Abstract
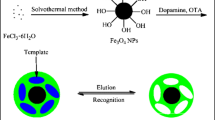
We report on a flow injection chemiluminescence assay for hydroquinone (HQ) using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles capped with oleic acid and coated with a polymer whose surface was molecularly imprinted for HQ to act as the recognition element. Dispersed in an oil phase, the surface imprinted particles display excellent adsorption capacity (63 mg∙g‾1) and a rapid adsorption rate. Packed into a flow cell, the addition of the reagents hexacyanoferrate(III), luminol and chlorhematin generates chemiluminescence whose intensity is linearly related to the concentration of HQ in the range from 2 × 10−7 to 1.0 × 10−5 mg∙mL‾1, with a detection limit of 7.9 × 10−8 mg∙mL‾1 and a relative standard deviation of 2.3 % at 1.0 × 10−7 mg∙mL‾1 HQ (n = 6). The method was successfully applied to the determination of HQ in spiked water samples.

The flow-injection chemiluminescence assay for hydroquinone uses Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles capped with oleic acid and coated with a polymer whose surface was molecularly imprinted for hydroquinone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang H, Chen D, Wei Y, Yu L, Zhang P, Zhao J (2011) A localized surface plasmon resonance light scattering-based sensing of hydroquinone via the formed silver nanoparticles in system. Spectrochim Acta A 79:2012–2016
Duarte-Davidson R, Courage C, Rushton L, Levy L (2001) Benzene in the environment: an assessment of the potential risks to the health of the population. Occup Environ Med 58:2–13
Bolton JL, Trush MA, Penning TM, Dryhurst G, Monks TJ (2000) Role of quinones in toxicology. Chem Res Toxicol 13:135–160
Luo L, Jiang L, Geng C, Cao J, Zhong L (2008) Hydroquinone-induced genotoxicity and oxidative DNA damage in HepG2 cells. Chem Biol Interact 173:1–8
Abernethy DJ, Kleymenova EV, Rose J, Recio L, Faiola B (2004) Human CD3 4+ hematopoietic progenitor cells are sensitive targets for toxicity induced by 1, 4-benzoquinone. Toxicol Sci 79:82–89
Xu G, Li B, Luo X (2013) Carbon nanotube doped poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for the electrocatalytic oxidation and detection of hydroquinone. Sensors Actuators B 176:69–74
Liu W, Li C, Tang L, Tong A, Gu Y, Cai R et al (2013) Nanopore array derived from l-cysteine oxide/gold hybrids: Enhanced sensing platform for hydroquinone and catechol determination. Electrochim Acta 88:15–23
Sirajuddin MI, Bhanger AN, Shah A, Rauf A (2007) Ultra-trace level determination of hydroquinone in waste photographic solutions by UV–vis spectrophotometry. Talanta 72:546–553
Gao WH, Quigley CL (2011) Fast and sensitive high performance liquid chromatography analysis of cosmetic creams for hydroquinone, phenol and six preservatives. J Chromatogr A 1218:4307–4311
Zhang YL, Xiao SX, Xie JL, Yang ZM, Pang PF, Gao YT (2014) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of catechol and hydroquinone based on graphene–TiO2nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B 204:102–108
Waseem A, Yaqoob M, Nabi A (2013) Analytical applications of flow injection chemiluminescence for the determination of pharmaceuticals–a review. Curr Pharm Anal 9:363–395
Wulff G (2013) Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: origin, features and perspectives. Microchim Acta 180:1359–1370
Lu F, Sun M, Fan L, Qiu H, Li X, Luo C (2012) Flow injection chemiluminescence system based on core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for determination of chrysoidine in food samples. Sensors Actuators B 173:591–598
Yu J, Wan F, Zhang C, Yan M, Zhang X, Wang S (2010) Molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres for determination of bovine serum albumin based on flow injection chemiluminescence system. Biosens Bioelectron 26:632–637
Xie C, Li H, Li S, Gao S (2011) Surface molecular imprinting for chemiluminescence detection of the organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos. Microchim Acta 174:311–320
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Yao GH, Liang RP, Huang CF, Wang Y, Qiu JD (2013) Surface plasmon resonance system based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers amplification for pesticide recognition. Anal Chem 85:11944–11951
Xu L, Pan J, Dai J et al (2012) Preparation of thermal-responsive magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 233–234:48–56
Lu S, Cheng G, Zhang H, Pang X (2006) Preparation and characteristics of Tryptophan-imprinted Fe3O4/P (TRIM) composite microspheres with magnetic susceptibility by inverse emulsion–suspension polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 99:3241–3250
Ikegami T, Mukawa T, Nariai H, Takeuchi T (2004) Bisphenol A-recognition polymers prepared by covalent molecular imprinting. Anal Chim Acta 504:131–135
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2011BL008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, L. et al. Determination of hydroquinone by flow injection chemiluminescence and using magnetic surface molecularly imprinted particles. Microchim Acta 182, 943–948 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1415-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1415-2