Abstract
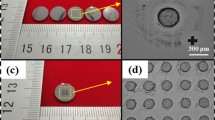
In order to manufacture high fill factor microlens array in batches, this paper researches into gapless hexagonal microlens array manufactured through hot embossing, adopts FEM to calculate the stress of PMMA in hot embossing process of gapless hexagonal high fill factor microlens array, and analyzes the influencing factors of adhesion strength between the die and PMMA. The analysis result reveals that with the decrease of hot demolding temperature, the normal stress of PMMA drops gradually (the minimum stress exists) and that adhesion stress between the mold and PMMA will decline with the decrease of normal stress in PMMA, and that when demolding temperature drops to 20 °C, the height fidelity of microlens arrays reaches 94.7 %, which eliminates the defects in embossing and forming on a large scale.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck M, Graczyk M, Maximov I et al (2002) Improving stamps for 10 nm level wafer scale nanoimprint lithography. Microelectron Eng 61–62:441–448
Chou SY, Krauss PR, Renstrom PJ (1995) Imprint of Sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers. Appl Phys Lett 67(21):3114–3116
Dengfeng K, Xiaoliang Z, Min G et al (2009) Hexagonal microlens array fabricated by direct laser writing and inductively coupled plasma etching on organic light emitting devices to enhance the outcoupling efficiency. Appl Opt 48(5):974–978
Dirckx ME, Hardt DE (2011) Analysis and characterization of demolding of hot embossed polymer microstructures. J Micromec Microeng 21(8):085024
Feng C, Hewei L, Qing Y et al (2010) Maskless fabrication of concave microlens arrays on silica glasses by a femtosecond-laser-enhanced local wet etching method. Opt Expr 18(19):20334–20343
Gordon NT, Jones CL, Purdy DJ (1991) Application of microlenses to infrared detector arrays. Infrared Phys 31(6):599–604
Gun-Young J, Zhiyong L, Wei W et al (2005) Vapor-phase self-assembled monolayer for improved mold release in nanoimprint lithography. Langmuir 21(4):1158–1161
Haochen M (2005) The research on surface effect and size effect of adhesion in MEMS (micro electro mechanical system). Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang
Hewei L, Chen F, Yang Q et al (2012) Fabrication of bioinspired omnidirectional and gapless microlens array for wide field-of-view detections. Appl Phys Lett 100(13):133701–133703
Kim NW, Kim KW, Sin HC (2008) Finite element analysis of low temperature thermal nanoimprint lithography using a viscoelastic model. Microelectron Eng 85(9):1858–1865
Lan S, Lee HJ, Lee SH et al (2009) Experimental and numerical study on the viscoelastic property of polycarbonate near glass transition temperature for micro thermal imprint process. Mater Des 30(9):3879–3884
Liu H, Chen F, Yang Q et al (2012) Facile and flexible fabrication of gapless microlens arrays using a femtosecond laser microfabrication and replication process. In: Proceeding SPIE8243, laser applications in microelectronic and optoelectronic manufacturing, vol 1. San Francisco, pp 2430–2436
Maokuo W, Su IL (2004) Method to evaluate the enhancement of luminance efficiency in planar OLED light emitting devices for microlens array. Opt Expr 12(23):5777–5782
Mirkhalaf M, Tor SB, Murukeshan VM et al (2010) Optimization of compression molding of stand-alone microlenses: simulation and experimental results. Polym Eng Sci 50(11):2216–2228
Pan CT, Su CH (2007) Fabrication of gapless triangular micro-lens array. Sens Actuators A Phys 134(2):631–640
Shuai C, Duan J, Zhong J (2006) Novel manufacturing method of optical fiber coupler. J Cent South Univ Technol 13(3):242–246
Stevens R, Miyashita T (2010) Review of standards for microlenses and microlens arrays. Imaging Sci J 58(4):202–212
Tao W, Yue Y, Lei L (2013) Study on rheological properties of transparent plastic melt. Eng Plast Appl 41(4):71–74
Worgull M, Heckele M, Hetu JF et al (2006) Modeling and optimization of the hot embossing process for micro- and nanocomponent fabrication. J Microlithogr Microfabr Microsyst 5(1):1005–1013
Yuhua G, Gang L, Xuelin Z et al (2007) Analysis of the demolding forces during hot embossing. Microsyst Technol 5(13):411–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., Kuang, X. et al. Research on hot embossing process of high fill factor microlens array. Microsyst Technol 21, 2109–2114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2352-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2352-z