Abstract
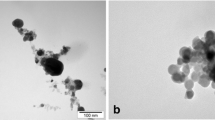
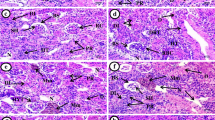
Considering the prevalence of emerging nanotechnology, predicting the environmental impact of nanomaterials has great importance. The aim of this study was to investigate the possible accumulation and histological damage resulting from the exposure of fish to silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Hence, rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were exposed for 21 days to sublethal concentrations of either colloidal or powdered forms of silver nanoparticles (cAgNPs or pAgNPs, respectively); the resulting histological changes (in gills, intestines, liver, and kidneys) and bioaccumulation (in gills, intestines, liver, and white muscles) were examined on days 11 and 21. In the case of cAgNPs, the highest concentrations of silver were observed in the liver, gills, and intestines. Meanwhile, in the case of pAgNPs, the highest concentrations of silver were observed in the intestines, liver, gills, and muscles. The greatest histopathological impacts were observed in the gills (mostly proliferation and inflammation), intestines (mostly necrosis and inflammation), and liver (mostly pigmentation). Thus, when taken together, the current findings indicate that both forms of AgNPs had a chronic effect on the rainbow trout (as a model aquatic organism); therefore, preventing the entry of these nanomaterials into the aquatic environment would seem to be essential.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agius C (1979) The role of melano-macrophage centres in iron storage in normal and diseased fish. J Fish Dis 2:337–343
Agius C, Roberts RJ (1981) Effects of starvation on the melano-macrophage centres of fish. J Fish Biol 19:161–169
Agius C, Roberts RJ (2003) Melano-macrophage centres and their role in fish pathology. J Fish Dis 26:499–509
Asghari S, Johari SA, Lee JH, Kim YS, Jeon YB, Choi HJ, Moon MC, Yu IJ (2012) Toxicity of various silver nanoparticles compared to silver ions in Daphnia magna. J Nanobiotechnol 10:14
Batley GE, Kirby JK, McLaughlin MJ (2013) Fate and risks of nanomaterials in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Acc Chem Res 46:854–862
Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T (1999) Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Dis 22:25–34
Best JH, Eddy FB, Codd GA (2003) Effects of microcystis cells, cell extracts and lipopolysaccharide on drinking and liver function in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum. Aquat Toxicol 64:419–426
Bilberg K, Døving KB, Beedholm K, Baatrup E (2011) Silver nanoparticles disrupt olfaction in Crucian carp (Carassius carassius) and Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Aquat Toxicol 104(1–2):145–152
Cong Y, Banta GT, Selck H, Berhanu D, Valsami-Jones E, Forbes VE (2014) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated silver nanoparticles in the estuarine polychaete, Nereis (Hediste) diversicolor. Aquat Toxicol 156C:106–115
Eddy FB (1982) Osmotic and ionic regulation in captive fish with particular reference to salmonids. Comp Biochem Physiol 73B:125–141
Farmen E, Mikkelsen HN, Evensen Ø, Einset J, Heier LS, Rosseland BO, Salbu B, Tollefsen KE, Oughton DH (2012) Acute and sub-lethal effects in juvenile Atlantic salmon exposed to low μg/L concentrations of Ag nanoparticles. Aquat Toxicol 108:78–84
Federici G, Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2007) Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat Toxicol 84:415–430
Gagné F, Auclair J, Fortier M, Bruneau A, Fournier M, Turcotte P, Pilote M, Gagnon C (2013) Bioavailability and immunotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to the freshwater mussel Elliptio complanata. J Toxic Environ Health A 76(13):767–777
Gaiser BK, Fernandes TF, Jepson M, Lead JR, Tyler CR, Stone V (2009) Assessing exposure, uptake and toxicity of silver and cerium dioxide nanoparticles from contaminated environments. Environ Heal 8(Suppl 1):S2
Giovanni M, Tay CY, Setyawati MI, Xie J, Ong CN, Fan R, Yue J, Zhang L, Leong DT (2014) Toxicity profiling of water contextual zinc oxide, silver, and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human oral and gastrointestinal cell systems. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.22015
Griffitt RJ, Weil R, Hyndman KA, Denslow ND, Powers K, Taylor D, Barber DS (2007) Exposure to copper nanoparticles causes gill injury and acute lethality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Sci Technol 41:8178–8186
Griffitt RJ, Hyndman K, Denslow ND, Barber DS (2009) Comparison of molecular and histological changes in zebrafish gills exposed to metallic nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci 107(2):404–415
Griffitt RJ, Brown-Peterson NJ, Savin DA, Manning CS, Boube I, Ryan RA, Brouwer M (2012) Effects of chronic nanoparticulate silver exposure to adult and juvenile sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus). Environ Toxicol Chem 31(1):160–167
Handy RD, Henry TB, Scown TM, Johnston BD, Tyler CR (2008) Manufactured nanoparticles: their uptake and effects on fish: a mechanistic analysis. Ecotoxicology 17:396–409
Heath AG (1995) Behavioral and nervous system function. In: Water pollution and fish physiology. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 271–297
Imani M, Halimi M, Khara H (2014) Effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on hematological parameters of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Comp Clin Pathol. doi:10.1007/s00580-014-1927-5
Johari SA, Kalbassi MR, Soltani M, Yu IJ (2013) Toxicity comparison of colloidal silver nanoparticles in various life stages of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Iran J Fish Sci 12(1):76–95
Johari SA, Sourinejad I, Bärsch N, Saed-Moocheshi S, Kaseb A, Nazdar N (2014) Does physical production of nanoparticles reduce their ecotoxicity? a case of lower toxicity of AgNPs produced by laser ablation to zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int J Aqua Biol 2(4):188–192
