Abstract
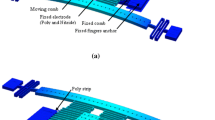
This paper reports design and performance of a new micro linear motor (MLM) driven by electrostatic comb-drive actuators based on SOI-MEMS technology. In this motor, a shuttle with six wings on the each side is moved by the electrostatic comb-drive actuators through ratchet teeth in the direction perpendicular to the movement direction of the ratchet racks. The MLM was fabricated from SOI (silicon on insulator) wafer by using only one photo mask. The bidirectional movement of the shuttle has been tested with AC driving voltage of V pp = 100 V and driving frequency ranged from 1 to 10 Hz. In our experiments, the displacement of the shuttle after each step is approximately 10 µm and the obtained travel equals 500 µm. Through measurement of the deflection of a test beam, the load capacity is estimated as 352.97 µN. This MLM has dimensions of 5 × 5 mm2 and can be applied in a micro assembling system to lift/drop micro samples or in micro transportation systems, etc.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haiwei Lu, Zhu Jianguo, Lin Zhiwei, Guo Youguang (2009) An inchworm mobile robot using electromagnetic linear actuator. Mechatronics 19:1116–1125
Hwang IH, Lee YG, Lee JH (2006) A micromachined friction meter for silicon sidewalls with consideration of contact surface shape. J Micromech Microeng 16:2475–2481
Kolesar et al (2004) Precision bi-directional motion of a linear mechanical shuttle with an electrothermal microengine. Thin Solid Films 469–470:450–454
Kurosawa MK et al (2003) Elastic friction drive of surface acoustic wave motor. Ultrasonics 41:271–275
Maloney J, Schreiber D, DeVoe D (2004) Large-force electrothermal linear micromotors. J Micromech Microeng 14:226–234
Morita T, Murakami H, Yokose T, Hosaka H (2012) A miniaturized resonant-type smooth impact drive mechanism actuator. Sens Actuators A 178:188–192
Pham PH et al (2007) Micro transportation system (MTS) with large movement of containers driven by electrostatic comb-drive actuators. J Micromech Microeng 17(10):2125–2131
Pham PH, Dang LB, Vu HN (2010) Micro robot system with moving micro-car driven by electrostatic comb-drive actuators. Microsyst Technol 16:505–510 No. 4
Pham PH, Dao DV, Dang LB, Sugiyama S (2012) Single mask, simple structure micro rotational motor driven by electrostatic comb-drive actuators. J Micromech Microeng 22:7 No. 1
Sacks E, Barnes SM (2001) Computer-aided kinematic design of a torsional ratcheting actuator. In: Proceeding of the fourth international conference on modeling and simulation of microsystems. Nara Sciences and Technology Institute, Hilton Head, SC
Sarajlic E et al (2009) An electrostatic 3-phase linear stepper motor fabricated by vertical trench isolation technology. J Micromech Microeng 19:7
Shay B, Hubbard T, Kujath M (2008) Linear frictional micro-conveyors. Sens Actuators A 148:290–298
Shutov MV et al (2004) Electrostatic inchworm microsystem with long range translation. Sens Actuators A 114:379–386
Shutov MV et al (2005) A microfabricated electromagnetic linear synchronous motor. Sens Actuators A 121:566–575
Tanner DM et al. (2001) Reliability of a MEMS torsional ratcheting actuator. In: IEEE—39th Annual International Reliability Physics Symposium, Orlando. IEEE, pp 81–90. doi:10.1109/RELPHY.2001.922886
Tas NR et al (1997) The shuffle motor: a high force, high precision linear electrostatic stepper motor. Solid State Sens Actuators TRANSDUCERS 2:330–336
Yeh R, Hollar S, Pister K (2002) Single mask, large force, and large displacement electrostatic linear inchworm motors. J Microelectromech Syst 11(4):330–336
Acknowledgments
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under Grant Number “107.01-2013.07”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, P.H., Nguyen, K.T. & Dang, L.B. Design and performance of a high loading electrostatic micro linear motor. Microsyst Technol 21, 2469–2474 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2392-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2392-4