Abstract
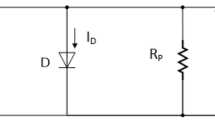
Photovoltaic (PV) is an important clean and free-pollution renewable energy. The performance of a photovoltaic module is mostly affected by array configuration and solar irradiance. Due to the intermittent feature of weather, it becomes an unreliable and intermitted source. The variations of solar irradiance are optimally tracked by the proposed incremental conductance (IC) technique with proportional integral regulator is maintain the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) of a three-phase grid-connected PV array. Simulations results show the proposed IC-MPPT method has achieved as fast response performance under sudden change of solar irradiation. The proposed MATLAB/Simulink ® model implemented as a PV inverter can be achieved with 95.0% peak MPPT efficiency.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhaskar MA et al (2011) A simple PV array modeling using MATLAB. In: proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Emerging trends in electrical and computer technology (ICETECT), Tamil Nadu, pp 122–126
Esram T, Chapman PL (2007) Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 22:439–449
Hussein KH, Mota I (1995) Maximum photovoltaic power tracking: an algorithm for rapidly changing atmospheric conditions. IEE Proc-Gener, Transm Distrib 142:59–64
Jiang Y, Qahouq JAA and Batarseh I (2010) Improved solar PV cell MATLAB simulation model and comparison. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and systems, Paris, pp 2770–2773
Kun D, Bian XG, Liu HH, Tao P (2012) A MATLAB-Simulink-based PV module model and its application under conditions of nonuniform irradiance. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 27:864–872
Lee JH, Bae HS and Cho BH (2006) Advanced incremental conductance MPPT algorithm with a variable step size. In: proceedings of the 12th international power electronics and motion control conference, Portoroz, pp 603–607
Ropp ME, Gonzalez S (2009) Development of a MATLAB/Simulink model of a single-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 24:195–202
Matlab and Simulink, The Mathworks, Inc. http://www.mathworks.com
SimPowerSystems for use with Simulink, user’s guide, The MathWorks Inc
Zainudin HN and Mekhilef S (2010) Comparison study of maximum power point tracker techniques for PV systems. In: proceedings of the 14th international middle east power systems conference (MEPCON’10), Cairo University, Paper ID 278
Acknowledgements
The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, ROC, under Grant most 105-2623-E-218-001-ET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, JM., Liu, PH. The performance analysis of photovoltaic generation using the improved incremental conductance method under varying solar irradiance. Microsyst Technol 24, 235–241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3247-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3247-y