Abstract
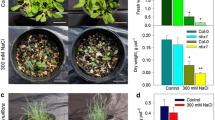
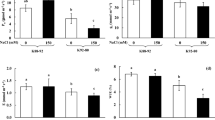
Vacuolar Ca2+-transporters could play an important role for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) root. Here, we compared the expression profiles of putative vacuolar cation/H+ exchanger (CAX) and calmodulin-regulated autoinhibited Ca2+-ATPase (ACA) in rice roots of salt tolerant cv. Pokkali and salt sensitive cv. IR29. In addition to five putative vacuolar CAX genes in the rice genome, a new CAX gene (OsCAX4) has been annotated. In the present study, we isolated the OsCAX4 gene and showed that its encoded protein possesses a unique transmembrane structure and is potentially involved in transporting not only Ca2+ but also Mn2+ and Cu2+. These six OsCAX genes differed in their mRNA expression pattern in roots of tolerant versus sensitive rice cultivars exposed to salt stress. For example, OsCAX4 showed abundant expression in IR29 (sensitive) upon prolonged salt stress. The mRNA expression profile of four putative vacuolar Ca2+-ATPases (OsACA4-7) was also examined. Under control conditions, the mRNA levels of OsACA4, OsACA5, and OsACA7 were relatively high and similar among IR29 and Pokkali. Upon salt stress, only OsACA4 showed first a decrease in its expression in Pokkali (tolerant), followed by a significant increase. Based on these results, a role of vacuolar Ca2+ transporter for salt tolerance in rice root was discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACAs:
-
autoinhibited calcium ATPase
- CAXs:
-
Ca2+/H+ exchangers
- TM:
-
transmembrane
References
Anil VS, Rajkumar P, Kumar P, Mathew MK (2008) A plant Ca2+ pump, ACA2, relieves salt hypersensitivity in yeast. Modulation of cytosolic calcium signature and activation of adaptive Na+ homeostasis. J Biol Chem 283:3497–3506
Baxter I, Tchieu J, Sussman MR, Boutry M, Palmgren MG, Gribskov M, Harper JF, Axelsen KB (2003) Genomic comparison of P-type ATPase ion pumps in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 132:618–628
Bonza MC, De Michelis M (2011) The plant Ca2+ ATPase repertoire: biochemical features and physiological functions. Plant Biol 13:421–430
Boursiac Y, Lee SM, Romanowsky S, Blank R, Sladek C, Chung S, Harper (2010) Disruption of the vacuolar calcium-ATPase in Arabidopsis results in the activation of a salicylic acid-dependent programmed cell death pathway. Plant Physiol 154:1158–1171
Bush DS (1995) Calcium regulation in plant cells and its role in signaling. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:95–122
Cha−um S, Singh HP, Samphumphuang T, Kirdmanee C (2012) Calcium-alleviated salt tolerance in indica rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. indica): physiological and morphological changes. Aust J Crop Sci 6:176–182
Cunningham KW, Fink GR (1996) Calcineurin inhibits VCX1-dependent H+/Ca2+ exchange and induces Ca2+ ATPases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 16:2226–2237
Emery L, Whelan S, Hirschi KD, Pittman JK (2012) Protein phylogenetic analysis of Ca2+/cation antiporters and insights into their evolution in plants. Front Plant Sci 13:1–19
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A, Grisafi P, Alper SL, Fink GR (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:1480–1485
Geisler M, Frangne N, Gomès E, Martinoia E, Palmgren MG (2000) The ACA4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a vacuolar membrane calcium pump that improves salt tolerance in yeast. Plant Physiol 124:1814–1827
Hwang I, Harper JF, Liang F, Sze H (2000) Calmodulin activation of an endoplasmic reticulum-located calcium pump involves an interaction with the N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. Plant Physiol 122:157–168
Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006) Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. BBRC 345:646–651
Kamiya T, Maeshima M (2004) Residues in internal repeats of the rice cation/H+ exchanger are involved in the transport and selection of cations. J Biol Chem 279:812–819
Kamiya T, Akahori T, Maeshima M (2005) Expression profile of the genes for rice cation/H+ exchanger family and functional analysis in yeast. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1735–1740
Kamrul Huda KM, Yadav S, Akhter Banu MS, Trivedi DK, Tuteja N (2013) Genome-wide analysis of plant-type II Ca2+ ATPases gene family from rice and Arabidopsis: potential role in abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 65:32–47
Khush GS (2005) What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030? Plant Mol Biol 59:1–6
Li QF, Sun SSM, Yuan DY, Yu HX, Gu MH, Liu QQ (2010) Validation of candidate reference genes for the accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data in rice during seed development. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:49–57
Manohar M, Shigaki T, Hirschi KD (2011) Plant cation/H+ exchangers (CAXs): biological functions and genetic manipulations. Plant Biol 13:561–569
Martinoia E, Maeshima M, Neuhaus HE (2007) Vacuolar transporters and their essential role in plant metabolism. J Exp Bot 58:83–102
Marty F (1999) Plant vacuoles. Plant Cell 11:587–599
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Pittman JK, Hirschi KD (2001) Regulation of CAX1, an Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ antiporter. Identification of an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. Plant Physiol 127:1020–1029
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:8436–8441
Qudeimat E, Faltusz AM, Wheeler G, Lang D, Holtorf H, Brownlee C, Reski R, Frank W (2008) A PIIB-type Ca2+-ATPase is essential for stress adaptation in Physcomitrella patens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19555–19560
Sanders D, Brownlee C, Harper JF (1999) Communicating with calcium. Plant Cell 11:691–706
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 14:401–417
Schaaf G, Catoni E, Fitz M, Schwacke R, Schneider A, von Wire’n N, Frommer WB (2002) A putative role for the vacuolar calcium/manganese proton antiporter AtCAX2 in heavy metal detoxification. Plant Biol 4:612–618
Senadheera P, Singh RK, Maathuis FJ (2009) Differentially expressed membrane transporters in rice roots may contribute to cultivar dependent salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 60:2553–2563
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6896–6901
Shigaki T, Rees I, Nakhleh L, Hirschi KD (2006) Identification of three distinct phylogenetic groups of CAX cation/proton antiporters. J Mol Evol 63:815–825
Sze H, Liang F, Hwang I, Curran AC, Harper JF (2000) Diversity and regulation of plant Ca2+ pumps: insights from expression in yeast. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:433–462
Zhao J, Shigaki T, Mei H, Guo YQ, Cheng NH, Hirschi KD (2009) Interaction between Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ exchangers CAX1 and CAX3. J Biol Chem 284:4605–4615
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by postdoctoral program of the National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA), Thailand to NY and partially granted by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan and the International Center for Green Biotechnology of Meijo University. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table 1
(PDF 17 kb)
Supplemental Table 2
(PDF 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, N., Theerawitaya, C., Cha-um, S. et al. Expression and functional analysis of putative vacuolar Ca2+-transporters (CAXs and ACAs) in roots of salt tolerant and sensitive rice cultivars. Protoplasma 251, 1067–1075 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0615-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0615-2