Abstract
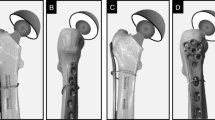
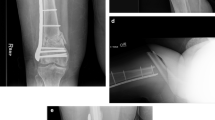
To promote rapid bone healing, an adequate stable fixation implant with a percutaneous reduction instrument should be used for Vancouver type B1 or C fractures. The objective of this study was to describe radiographic and clinical outcomes of patients with periprosthetic fracture (PPF) around a stable femoral stem, treated with a distal femoral locking plate alone or with a cerclage cable. A total of 21 patients with PPF amenable to either a reverse distal femoral locking plate (LCP DF®) alone or with a cerclage cable, with a mean age of 75.7 years, were included. In these patients, ten fractures were treated with a reverse LCP DF® alone and were classified as group I, and 11 additionally received a cerclage cable and were classified as group II. Group II had a significantly longer operation time (P = 0.019) than group I and included one patient with nonunion at the final 24-month follow-up visit after the initial fracture reduction. However, this difference in nonunion rate for the two groups is more likely to inappropriate indications than surgical techniques. When comparing the stability of the fractures in both groups, there was no statistically significant difference, which might be attributed to the stable fixed-angle implant.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regnér H, Herberts P, Malchau H (2006) Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(6):1215–1222
Pellicci P, Tria AJ, Garvin K (2000) Orthopaedic knowledge update (hip and knee reconstruction 2). American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Rosemont (III)
Laurer HL, Wutzler S, Possner S, Geiger EV, El Saman A, Marzi I, Frank J (2011) Outcome after operative treatment of Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fractures: open reduction and internal fixation versus revision arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(7):983–989
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2000) The reliability of validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty 15(1):59–62
Ninan T, Costa ML, Krikler S (2007) Classification of femoral periprosthetic fractures. Injury 38(6):661–668
Abhaykumar S, Elliott D (2000) Percutaneous plate fixation for periprosthetic femoral fractures—a preliminary report. Injury 31(8):627–630
Tsiridis E, Narvani A, Noorda RJ, Wuisman PI (2003) Mennen plate fixation for the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85(9):1851
Haddad FS, Duncan CP, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Gross AE, Chandler HP (2002) Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed implants: use of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84(6):945–950
Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR, Loftus T, Cox C, Mitchell S, Borrelli J Jr (2005) Indirect reduction and plate fixation, without grafting, for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures about a stable intramedullary implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(10):2240–2245
Kolb W, Guhlmann H, Friedel R, Nestmann H (2003) Fixation of periprosthetic femur fractures with the less invasive stabilization system (LISS)—a new minimally invasive treatment with locked fixed-angle screws. Zent Chir 128(1):53–59
Fulkerson E, Tejwani N, Stuchin S, Egol K (2007) Management of periprosthetic femur fractures with a first generation locking plate. Injury 38(8):965–972
Chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J (2007) Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver Type B1 and Type C periprosthetic fractures of femur: a report on 12 patients. Injury 38(6):725–733
Wood GC, Naudie DR, McAuley J, McCalden RW (2011) Locking compression plates for the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed total hip and knee implants. J Arthroplasty 26(6):886–892
Shi HY, Chang JK, Wong CY, Wang JW, Tu YK, Chiu HC, Lee KT (2010) Responsiveness and minimal important differences after revision total hip arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:261
Tsiridis E, Haddad FS, Gie GA (2003) Dall-Miles plates for periprosthetic femoral fractures: a critical review of 16 cases. Injury 34(2):107–110
Venu K, Koka R, Garikipati R, Shenava Y, Madhu T (2001) Dall-Miles cable and plate fixation for the treatment of peri-prosthetic femoral fractures-analysis of results in 13 cases. Injury 32(5):395–400
Springer BD, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG (2003) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty with femoral component revision. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85(11):2156–2162
Buttaro M, Farfalli G, Núñez MP, Comba F, Piccaluga F (2007) Locking compression plate fixation of Vancouver type-B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(9):1964–1969
Bryant GK, Morshed S, Agel J, Henley MB, Barei DP, Taitsman LA, Nork SE (2009) Isolated locked compression plating for Vancouver Type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury 40(11):1180–1186
O’Toole RV, Gobezie R, Hwang R, Chandler AR, Smith RM, Estok DM, Vrahas MS (2006) Low complication rate of LISS for femur fractures adjacent to stable hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 450:203–210
Xue H, Tu Y, Cai M, Yang A (2011) Locking compression plate and cerclage band for type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures: preliminary results at average 30-month follow-up. J Arthroplasty 26(3):467–471
Erhardt J, Grob K, Roderer G, Hoffmann A, Forster T, Kuster M (2008) Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with the non-contact bridging plate: a new angular stable implant. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(4):409–416
Ebraheim NA, Gomez C, Ramineni SK, Liu J (2009) Fixation of periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures adjacent to a well-fixed femoral stem with reversed distal femoral locking plate. J Trauma 66(4):1152–1157
Lenz M, Perren SM, Gueorguiev B, Richards RG, Hofmann GO, Fernandez dell’Oca A, Höntzsch D, Windolf M (2014) A biomechanical study on proximal plate fixation techniques in periprosthetic femur fractures. Injury 45:S71–S75
Kampshoff J, Stoffel KK, Yates PJ, Erhardt JB, Kuster MS (2010) The treatment of periprosthetic fractures with locking plates: effect of drill and screw type on cement mantles: a biomechanical analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(5):627–632
Funding
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article, nor have any funds been received in support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, YS., Han, SB. Periprosthetic fracture around a stable femoral stem treated with locking plate osteosynthesis: distal femoral locking plate alone versus with cerclage cable. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27, 623–630 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-017-1900-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-017-1900-5