Abstract
Objective
To determine the role of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia or the combination of both as independent risk factors for falls in a hospital population. Secondary objectives included evaluation of other risk factors for falling and their relationships with glucose levels.
Research design and methods
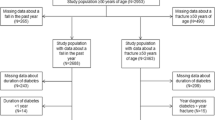
Retrospective cohort study over 2 years on hospitalized subjects (N = 57411) analyzing in-hospital-falls and capillary glucose values. Bivariate analysis (χ2 test) and multivariate analysis (logistic regression) were performed to test for correlation of glucose values, age, sex, Charlson index, service of care, diagnosis at discharge and diabetes treatment with risk of in-hospital-falls.
Results
The comparison of patients who experienced a fall (fall population) with the non-fall population suggested that: glucose determinations were significantly more frequent in the fall population (OR 3.45; CI 2.98–3.99; p < 0.0001); values of glucose below 70 mg/dl and over 200 mg/dl were significantly associated to falls during hospitalization (OR 1.76; CI 1.42–2.19; p < 0.001) as compared to glycemic values between 70 and 200 mg/dl; diabetes treatment was significantly correlated to risk of fall (OR 2.97; CI 2.54–3.49; p < 0.001); the frequency of glycemia measurements below 70 mg/dl and over 200 mg/dl in the same subject was significantly associated to falls during hospitalization (OR 1.01; CI 1.01–1.02; p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia during hospital stays are correlated with an increased risk for falls in the hospitalized population. Presence of diabetes, use of insulin or glucose variability could potentially constitute risk factors for falls inside the hospital as well.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimbell S (2002) Breaking the fall factor. Nurs Manage 33(9):22–25
Bergen G, Stevens MR, Burns ER (2016) Falls and fall injuries among adults aged ≥ 65 years—United States, 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 23(37):993–998 65(
Rau CS, Lin TS, Wu SC, Yang JC, Hsu SY, Cho TY, Hsieh CH (2014 Nov) Geriatric hospitalizations in fall-related injuries. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 12:22:63
Rudzińska M, Bukowczan S, Stożek J, Zajdel K, Mirek E, Chwała W, Wójcik-Pędziwiatr M, Banaszkiewicz K, Szczudlik A. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2013 47(5):423–30
Lee K, Pressler SJ, Titler M. Falls in patients with heart failure: a systematic review. J Cardiovasc Nurs 29, 2015
Minet LR, Peterson E, von Koch L, Ytterberg C (2015) Occurrence and predictors of falls in people with stroke: six-year prospective study. Stroke 46:2688–2690
Mamoto K, Inui K, Okano T, Sugioka Y, Tada M, Koike T, Nakamura H (2017) Incidence rate of falls and its risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to controls: four years of the TOMORROW study. Mod Rheumatol 27(1):8–14. (Epub 2016 May 4)
Ham AC, Swart KM, Enneman AW, van Dijk SC, Oliai Araghi S, van Wijngaarden JP, van der Zwaluw NL, Brouwer-Brolsma EM, Dhonukshe-Rutten RA, van Schoor NM, van der Cammen TJ, Lips P, de Groot LC, Uitterlinden AG, Witkamp RF, Stricker BH van der (2014) Velde N. Medication-related fall incidents in an older, ambulant population: the B-PROOF study. Drugs Aging 31(12):917–927
Doherty K, Archambault E, Kelly B, Rudolph JL (2014 Nov) Delirium markers in older fallers: a case-control study. Clin Interv Aging 21:9:2013–2018
OʼNeil CA, Krauss MJ, Bettale J, Kessels A, Costantinou E, Dunagan WC, Fraser VJ (2018) Medications and Patient Characteristics Associated With Falling in the Hospital. J Patient Saf 14(1):27–33
Kozono A, Isami K, Shiota K, Tsumagari K, Nagano M, Inoue D, Adachi R, Hiraki Y, Nakagawa Y, Kamimura H, Yamamichi K (2016) Relationship of prescribed drugs with the risk of fall in inpatients. Yakugaku Zasshi 136(5):769–776
