, Cleroux M, Guy PA, Breton I, Bibiloni R, Thorimbert A, Tavazzi I, Tornier L, Bebuis A, Bruce SJ, Beaumont M, Fay LB, Kochhar S (2013) A whole-grain-rich diet reduces urinary excretion of markers of protein catabolism and gut microbiota metabolism in healthy men after one week. J Nutr 143:766–773
Russell WR, Gratz SW, Duncan SH, Holtrop G, Ince J, Scobbie L, Duncan G, Johnstone AM, Lobley GE, Wallace RJ, Duthie GG, Flint HJ (2011) High-protein, reduced-carbohydrate weight-loss diets promote metabolite profiles likely to be detrimental to colonic health. Am J Clin Nutr 93:1062–1072
Sacks FM, Bray GA, Carey VJ, Smith SR, Ryan DH, Anton SD, McManus K, Champagne CM, Bishop LM, Laranjo N, Leboff MS, Rood JC, de Jonge L, Greenway FL, Loria CM, Obarzanek E, Williamson DA (2009) Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. New Engl J Med 360:859–873
Salek RM, Maguire ML, Bentley E, Rubtsov DV, Hough T, Cheeseman M, Nunez D, Sweatman BC, Haselden JN, Cox RD, Connor SC, Griffin JL (2007) A metabolomic comparison of urinary changes in type 2 diabetes in mouse, rat, and human. Physiol Genomics 29:99–108
Schicho R, Shaykhutdinov R, Ngo J, Nazyrova A, Schneider C, Panaccione R, Kaplan GG, Vogel HJ, Storr M (2012) Quantitative metabolomic profiling of serum, plasma, and urine by H-1 NMR spectroscopy discriminates between patients with inflammatory bowel disease and healthy individuals. J Proteome Res 11:3344–3357
Schwarz J, Tome D, Baars A, Hooiveld GJEJ, Muller M (2012) Dietary protein affects gene expression and prevents lipid accumulation in the liver in mice. Plos One 7:e47303
Seyfried F, Li JV, Miras AD, Cluny NL, Lannoo M, Fenske WK, Sharkey KA, Nicholson JK, le Roux CW, Holmes E (2013) Urinary Phenotyping indicates weight loss-independent metabolic effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in mice. J Proteome Res 12:1245–1253
Solon-Biet SM, McMahon AC, Ballard JW, Ruohonen K, Wu LE, Cogger VC, Warren A, Huang X, Pichaud N, Melvin RG, Gokarn R, Khalil M, Turner N, Cooney GJ, Sinclair DA, Raubenheimer D, Le Couteur DG, Simpson SJ (2014) The ratio of macronutrients, not caloric intake, dictates cardiometabolic health, aging, and longevity in ad libitum-fed mice. Cell Metab 19:418–430
Stepien M, Gaudichon C, Fromentin G, Even P, Tome D, Azzout-Marniche D (2011) Increasing protein at the expense of carbohydrate in the diet down-regulates glucose utilization as glucose sparing effect in rats. Plos One 6:e14664
Steuer R (2006) Review: on the analysis and interpretation of correlations in metabolomic data. Brief Bioinform 7:151–158
Tiffany T, Jansen J, Burtis C, Overton J, Scott C (1972) Enzymatic kinetic rate and end-point analyses of substrate, by use of a GeMSAEC fast analyzer. Clin Chem 18:829–840
Wiklund S, Johansson E, Sjostrom L, Mellerowicz EJ, Edlund U, Shockcor JP, Gottfries J, Moritz T, Trygg J (2008) Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal Chem 80:115–122
Xia JG, Psychogios N, Young N, Wishart DS (2009) MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W652–W660
Xia JG, Broadhurst DI, Wilson M, Wishart DS (2013) Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: an introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 9:280–299
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127300), Natural Science Foundation of China (31430082) and Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation (BK20130058).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: F. Blachier.
C. Mu and Y. Yang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, C., Yang, Y., Luo, Z. et al. Metabolomic analysis reveals distinct profiles in the plasma and urine of rats fed a high-protein diet. Amino Acids 47, 1225–1238 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1949-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1949-6