Abstract
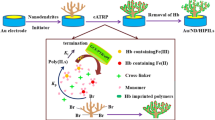
A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was prepared by self-polymerization of dopamine in the presence of bovine hemoglobin (BHb) and then deposited on the surface of an electrode modified with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Scanning electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and differential pulse voltammetry were employed to characterize the modified electrode using the hexacyanoferrate redox system as an electroactive probe. The effects of BHb concentration, dopamine concentration, and polymerization time were optimized. Under optimized conditions, the modified electrode selectively recognizes BHb even in the presence of other proteins. The peak current for hexacyanoferrate, typically measured at + 0.17 V (vs. SCE), depends on the concentration of BHb in the 1.0 × 10−11 to 1.0 × 10−2 mg mL−1 range. Due to the ease of preparation and tight adherence of polydopamine to various support materials, the present strategy conceivably also provides a platform for the recognition and detection of other proteins.

Gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted self-polymerization dopamine were modified on gold electrode surface to recognize and determine bovine hemoglobin. Under the optimized conditions, the modified electrode showed specific adsorption, selective recognition, and sensitive detection of bovine hemoglobin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv YQ, Tan TW, Svec F (2013) Molecular imprinting of proteins in polymers attached to the surface of nanomaterials for selective recognition of biomacromolecules. Biotechnol Adv 31:1172–1186
Zheng B, Wang F, Dong SY, Huang FH (2012) Supramolecular polymers constructed by crown ether-based molecular recognition. Chem Soc Rev 41:1621–1636
Lehn JM (1990) Perspectives in supramolecular chemistry-from molecular recognition towards molecular information processing and self-organization. Angew Chem Int Ed 29:1304–1319
Mayes AG, Mosbach K (1996) Molecularly imprinted polymer beads: suspension polymerization using a liquid perfluorocarbon as the dispersing phase. Anal Chem 68:3769–3774
Tretjakov A, Syritski V, Reut J, Boroznjak R, Volobujeva O, Öpik A (2013) Surface molecularly imprinted polydopamine films for recognition of immunoglobulin G. Microchim Acta 180:1433–1442
Chianella I, Guerreiro A, Moczko E, Caygill JS, Piletska EV, Perez De Vargas Sansalvador IM, Whitcombe MJ, Piletsky SA (2013) Direct replacement of antibodies with molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in ELISA development of a novel assay for vancomycin. Anal Chem 85:8462–8468
Huang BY, Chen YC, Wang GR, Liu CY (2011) Preparation and evaluation of a monolithic molecularly imprinted polymer for the chiral separation of neurotransmitters and their analogues by capillary electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:849–855
Lucci P, Núnez O, Galceran MT (2011) Solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of natural and synthetic estrogens from aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:4828–4833
Xie CG, Gao S, Guo QB, Xu K (2010) Electrochemical sensor for 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid using molecularly imprinted polypyrrole membrane as recognition element. Microchim Acta 169:145–152
Kolarov F, Niedergall K, Bach M, Tovar GEM, Gauglitz G (2012) Optical sensors with molecularly imprinted nanospheres: a promising approach for robust and label-free detection of small molecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:3245–3252
Veerapandian M, Seo YT, Yun K, Lee MH (2014) Graphene oxide functionalized with silver@silica-polyethylene glycolhybrid nanoparticles for direct electrochemical detection of quercetin. Biosens Bioelectron 58:200–204
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Qin L, He XW, Zhang W, Li WY, Zhang YK (2009) Macroporous thermosensitive imprinted hydrogel for recognition of protein by metal coordinate interaction. Anal Chem 81:7206–7216
Hua ZD, Chen ZY, Li YZ, Zhao MP (2008) Thermosensitive and salt-sensitive molecularly imprinted hydrogel for bovine serum albumin. Langmuir 24:5773–5780
Lian WJ, Liu S, Yu JH, Xing XR, Li J, Cui M, Huang JD (2012) Electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles fabricated molecularly imprinted polymer film at chitosan-platinum nanoparticles/graphene-gold nanoparticles double nanocomposites modified electrode for detection of erythromycin. Biosens Bioelectron 38:163–169
Zeng YB, Zhou Y, Zhou TS, Shi GY (2014) A novel composite of reduced graphene oxide and molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensing 4-nitrophenol. Electrochim Acta 130:504–511
Kan XW, Xing ZL, Zhu AH, Zhao Z, Xu GL, Li C, Zhou H (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin recognition. Sensors Actuators B 20:395–401
Li YX, Li YJ, Hong M, Bin Q, Lin ZY, Lin Z, Cai ZW, Chen GN (2013) Highly sensitive protein molecularly imprinted electro-chemical sensor based on gold microdendrites electrode and prussian blue mediated amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 42:612–617
Wu SG, Tan WG, Xu HH (2010) Protein molecularly imprinted polyacrylamide membrane: for hemoglobin sensing. Analyst 135:2523–2527
Lee H, Dellatore SM, Miller WM, Messersmith PB (2007) Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 318:426–430
Lee H, Rho J, Messersmith PB (2009) Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Adv Mater 21:431–434
Peng HP, Liang RP, Zhang L, Qiu JD (2013) General preparation of novel core-shell heme protein-Au-polydopamine-Fe3O4 magnetic bionanoparticles for direct electrochemistry. J Electroanal Chem 700:70–76
Xia ZW, Lin Z, Xiao Y, Wang L, Zheng JN, Yang HH, Chen GN (2013) Facile synthesis of polydopamine-coated molecularly imprinted silica nanoparticles for protein recognition and separation. Biosens Bioelectron 47:120–126
Zhang M, Zhang XH, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2012) A self-assembled polydopamine film on the surface of magneticnanoparticles for specific capture of protein. Nanoscale 4:3141–3147
Chen T, Shao MW, Xu HY, Zhuo SJ, Liu SS, Lee ST (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymer-coated silicon nanowires for protein specific recognition and fast separation. J Mater Chem 22:3990–3996
Gao RX, Zhang LL, Hao Y, Cui XH, Tang YH (2014) Specific removal of protein using protein imprinted polydopamine shells on modified amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv 4:64514–64524
Zhou WH, Liu CH, Guo XC, Chen FR, Yang HH, Wang XR (2010) Mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer coating superparamagnetic nanoparticles for protein recognition. J Mater Chem 20:880–883
Jia XP, Xu ML, Wang YZ, Ran D, Yang S, Zhang M (2013) Polydopamine-based molecular imprinting on silicon-modified magnetic nanoparticles for recognition and separation of bovine hemglobin. Analyst 138:651–658
Luo J, Jiang SS, Liu XY (2014) Electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin based on a novel graphene-molecular imprinted polymers composite as recognition element. Sensors Actuators B 203:782–789
Ouyang RZ, Lei JP, Ju HX (2010) Artificial receptor-functionalized nanoshell: facile preparation, fast separation and specific protein recognition. Nanotechnology 21:185502–185510
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China for young program (21005002), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Young Program (11040606Q35), Anhui University Provincial Natural Science Foundation Key program (KJ2010A138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 949 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Fan, L., Dai, Y. et al. Recognition and determination of bovine hemoglobin using a gold electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted self-polymerized dopamine. Microchim Acta 182, 2477–2483 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1594-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1594-5