Abstract
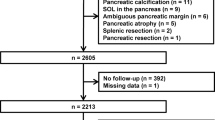
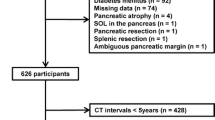
Pancreatic volume and fat content might be associated with β-cell function or insulin resistance (IR). We investigated the difference in pancreatic volume and fat content between age- and body mass index (BMI)-matched normal subjects and patients with having different durations of type 2 diabetes (T2D). We compared pancreatic volume and fat parameters between 50 age- and BMI-matched normal subjects, 51 subjects with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D-new), 53 subjects with T2D <5 years (T2D<5Y), and 52 subjects with T2D ≥5 years (T2D≥5Y). Age and BMI were matched to range of ±2 years and ±0.5 kg/m2, respectively. Pancreatic volume and fat were measured by multidetector-row computed tomography with 64 detector-row scanner. The difference in Hounsfield units between pancreas and spleen (HUp–s) was investigated for fat density. Anthropometric and biochemical parameters including the homeostasis model assessment of IR (HOMA-IR) and the insulinogenic index (IGI) were measured. Compared with normal subjects, patients with T2D had significantly smaller pancreatic volume, greater pancreatic fat, and lower HUp–s. Among the groups with T2D, pancreatic volume decreased and pancreatic fat percentage and HUp–s increased from the T2D-new to the T2D<5Y and T2D>5Y groups. Pancreatic volume and fat and HUp–s values were associated with HbA1c and triglyceride levels. Pancreatic volume was correlated with IGI while pancreatic fat and HUp–s values were correlated with HOMA-IR. The current study suggests that pancreatic volume and fat deposition might be associated with the development and progression of T2D in Korean subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector-row computed tomography
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- OGTT:
-
Oral glucose tolerance test
- FPG:
-
Fasting plasma glucose
- PG:
-
Post-glucose load glucose
- FPI:
-
Fasting plasma insulin
- IGI:
-
Insulinogenic index
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- HU:
-
Hounsfield units
References
Fonseca V, Berger LA, Beckett AG, Dandona P (1985) Size of pancreas in diabetes mellitus: a study based on ultrasound. Br Med J 291:1240–1241
Sakata N, Egawa S, Rikiyama T, Yoshimatsu G, Masuda K, Ohtsuka H, Ottomo S, Nakagawa K, Hayashi H, Morikawa T, Onogawa T, Yamamoto K, Yoshida H, Akada M, Motoi F, Naitoh T, Katayose Y, Unno M (2011) Computed tomography reflected endocrine function of the pancreas. J Gastrointest Surg 15:525–532
Goda K, Sasaki E, Nagata K, Fukai M, Ohsawa N, Hahafusa T (2001) Pancreatic volume in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol 38:145–149
Williams AJ, Thrower SL, Sequeiros IM, Ward A, Bickerton AS, Triay JM, Callaway MP, Dayan CM (2012) Pancreatic volume is reduced in adult patients with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E2109–E2113
Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY (2006) Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet 368:1681–1688
Ramachandran A, Ma RC, Snehalatha C (2010) Diabetes in Asia. Lancet 375:408–418
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB (2009) Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 301:2129–2140
Tushuizen ME, Bunck MC, Pouwels PJ, Bontemps S, van Waesberghe JH, Schindhelm RK, Mari A, Heine RJ, Diamant M (2007) Pancreatic fat content and beta-cell function in men with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:2916–2921
Rasouli N, Molavi B, Elbein SC, Kern PA (2007) Ectopic fat accumulation and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab 9:1–10
Pinnick KE, Collins SC, Londos C, Gauguier D, Clark A, Fielding BA (2008) Pancreatic ectopic fat is characterized by adipocyte infiltration and altered lipid composition. Obesity 16:522–530
van der Zijl NJ, Goossens GH, Moors CC, van Raalte DH, Muskiet MH, Pouwels PJ, Blaak EE, Diamant M (2011) Ectopic fat storage in the pancreas, liver, and abdominal fat depots: impact on beta-cell function in individuals with impaired glucose metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:459–467
Heni M, Machann J, Staiger H, Schwenzer NF, Peter A, Schick F, Claussen CD, Stefan N, Haring HU, Fritsche A (2010) Pancreatic fat is negatively associated with insulin secretion in individuals with impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance: a nuclear magnetic resonance study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26:200–205
Djuric-Stefanovic A, Masulovic D, Kostic J, Randjic K, Saranovic D (2012) CT volumetry of normal pancreas: correlation with the pancreatic diameters measurable by the cross-sectional imaging, and relationship with the gender, age, and body constitution. Surg Radiol Anat 34:811–817
Saisho Y, Butler AE, Meier JJ, Monchamp T, Len-Auerbach M, Rizza RA, Butler PC (2007) Pancreas volumes in humans from birth to age one hundred taking into account sex, obesity, and presence of type-2 diabetes. Clin Anat 20:933–942
Schrader H, Menge BA, Schneider S, Belyaev O, Tannapfel A, Uhl W, Schmidt WE, Meier JJ (2009) Reduced pancreatic volume and beta-cell area in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 136:513–522
Kim TH, Yu SH, Choi SH, Yoon JW, Kang SM, Chun EJ, Choi SI, Shin H, Lee HK, Park KS, Jang HC, Lim S (2011) Pericardial fat amount is an independent risk factor of coronary artery stenosis assessed by multidetector-row computed tomography: the Korean Atherosclerosis Study 2. Obesity 19:1028–1034