McDonnell ME, Umpierrez GE (2012) Insulin therapy for the management of hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 41(1):175–201. Epub 2012 Feb 17
Kalfon P, Le Manach Y, Ichai C, Bréchot N, Cinotti R, Dequin PF, Riu-Poulenc B, Montravers P, Annane D, Dupont H, Sorine M, Riou B, CGAO-REA Study Group (2015) Severe and multiple hypoglycemic episodes are associated with increased risk of death in ICU patients. Crit Care 8:19:153
Timmons JG, Cunningham SG, Sainsbury CA, Jones GC (2017) Inpatient glycemic variability and long-term mortality in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 31(2):479–482
Takeishi S, Mori A, Hachiya H, Yumura T, Ito S, Shibuya T, Hayashi S, Fushimi N, Ohashi N, Kawai H (2016) Hypoglycemia and glycemic variability are associated with mortality in non-intensive care unit hospitalized infectious disease patients with diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig 7(3):429–435
Mendez CE, Mok KT, Ata A, Tanenberg RJ, Calles-Escandon J, Umpierrez GE (2013) Increased glycemic variability is independently associated with length of stay and mortality in noncritically ill hospitalized patients. Diabetes Care 36(12):4091–4097
Chiba Y, Kimbara Y, Kodera R, Tsuboi Y, Sato K, Tamura Y, Mori S, Ito H, Araki A (2015) Risk factors associated with falls in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 29(7):898–902
Lu CL1, Hsu PC, Shen HN, Chang YH, Chen HF, Li CY. Association between history of severe hypoglycemia and risk of falls in younger and older patients with diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 94(33):e1339
Hung YC, Lin CC, Chen HJ, Chang MP, Huang KC, Chen YH, Chen CC (2017) Severe hypoglycemia and hip fracture in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Osteoporos Int 28(7):2053–2060
Johnston SS, Conner C, Aagren M, Ruiz K, Bouchard J (2012) Association between hypoglycaemic events and fall-related fractures in Medicare-covered patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(7):634–643
Yau RK, Strotmeyer ES, Resnick HE, Sellmeyer DE, Feingold KR, Cauley JA, Vittinghoff E, De Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Nevitt MC, Cummings SR, Shorr RI, Schwartz AV (2013) Diabetes and risk of hospitalized fall injury among older adults. Diabetes Care 36(12):3985–3991
Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P et al. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care 2005 43(11):1073–1077
Quan H, Parsons GA, Ghali WA. Validity of information on comorbidity derived from ICD-9-CM administrative data. Med Care 2002 40(8):675–685
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, McKenzie CR (1987) A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chron Dis 40(5):373–383
Inouye SK, Brown CJ, Tinetti ME (2009) Medicare nonpayment, hospital falls, and unintended consequences. N Engl J Med 360:2390–2393
Cameron ID, Gillespie LD, Robertson MC et al (2012) Interventions for preventing falls in older people in care facilities and hospitals. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD005465
al Tehewy MM, Amin GE, Nassar NW (2015) A study of rate and predictors of fall among elderly patients in a university hospital. J Patient Saf 11:210–214
Anderson DC, Postler TS, Dam TT. Epidemiology of hospital system patient falls: a retrospective analysis. Am J Med Qual 2015
Basic D, Hartwell TJ (2015) Falls in hospital and new placement in a nursing home among older people hospitalized with acute illness. Clin Interv Aging 10:1637–1643
Twibell RS, Siela D, Sproat T, Coers G (2015) Perceptions related to falls and fall prevention among hospitalized adults. Am J Crit Care 24:e78–e85
Sircar M, Bhatia A, Munshi M (2016) Review of hypoglycemia in the older adult: clinical implications and management. Can J Diabetes 40(1):66–72
