Summary
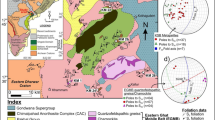
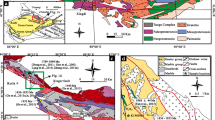
¶The petrology and P-T evolution of mica schists from two regional scale tectonic (shear) zones that separate high grade terrains (“mobile belts”) from cratons are described. These are the 2.4–1.9 Ga Tanaelv Belt, a suture zone that separates the Lapland granulite complex from the Karelian craton (Kola Peninsula–Fennoscandia), and the 2.69 Ga Hout River Shear Zone that separates the > 2.9 Ga Kaapvaal craton from the 2.69 Ga South Marginal Zone of the Limpopo high-grade terrain (South Africa).
Two metamorphic zones are identified in strongly deformed mica schists from the 1.9 Ga Korva Tundra Group of the Tanaelv belt: (1) a chlorite-staurolite zone tectonically overlaying gneisses of the Karelian craton, and (2) a kyanite-biotite zone tectonically underlying garnet amphibolites of the Tanaelv Belt, which are in tectonic contact with the Lapland granulite complex. The prograde reaction Chl+St+Ms ↠ Ky+Bt+Qtz+H2O clearly defines a boundary between zones (1) and (2). Rotated garnet porphyroblasts from zone (1) contain numerous inclusions (Otz, Chl, Ms), and show clear Mg/Fe chemical zoning, suggesting garnet growth during prograde metamorphism. The metamorphic peak, T = 650°C and P = 7.5 kbar, is recorded in the kyanite-biotite zone and characterized by unzoned snowball garnet. In many samples of mica schists euhedral garnet porphyroblasts of the retrograde stage are completely devoid of mineral inclusions while N Mg decreases from core to rim, indicating a decrease in P-T from 650°C, 7.5 kbar to 530°C, 5 kbar.
The Hout River Shear Zone (South Africa) shows metamorphic zonation from greenschists through epidote amphibolites to garnet amphibolites. Rare strongly deformed mica schists (Chl+Grt+Pl+Ms+Bt+Qtz) occur as thin layers among epidote-amphibolites only. Garnet porphyroblasts in the schists are similar to that of the Tanaelv Belt recording a prograde P-T path with peak conditions of T = 600°C and P∼ 5.5 kbar. The retrograde stage is documented by the continuous reaction Prp+2Ms+Phl ↠ 6Qtz+3East recording a minimum T = 520°C and P ∼ 3.3 kbar. Similar narrow clock-wise P-T loops recorded in mica schists from both studied shear zones suggest similarities in the geodynamic history of both shear zones under consideration.
Zusammenfassung
¶P-T Pfade und tektonische Entwicklung von Scherzonen, die hochgradige Terranes von Kratonen trennen: Zwei Beispiele von der Halbinsel Kola (Russland) und der Limpopo-Region (Südafrika)
Die Petrologie und P-T Entwicklung von Glimmerschiefern aus zwei regionalen tektonischen Scherzonen, die hochgradige Terranes (“mobile belts”) von Kratonen trennen, werden beschrieben. Diese sind der 2.4−1.9 Ga Tanaev Belt, eine Suturzone, die die Lappland Granulite vom karelischen Pluton (Halbinsel Kola - Fennoskandien) trennt, sowie die 2.69 Ga Hout River Shear Zone, die den > 2.9 Ga Kaapvaal Kraton von der 2.69 Ga South Marginal Zone des hochgradigen Limpopo Terranes (Südafrika) trennt.
Zwei metamorphe Zonen sind in stark deformierten Glimmerschiefern der 1.9 Ga Korva Tundra Group zu unterscheiden: (1) eine Chlorit-Staurolith-Zone, die den Gneisen des karelischen Kratons auflagert, und (2) eine Kyanit-Biotit-Zone, die die Granatamphibolite des Tanaev Belt unterlagert und in tektonischem Kontakt mit dem Lappland Granulitkomplex steht. Die prograde Reaktion Chl+St+Ms ↠ Ky+Bt+Qtz+H2O trennt die beiden Zonen. Rotierte Granatporphyroblasten aus der Zone (1) enthalten zahlreiche Einschlüsse (Qtz, Chl, Ms) und zeigen eine Mg/Fe Zonierung, die Granatwachstum während des prograden Metamorphosestadiums nahelegen. Der Metamorphosehöhepunkt (650°C, 7.5 kbar) wurde in der Kyanit-Biotit-Zone erreicht und ist durch nicht zonierte Schneeballgranate charakterisiert. In vielen Glimmerschieferproben sind die euhedralen Granatporphyroblasten des retrograden Stadiums vollkommen einschlußfrei und N Mg nimmt vom Kern zum Rand hin ab. Das zeigt eine Abnahme der P-T Bedingungen von 650°C, 7.5 kbar auf 530°C, 5 kbar an. Die Hout River Shear Zone in Südafrika zeigt eine metamorphe Zonierung von Grünschiefern, über Epidotamphibolite zu Granatamphiboliten. Selten kommen stark deformierte Glimmerschiefer (Chl+Grt+Pl+Ms+Bt+Qtz) als dünne Lagen zwischen den Epidotamphiboliten vor. Die Granatporphyroblasten sind ähnlich wie die aus dem Tanaev Belt und belegen eine prograde P-T Entwicklung mit Peak-Bedingungen von 600°C und ≈ 5.5 kbar. Das retrograde Stadium ist durch die kontinuierliche Reaktion Prp+2Ms+Phl ↠ 6Qtz+3East mit minimal 530°C und ≈ 3.3 kbar dokumentiert. Die sehr ähnlichen P-T Pfade der Glimmerschiefer belegen Ähnlichkeiten in der geodynamischen Geschichte der beiden bearbeiteten Scherzonen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 29, 1999;/revised version accepted August 10, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perchuk, L., Gerya, T., Van Reenen, D. et al. P-T paths and tectonic evolution of shear zones separating high-grade terrains from cratons: examples from Kola Peninsula (Russia) and Limpopo Region (South Africa). Mineralogy and Petrology 69, 109–142 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007100050020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007100050020