American Diabetes Association (2012) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 35(Suppl 1):S64–S71
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Wareham NJ, Phillips DI, Byrne CD, Hales CN (1995) The 30 minute insulin incremental response in an oral glucose tolerance test as a measure of insulin secretion. Diabet Med 12:931
Tura A, Kautzky-Willer A, Pacini G (2006) Insulinogenic indices from insulin and C-peptide: comparison of beta-cell function from OGTT and IVGTT. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 72:298–301
Stumvoll M, Mitrakou A, Pimenta W, Jenssen T, Yki-Jarvinen H, Van HT, Renn W, Gerich J (2000) Use of the oral glucose tolerance test to assess insulin release and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 23:295–301
Park SH, Kim PN, Kim KW, Lee SW, Yoon SE, Park SW, Ha HK, Lee MG, Hwang S, Lee SG, Yu ES, Cho EY (2006) Macrovesicular hepatic steatosis in living liver donors: use of CT for quantitative and qualitative assessment. Radiology 239:105–112
Gilbeau JP, Poncelet V, Libon E, Derue G, Heller FR (1992) The density, contour, and thickness of the pancreas in diabetics: CT findings in 57 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159:527–531
Vesterhus M, Haldorsen IS, Raeder H, Molven A, Njolstad PR (2008) Reduced pancreatic volume in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A-maturity-onset diabetes of the young. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3505–3509
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC (2003) Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52:102–110
Kin T, Murdoch TB, Shapiro AM, Lakey JR (2006) Estimation of pancreas weight from donor variables. Cell Transplant 15:181–185
Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Won YJ, Choi SH, Cho SI, Park KS, Lee HK, Jang HC, Koh KK (2011) Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998–2007. Diabetes Care 34:1323–1328
Bhowmik B, Afsana F, My DL, Binte MS, Wright E, Mahmood S, Khan AK, Hussain A (2013) Increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes in a rural Bangladeshi population: a population based study for 10 years. Diabetes Metab J 37:46–53
Cnop M (2008) Fatty acids and glucolipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Biochem Soc Trans 36:348–352
Karunakaran U, Park KG (2013) A systematic review of oxidative stress and safety of antioxidants in diabetes: focus on islets and their defense. Diabetes Metab J 37:106–112
El-Assaad W, Buteau J, Peyot ML, Nolan C, Roduit R, Hardy S, Joly E, Dbaibo G, Rosenberg L, Prentki M (2003) Saturated fatty acids synergize with elevated glucose to cause pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology 144:4154–4163
Cnop M, Hannaert JC, Hoorens A, Eizirik DL, Pipeleers DG (2001) Inverse relationship between cytotoxicity of free fatty acids in pancreatic islet cells and cellular triglyceride accumulation. Diabetes 50:1771–1777
Kim KW, Lee J, Lee H, Jeong WK, Won HJ, Shin YM, Jung DH, Park JI, Song GW, Ha TY, Moon DB, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Hwang S, Lee SG (2010) Right lobe estimated blood-free weight for living donor liver transplantation: accuracy of automated blood-free CT volumetry—preliminary results. Radiology 256:433–440
Schneider S (2008) Efforts to develop methods for in vivo evaluation of the native beta-cell mass. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(Suppl 4):109–118
Rahier J, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Sempoux C, Henquin JC (2008) Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(Suppl 4):32–42
Sabek OM, Cowan P, Fraga DW, Gaber AO (2006) The effect of donor factors on human islet yield and their in vivo function. Prog Transplant 16:350–354
Bae KT (2010) Intravenous contrast medium administration and scan timing at CT: considerations and approaches. Radiology 256:32–61
Nishino M, Kubo T, Kataoka ML, Raptopoulos V, Hatabu H (2006) Coronal reformations of the chest on 64-row multi-detector row CT: evaluation of image quality in comparison with 16-, 8- and 4-row multi-detector row CT. Eur J Radiol 59:231–237
Goshima S, Kanematsu M, Nishibori H, Sakurai K, Miyazawa D, Watanabe H, Kondo H, Shiratori Y, Onozuka M, Moriyama N, Bae KT (2011) CT of the pancreas: comparison of anatomic structure depiction, image quality, and radiation exposure between 320-detector volumetric images and 64-detector helical images. Radiology 260:139–147
Normandin MD, Petersen KF, Ding YS, Lin SF, Naik S, Fowles K, Skovronsky DM, Herold KC, McCarthy TJ, Calle RA, Carson RE, Treadway JL, Cline GW (2012) In vivo imaging of endogenous pancreatic beta-cell mass in healthy and type 1 diabetic subjects using 18F-fluoropropyl-dihydrotetrabenazine and PET. J Nucl Med 53:908–916
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant of the Korean Health Technology Research and Development project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A090623 and A092077) and a Grant from the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund (No. 03-2009-003).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of SNUBH (B-0809/061- 104) and performed according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Managed by Massimo Porta.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, S., Bae, J.H., Chun, E.J. et al. Differences in pancreatic volume, fat content, and fat density measured by multidetector-row computed tomography according to the duration of diabetes. Acta Diabetol 51, 739–748 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0581-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0581-3