Wong CW (2015) Avoiding hypoglycaemia: a new target of care for elderly diabetic patients. Hong Kong Med J 21(5):444–454
Malabu UH, Vangaveti VN, Kennedy RL (2014) Disease burden evaluation of fall-related events in the elderly due to hypoglycemia and other diabetic complications: a clinical review. Clin Epidemiol 14:6:287–294
Kachroo S, Kawabata H, Colilla S, Shi L, Zhao Y, Mukherjee J, Iloeje U, Fonseca V (2015) Association between hypoglycemia and fall-related events in type 2 diabetes mellitus: analysis of a U.S. commercial database. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 21(3):243–253
Wu TY, Chie WC, Yang RS, Liu JP, Kuo KL, Wong WK, Liaw CK (2013) Factors associated with falls among community-dwelling older people in Taiwan. Ann Acad Med Singapore 42(7):320–327
Federici M, Hribal M, Perego L, Ranalli M, Caradonna Z, Perego C, Usellini L, Nano R, Bonini P, Bertuzzi F, Marlier LN, Davalli AM, Carandente O, Pontiroli AE, Meino G, Marchetti P, Lauro R, Sesti G, Folli F. High glucose causes apoptosis in cultured hman pancreatic islets of Langerhans: a potential role for regulation of specific Bcl family genes toward an apoptotic cell death program. Diabetes 2001 50 (6): 1290–1301
Folli F, Okada T, Perego C, Gunton J, Liew CW, Akiyama M, D’Amico A, La Rosa S, Placidi C, Lupi R, Marchetti P, Sesti G, Hellerstein M, Perego L, Kulkarni RN. Altered insulin receptor signalling and beta-cell cycle dynamics in type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 6(11): e28050
Guardado-Mendoza R, Davalli AM, Chavez AO, Hubbard GB, Dick EJ, Majluf-Cruz A, Tene-Perez CE, Goldschmidt L, Hart J, Perego C, Comuzzie AG, Tejero ME, Finzi G, Placidi C, La Rosa S, Capella C, Halff G, Gastaldelli A, De Fronzo RA, Folli F. Pancreatic islet amyloidosis, beta-cell apoptosis, and alfa-cell proliferation are determinants of islet remodeling in type-2 diabetic baboons PNAS 2009, 106 33 13992–13997
Folli F, La Rosa S, Finzi G, Davalli AM, Galli A, Dick EJ, Perego C, Guardado-Mendoza R (2018) Pancreatic islets of Langherans cytoarchitecture and ultrastructure in normal glucose tolerance and in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 20(Suppl 2):137–144
Keenan HA, Sun JK, Levine J, Doria A, Aiello LP, Eisenbarth G, Bonner-Weir S, King GL. Residual insulin production and pancreatic beta-cell turnover after 50 years of diabetes: Joslin medalist study. Diabetes 2010; 59 (11): 2846–53
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC (2003) Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52(1):102–110
Jurgens CA, Toukatly MN, Fligner CL, Udayasankar J, Subramanian SL, Zraika S, Aston-Mourney K, Carr DB, Westermark P, Westermark GT, Kahn SE, Hull RL (2011) β-cell loss and β-cell apoptosis in human type 2 diabetes are related to islet amyloid deposition. Am J Pathol 178(6):2632–2640
Berra C, Azzolini E, Zangrandi F, Mirani M, Albini M, De Fazio F, Favacchio G, Mauer N, Meroni P In-hospital glucose monitoring: adequacy and resource management. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 5 (5): 2018
Acknowledgements
Parts of this work have been presented in abstract form at the meetings of IDF 2017 and EASD in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Humanitas Research Hospital, Rozzano, Milano, Italy.
Informed consent
All clinical and laboratory informations came from retrospective analysis from non identifiable data, informed consent was not deemed necessary by the Ethical Committee.
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Porta.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berra, C., De Fazio, F., Azzolini, E. et al. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are risk factors for falls in the hospital population. Acta Diabetol 56, 931–938 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01323-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-019-01323-8