Abstract
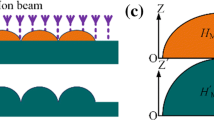
An asymmetric microlens with a given inclination angle was fabricated. Two circular pattern masks with different diameters were used to form a metal pattern and photoresist column on the substrate using the photolithography process. The metal pattern on the substrate was used to control the asymmetric microlens profile using thermal reflow. A lift-off process was applied to the first lithography to precisely define the metal pattern. A second lithography used deviation counterpoint exposure to pattern the photoresist column. The photoresist column was converted into a rubbery state when its temperature was increased to its glass transition temperature (Tg) during the thermal reflow. The asymmetric microlens structure was formed by shifting the arc vertex of the microlens toward one direction taking into account the fact that the copper coating surface has superior hydrophobicity to the silicon substrate surface. A 55° asymmetric microlens array was fabricated in this research by properly controlling the copper pattern size and the offset of two centers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang SI, Yoon JB (2004) Shape-controlled high fill factor microlens arrays fabricated by a 3D diffuser lithography and plastic replication method. Opt Express 12:6366–6371
Duparre J, Dannberg P, Schreiber P, Brauer A, Tunnermann A (2004) Artificial apposition compound eye fabricated by micro-optics technology. Appl Optics 43:4303–4310
Duparre J, Dannberg P, Schreiber P, Brauer A, Tunnermann A (2005) Thin compound-eye camera. Appl Optics 44:2949–2956
Hartmann DM, Kibar O, Esener SC (2000) Characterization of a polymer microlens fabricated by use of the hydrophobic effect. Opt Lett 25:975–977
Kang JM, Wei MK, Lin HY, Lee JH, HY Lin, Tsai JH, Wu TC (2010) Shape-controlled microlens arrays fabricated by diffuser lithography. Microelectron Eng 87:1420–1423
Lin CP, Yang H, Chao CK (2003) A new microlens array fabrication method using UV proximity printing. J Micromech Microeng 13:748–757
Pan CT, Su CH (2007) Fabrication of gapless triangular microlens array. Sens Actuators A 134:631–640
Schilling A, Merz R, Ossmann C, Herzig HP (2000) Surface profiles of reflow microlenses under the influence of surface tension and gravity. Opt Eng 39:2171–2176
Tanida J, Kumagai T, Yamada K, Miyatake S, Ishida K, Morimoto T, Kondou N, Miyazaki D, Ichioka Y (2000) Thin observation module by bound optics (TOMBO): concept and experimental verification. Appl Optics 40:1806–1813
Yang H, Pan CT, Chou MC (2001) Ultra-fine machining tool/molds by LIGA technology. J Micromech Microeng 11:94–99
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Council (series no. NSC98-2221-E-005-058-MY3) and Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology in Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, TY., Hung, CH., Chang, PS. et al. Asymmetric focusing microlens array fabricated using off-axis lithography. Microsyst Technol 19, 861–869 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1745-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1745-8