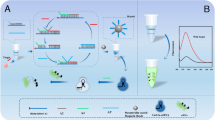
Abstract
We report on a microfluidic assay for microRNA using quantum dots as labels and capture probes immobilized in a bead array. Target microRNA flows along the microfluidic channel to hit the beads array where it hybridizes with the immobilized capture probes. Next, the hybrid is labeled by using the bound microRNAs as a primer for enzymatic elongation with biotin-labeled nucleotides. Due to the specificity of (a) the hybridization assay and (b) the enzymatic elongation step, this assay is quite selective and only the completely matched duplex can be labeled, in a final step, with streptavidin-labeled quantum dots. The method was applied to the specific detection of microRNAs that occur in the miRNA-29 family and display minute differences only in their nucleotide sequence. It does not require (a) a labeling step before hybridization and (b) no amplification. This on-chip assay for microRNA can detect concentrations as low as 0.1 pmol·L−1 (at an SNR of >3) when using synthetic microRNA. The 200-fold better sensitivity than that of an off-chip test is ascribed to the microfluidic-based signal enhancement. Other features include rapid binding kinetics, the advantages of a homogeneous assay in a suspended microbead array, the detection sensitivity resulting from the use of quantum dots, small reagent consumption, short assay time, and parallel detection.

A microfluidic bead-based enzymatic amplification assay was for the first time developed for microRNA detection using quantum dots as labels with high specificity and sensitivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilsen TW (2007) Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet 23:243–249
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W (2007) Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms. Trends Cell Biol 17:118–126
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Callis TE, Wang DZ (2008) Taking microRNAs to heart. Trends Mol Med 14:254–260
Stern-Ginossar N, Elefant N, Zimmermann A, Wolf DG, Saleh N, Biton M, Horwitz E, Prokocimer Z, Prichard M, Hahn G, Goldman-Wohl D, Greenfield C, Yagel S, Hengel H, Altuvia Y, Margalit H, Mandelboim O (2007) Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA. Science 317:376–383
Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Townsend M, Yoshii A, Sestan N, Rakic P, Constantine-Paton M, Horvitz HR (2004) Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in the developing mammalian brain. Genome Biol 5:R68
Chen Y, Gelfond JA, McManus LM, Shireman PK (2009) Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC Genomics 10:407
Sun Y, Gregory KJ, Chen NG, Golovlev V (2012) Rapid and direct microRNA quantification by an enzymatic luminescence assay. Anal Biochem 429:11–17
Friedländer MR, Chen W, Adamidi C, Maaskola J, Einspanier R, Knespel S, Rajewsky N (2008) Discovering microRNAs from deep sequencing data using miRDeep. Nat Biotechnol 26:407–415
Peng Y, Gao Z (2011) Amplified detection of microRNA based on ruthenium oxide nanoparticle-initiated deposition of an insulating film. Anal Chem 83:820–827
Nelson PT, Baldwin DA, Scearce LM, Oberholtzer JC, Tobias JW, Mourelatos Z (2004) Microarray-based, high-throughput gene expression profiling of microRNAs. Nat Methods 1:155–161
Chen J, Lozach J, Garcia EW, Barnes B, Luo S, Mikoulitch I, Zhou L, Schroth G, Fan JB (2008) Highly sensitive and specific microRNA expression profiling using BeadArray technology. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e87
Dittrich PS, Tachikawa K, Manz A (2006) Micro total analysis systems. Latest advancements and trends. Anal Chem 78:3887–3908
Vilkner T, Janasek D, Manz A (2004) Micro total analysis systems. Recent developments. Anal Chem 76:3373–3386
Sato K, Tokeshi M, Kimura H, Kitamori T (2001) Determination of carcinoembryonic antigen in human sera by integrated bead-bed immunoassay in a microchip for cancer diagnosis. Anal Chem 73:1213–1218
Vorwerk S, Ganter K, Cheng Y, Hoheisel J, Stähler PF, Beier M (2008) Microfluidic-based enzymatic on-chip labeling of miRNAs. New Biotechnol 25:142–149
Beier M, Boisguérin V (2012) Microfluidic primer extension assay. Methods Mol Biol 822:143–152
Monaghan PB, McCarney KM, Ricketts A, Littleford RE, Docherty F, Smith WE, Graham D, Cooper JM (2007) Bead-based DNA diagnostic assay for chlamydia using nanoparticle-mediated surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering detection within a lab-on-a-chip format. Anal Chem 79:2844–2849
Geng T, Bao N, Sriranganathanw N, Li L, Lu C (2012) Genomic DNA extraction from cells by electroporation on an integrated microfluidic platform. Anal Chem 84:9632–9639
