Abstract
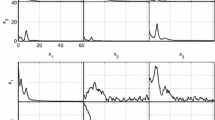
The autoregressive (AR) estimator, a non-parametric method, is used to analyze functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data. The same method has been used, with success, in several other time series data analysis. It uses exclusively the available experimental data points to estimate the most plausible power spectra compatible with the experimental data and there is no need to make any assumption about non-measured points. The time series, obtained from fMRI block paradigm data, is analyzed by the AR method to determine the brain active regions involved in the processing of a given stimulus. This method is considerably more reliable than the fast Fourier transform or the parametric methods. The time series corresponding to each image pixel is analyzed using the AR estimator and the corresponding poles are obtained. The pole distribution gives the shape of power spectra, and the pixels with poles at the stimulation frequency are considered as the active regions. The method was applied in simulated and real data, its superiority is shown by the receiver operating characteristic curves which were obtained using the simulated data.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ogawa, D.W. Tank, R. Menon, J.M. Ellermann, S.G. Kim, H. Merkle, K. Ugarbil, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5951 (1992)
J.W. Belliveau, D.N. Kennedy, R.C. Mckinstry, B.R. Buchbinder, R.M. Weisskoff, M.S. Cohen, J.M. Vevea, T.J. Brady, B.R. Rosen, Science 254(5032), 716–719 (1991)
K.K. Kwong, J.W. Belliveau, D.A. Chesler, I.E. Goldberg, R.M. Weisskoff, B.P. Poncelet, D.N. Kennedy, B.E.H.M.S. Cohen, R. Turner, H.M. Cheng, J.J. Brady, B.R. Rosen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5675 (1992)
A.L. Baert, K. Sartor, J.E. Youler, Funcional MRI (Springer, New York, 2000)
N. Lange, in Functional MRI, ed. by C. Moonen, P. Bandettini, Medical Radiology-Diagnostic Imaging and Radiation Oncology, vol. 27 (Springer, New York, 1999), pp. 301–335
N. Lange, S.L. Zeger, Appl. Stat. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 46(1), 1–19 (1997)
J.L. Marchini, B.D. Ripley, Neuroimage 12(4), 366–380 (2000)
S. Haykin (ed.), Nonlinear Methods of Spectral Analysis (Springer, New York, 1979)
P.S. Naidu, Modern Spectrum Analysis of Time Series (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996)
R.D. Brockwell, Time Series: Theory and Methods (Springer, New York, 1991)
D.M. Lin, E.K. Wong, Phys. Rep. 193(2), 41–135 (1990)
S. Ogawa, D.W. Tank, R. Menon, J.M. Ellermann, S.G. Kim, H. Merkle, K. Ugurbil, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89(13), 5951–5955 (1992)
K.K. Kwong, J.W. Belliveau, D.A. Chesler, I.E. Goldberg, R.M. Weisskoff, B.P. Poncelet, D.N. Kennedy, B.E. Hoppel, M.S. Cohen, R. Turner, H.M. Cheng, T.J. Brady, B.R. Rosen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89(12), 5675–5679 (1992)
C.T.W. Moonen, P.A. Bandettini, in Medical Radiology Diagnostic Imaging. Functional MRI, volume 27, ed. by A.L. Baert, K. Sartor, J.E. Youker (Springer, Berlin, 2000)
K.J. Friston, J.T. Ashburner, S. Kiebel, T.E. Nichols, W.D. Penny (eds.), Statistical Parametric Mapping: The Analysis of Functional Brain Images (Academic Press, New York, 2007)
D.B. Rowe, B.R. Logan, Neuroimage 23(3), 1078–1092 (2004)
R.H. Cervantes, S.R. Rabbani, Solid State Commun. 110(4), 215–220 (1999)
J.P. Burg, A New Analysis Technique for Time Series Data (NATO, Enschede, 1968)
S.D.R. Amaral, S.R. Rabbani, N. Caticha, Neuroimage 23(2), 654–662 (2004)
N. Caticha, S.D. Amaral, S.R. Rabbani, Bayesian Inference Maximum Entropy Methods Sci. Eng. 735, 27–34 (2004)
C. Gossl, L. Fahrmeir, D.P. Auer, Neuroimage 14(1), 140–148 (2001)
K.J. Friston, W. Penny, C. Phillips, S. Kiebel, G. Hinton, J. Ashburner, Neuroimage 16(2), 465–483 (2002)
R. Ihaka, R. Gentleman, R, J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5(3), 299–314 (1996). http://www.amstat.org/publications/jcgs/
R: Development Core Team, R: a language and environment for statistical computing, R foundation for statistical computing (2010). http://www.R-project.org/
W.Y. Chen, G.R. Stegen, J. Geophys. Res. 79(20), 3019–3022 (1974)
Acknowledgments
We thank S.D.R. Amaral and N. Caticha, for the simulated fMRI data set, and D. B. Araujo, for the real fMRI data set. This work received the support of FAPESP and CNPq. Script program can be made available by request to hernan@if.usp.br
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cervantes, H., Jousseph, C.A.C. & Rabbani, S.R. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data Analysis by Autoregressive Estimator. Appl Magn Reson 43, 321–330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0371-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-012-0371-4