Keller AA, McFerran S, Lazareva A, Suh S (2013) Global life cycle releases of engineered nanomaterials. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1692
Li H, Turner A, Brown MT (2012) Accumulation of aqueous and nanoparticulate silver by the marine gastropod Littorina littorea. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1354
Little E, Finger S (1990) Swimming behavior as an indicator of sub lethal toxicity in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:13–19
López-Serrano A, Muñoz-Olivas R, Sanz-Landaluze J, Olasagasti M, Rainieri S, Cámara C (2014) Comparison of bioconcentration of ionic silver and silver nanoparticles in zebrafish eleutheroembryos. Environ Pollut 191:207–214
McTeer J, Dean AP, White KN, Pittman JK (2014) Bioaccumulation of silver nanoparticles into Daphnia magna from a freshwater algal diet and the impact of phosphate availability. Nanotoxicology 8(3):305–316
Nickum JG, Bart HL Jr, Bowser PR, Greer IE, Hubbs C, Jenkins JA, MacMillan JR, Rachlin JW, Rose JD, Sorensen PW, Tomasso JR (2004) Guidelines for the use of fishes in research. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, 54 pages
NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) (1999) NIOSH manual of analytical methods, method no. 7300. NIOSH, Cincinnati
OECD (1984) OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals. Test no. 204: fish, prolonged toxicity test: 14-day study. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oliver AL, Croteau MN, Stoiber TL, Tejamaya M, Römer I, Lead JR, Luoma SN (2014) Does water chemistry affect the dietary uptake and toxicity of silver nanoparticles by the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis? Environ Pollut 189:87–91
Oukarroum A, Samadani M, Dewez D (2014) Influence of pH on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles in the green alga Chlamydomonas acidophila. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:2038
Pavagadhi S, Sathishkumar M, Balasubramanian R (2014) Uptake of Ag and TiO2 nanoparticles by zebrafish embryos in the presence of other contaminants in the aquatic environment. Water Res 15(55):280–291
Prabhu S, Poulose EK (2012) Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett 2:32
Ribeiro F, Gallego-Urrea JA, Jurkschat K, Crossley A, Hassellöv M, Taylor C, Soares AM, Loureiro S (2013) Silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate induce high toxicity to Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Daphnia magna and Danio rerio. Sci Total Environ 466–467:232–241
Salari Joo H, Kalbassi MR, Yu IJ, Lee JH, Johari SA (2013) Bioaccumulation of silver nanoparticles in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): influence of concentration and salinity. Aquat Toxicol 140–141:398–406
Scown TM, Santos EM, Johnston BD, Gaiser B, Baalousha M, Mitov S, Lead JR, Stone V, Fernandes TF, Jepson M, van Aerle R, Tyler CR (2010) Effects of aqueous exposure to silver nanoparticles of different sizes in rainbow trout. Toxicol Sci 115(2):521–534
Setyawati MI, Yuan X, Xie J, Leong DT (2014) The influence of lysosomal stability of silver nanomaterials on their toxicity to human cells. Biomaterials 35(25):6707–6715
Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2011) Physiological effects of nanoparticles on fish: a comparison of nanometals versus metal ions. Environ Int 37(6):1083–1097
Smith CJ, Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2007) Toxicity of single walled carbon nanotubes on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): respiratory toxicity, organ pathologies, and other physiological effects. Aquat Toxicol 82:94–109
Spry DJ, Wood CM (1988) Zinc influx across the isolated, perfused head preparation of the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in hard and soft water. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:2206–2215
Webb NA, Wood CM (2000) Bioaccumulation and distribution of silver in four marine teleosts and two marine elasmobranchs: influence of exposure duration, concentration, and salinity. Aquat Toxicol 49:111–129
Welsh PG, Lipton J, Mebane CA, Marr JCA (2008) Influence of flow-through and renewal exposures on the toxicity of copper to rainbow trout. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:199–208
Wolke RE (1992) Piscine macrophage aggregates: a review. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:91–108
Woodrow Wilson Database, 2013. Nanotechnology consumer product inventory. http://www.nanotechproject.org/cpi/about/analysis/. Accessed 28 Aug 2014
Yuan X, Setyawati MI, Tan AS, Ong CN, Leong DT, Xie J (2013) Highly luminescent silver nanoclusters with tunable emissions: cyclic reduction-decomposition synthesis and antimicrobial property. Nat Publ Group Asia Mat 5:e39. doi:10.1038/am.2013.3
Yuan X, Setyawati MI, Leong DT, Xie J (2014) Ultrasmall Ag+-rich nanoclusters as highly efficient nanoreservoirs for bacterial killing. Nano Res 7(3):301–307
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Tarbiat Modares University of Islamic Republic of Iran, who funded this research through a Ph.D. thesis project. This research was also supported by the Nanomaterial Technology Development Program (Green Nanotechnology Development Program) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (no. 2012-006648). We also appreciate the assistance of Mrs. Saba Asghari in tissue sampling and preparation of histological sections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johari, S.A., Kalbassi, M.R., Yu, I.J. et al. Chronic effect of waterborne silver nanoparticles on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): histopathology and bioaccumulation. Comp Clin Pathol 24, 995–1007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-2019-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-2019-2