Geng T, Novak R, Mathies RA (2014) Single-cell forensic short tandem repeat typing within microfluidic droplets. Anal Chem 86:703–712
Sato K, Yamanaka M, Takahashi H, Tokeshi M, Kimura H, Kitamori T (2002) Microchip-based immunoassay system with branching multichannels for simultaneous determination of interferon-gamma. Electrophoresis 23:734–739
Sato K, Tokeshi M, Odake T, Kimura H, Ooi T, Nakao M, Kitamori T (2000) Integration of an immunosorbent assay system: analysis of secretory human immunoglobulin A on polystyrene beads in a microchip. Anal Chem 72:1144–1147
Zhou LJ, Wang KM, Tan WH, Chen YQ, Zuo X, Wen J, Liu B, Tang H, He L, Yang X (2006) Quantitative intracellular molecular profiling using a one-dimensional flow system. Anal Chem 78:6246–6251
Zhang H, Liu L, Li CW, Fu HY, Chen Y, Yang MS (2011) Multienzyme-nanoparticles amplification for sensitive virus genotyping in microfluidic microbeads array using Au nanoparticle probes and quantum dots as labels. Biosens Bioelectron 29:89–96
Zhang H, Fu X, Liu L, Zhu ZJ, Yang K (2012) Microfluidic bead-based enzymatic primer extension for single-nucleotide discrimination using quantum dots as labels. Anal Biochem 426:30–39
Zhang H, Liu L, Fu X, Zhu ZJ (2013) Microfluidic beads-based immunosensor for sensitive detection of cancer biomarker proteins using multienzyme-nanoparticle amplification and quantum dots labels. Biosens Bioelectron 42:23–30
Zhang H, Fu X, Hu JY, Zhu ZJ (2013) Microfluidic bead-based multienzyme-nanoparticle amplification for detection of circulating tumor cells in the blood using quantum dots labels. Anal Chim Acta 779:64–71
Stroh M, Zimmer JP, Duda DG, Levchenko TS, Cohen KS, Brown EB, Scadden DT, Torchilin VP, Bawendi MG, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2005) Quantum dots spectrally distinguish multiple species within the tumor milieu in vivo. Nat Med 11:678–682
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Li CW, Yang J, Yang MS (2006) Dose-dependent cell-based assays in V-shaped microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 6:921–929
Petersen J, Poulsen L, Petronis S, Birgens H, Dufva M (2008) Use of a multi-thermal washer for DNA microarrays simplifies probe design and gives robust genotyping assays. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e10
Schmitt MJ, Margue C, Behrmann I, Kreis S (2013) MiRNA-29: a microRNA family with tumor-suppressing and immune-modulating properties. Curr Mol Med 13:572–585
Gunderson KL, Steemers FJ, Lee G, Mendoza LG, Chee MS (2005) A genome-wide scalable SNP genotyping assay using microarray technology. Nat Genet 37:549–554
Brenner S, Johnson M, Bridgham J, Golda G, Lloyd DH, Johnson D, Luo S, McCurdy S, Foy M, Ewan M, Roth R, George D, Eletr S, Albrecht G, Vermaas E, Williams SR, Moon K, Burcham T, Pallas M, DuBridge RB, Kirchner J, Fearon K, Mao J, Corcoran K (2000) Gene expression analysis by massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) on microbead arrays. Nat Biotechnol 18:630–634
Geng T, Bao N, Gall OZ, Lu C (2009) Modulating DNA adsorption on silica beads using an electrical switch. Chem Commun (Camb) 800–802
Geng T, Bao N, Litt MD, Glaros TG, Li L, Lu C (2011) Histone modification analysis by chromatin immunoprecipitation from a low number of cells on a microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 11:2842–2848
Zhang H, Xu T, Li CW, Yang MS (2010) A microfluidic device with microbead array for sensitive virus detection and genotyping using quantum dots as fluorescence labels. Biosens Bioelectron 25:2402–2407
Planell-Saguera M, Rodiciob MC (2011) Analytical aspects of microRNA in diagnostics: a review. Anal Chim Acta 699:134–152
Cissell KA, Rahimi Y, Shrestha S, Hunt EA, Deo SK (2008) Bioluminescence-based detection of microRNA, miR21 in breast cancer cells. Anal Chem 80:2319–2325
Driskell JD, Seto AG, Jones LP, Jokela S, Dluhy RA, Zhao YP, Tripp RA (2008) Rapid microRNA (miRNA) detection and classification via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Biosens Bioelectron 24:923–928
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (21005067), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (11JJ4015, 14JJ3133), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (12B029).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 24 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Fu, X. et al. Microfluidic bead-based assay for microRNAs using quantum dots as labels and enzymatic amplification. Microchim Acta 182, 661–669 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1372-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1372-9