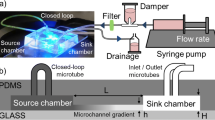
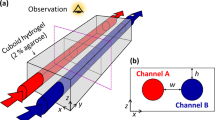
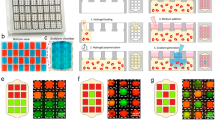
Abstract
Spatial and temporal in vivo variations of biochemical cues affect the cellular behavior and responses in live systems. To study the biological phenomena, an appropriate environment that could facilitate generation of gradients within extracellular spaces is highly desirable. Microfluidic platforms have been widely used in cellular biology research because of their ability to mimic in vivo environments. This paper discusses the design and simulation of a microfluidic device to generate predictable profiles of various stable gradient concentrations in a hydrogel-filled chamber. Simulations have been carried out by using Coventorware for steady state, transient mode and overlapping gradients to fine-tune the design parameters. The design will have applications in three-dimensional biological cell cultures and studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhyankar VV, Toepke MW, Cortesio CL, Lokuta MA, Huttenlocher A, Beebe DJ (2008) A platform for assessing chemotactic migration within a spatiotemporally defined 3D microenvironment. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 8:1507–1515
Ashe HL, Briscoe J (2006) The interpretation of morphogen gradients. Development 133:385–394
Bhattacharjee N, Li N, Keenan TM, Folch A (2010) A neuron-benign microfluidic gradient generator for studying the response of mammalian neurons towards axon guidance factors. Integr Biol 2:669–679
Cimetta E, Cannizzaro C, James R, Biechele T, Moon RT, Elvassore N, Vunjak-Novakovic G (2010) Microfluidic device generating stable concentration gradients for long term cell culture: application to Wnt3a regulation of β-catenin signaling. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 10:3277–3283
Cooksey GA, Sip CG, Folch A (2009) A multi-purpose microfluidic perfusion system with combinatorial choice of inputs, mixtures, gradient patterns, and flow rates. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 9:417–426
El-Ali J, Sorger PK, Jensen KF (2006) Cells on chips. Nature 442:403–411
Feng X, Du W, Luo Q, Liu BF (2009) Microfluidic chip: next-generation platform for systems biology. Anal Chim Acta 650:83–97
Gurdon JB, Bourillot PY (2001) Morphogen gradient interpretation. Nature 413:797–803
Haessler U, Kalinin Y, Swartz MA, Wu M (2009) An agarose-based microfluidic platform with a gradient buffer for 3D chemotaxis studies. Biomed Microdevices 11:827–835
Jedrych E, Flis S, Sofinska K, Jastrzebski Z, Chudy M, Dybko A, Brzozka Z (2011) Evaluation of cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil on human carcinoma cells in microfluidic system. Sensors Actuators, B: Chemi 160:1544–1551
Kartalov EP, Scherer A, Quake SR, Taylor CR, Anderson WF (2007) Experimentally validated quantitative linear model for the device physics of elastomeric microfluidic valves. J Appl Phy 101:064505-1–4
Keenan TM, Folch A (2007) Biomolecular gradients in cell culture systems. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 8:34–57
Kim M, Kim T (2010) Diffusion-based and long-range concentration gradients of multiple chemicals for bacterial chemotaxis assays. Anal Chem 82:9401–9409
Kim D, Lokuta MA, Huttenlocher A, Beebe DJ (2009a) Selective and tunable gradient device for cell culture and chemotaxis study. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 9:1797–1800
Kim T, Pinelis M, Maharbiz MM (2009b) Generating steep, shear-free gradients of small molecules for cell culture. Biomed Microdevices 11:65–73
Kim S, Kim HJ, Jeon NL (2010) Biological applications of microfluidic gradient devices. Integr Biol 2:584–603
Kothapalli CR, Van Veen E, De Valence S, Chung S, Zervantonakis IK, Gertler FB, Kamm RD (2011) A high-throughput microfluidic assay to study neurite response to growth factor gradients. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 11:497–507
Lebrun L, Junter GA (1993) Diffusion of sucrose and dextran through agar gel membranes. Enzyme Microbial Technol 15:1057–1062
Li GN, Liu J, Hoffman-Kim D (2008) Multi-molecular gradients of permissive and inhibitory cues direct neurite outgrowth. Ann Biomed Eng 36:889–904
Melin J, Quake SR (2007) Microfluidic Large-Scale Integration: the Evolution of Design Rules for Biological Automation. Ann Biophy Biomol Struct 36:213–231
Millet LJ, Stewart ME, Nuzzo RG, Gillette MU (2010) Guiding neuron development with planar surface gradients of substrate cues deposited using microfluidic devices. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 10:1525–1535
Mosadegh B, Huango C, Park JW, Shin HS, Chung BG, Hwang SK, Lee KH, Kim HJ, Brody J, Jeon NL (2007) Generation of stable complex gradients across two-dimensional surfaces and three-dimensional gels. Langmuir 23:10910–10912
Park JY, Yoo SJ, Hwang CM, Lee SH (2009a) Simultaneous generation of chemical concentration and mechanical shear stress gradients using microfluidic osmotic flow comparable to interstitial flow. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 9:2194–2202
Park JY, Kim SK, Woo DH, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Lee SH (2009b) Differentiation of neural progenitor cells in a microfluidic chip-generated cytokine gradient. Stem Cells 27:2646–2654
Ruan J, Wang L, Xu M, Cui D, Zhou X, Liu D (2009) Fabrication of a microfluidic chip containing dam, weirs and gradient generator for studying cellular response to chemical modulation. Mater Sci Eng C 29:674–679
Saadi W, Rhee SW, Lin F, Vahidi B, Chung BG, Jeon NL (2007) Generation of stable concentration gradients in 2D and 3D environments using a microfluidic ladder chamber. Biomed Microdevices 9:627–635
Shin Y, Jeon JS, Han S, Jung GS, Shin S, Lee SH, Sudo R, Kamm RD, Chung S (2011) In vitro 3D collective sprouting angiogenesis under orchestrated ANG-1 and VEGF gradients. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 11:2175–2181
Sip CG, Bhattacharjee N, Folch A (2011) A modular cell culture device for generating arrays of gradients using stacked microfluidic flows. Biomicrofluidics 5:022210-1–9
Squires TM, Quake SR (2005) Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev Mod Phys 77:977–1026
Steffen Hardt FS (2007) Microfluidic technologies for miniaturized analysis systems. Springer, New York
Stone HA, Kim S (2001) Microfluidics: basic issues, applications, and challenges. AIChE J 47:1250–1254
Tan DCW, Yung LYL, Roy P (2010) Controlled microscale diffusion gradients in quiescent extracellular fluid. Biomed Microdevices 12:523–532
Tehrani-Rokh M, Kouzani AZ, Kanwar JR (2012) Gradient Generating Microfluidic Devices for Cell Cultivation. Procedia Eng 29:1740–1744
Wang CJ, Li X, Lin B, Shim S, Ming GL, Levchenko A (2008a) A microfluidics-based turning assay reveals complex growth cone responses to integrated gradients of substrate-bound ECM molecules and diffusible guidance cues. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 8:227–237
Wang L, Liu D, Wang B, Sun J, Li L (2008b) Design of parallel microfluidic gradient-generating networks for studying cellular response to chemical stimuli. Front Chem China 3:384–390
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Wu H, Huang B, Zare RN (2006) Generation of complex, static solution gradients in microfluidic channels. J Am Chem Soc 128:4194–4195
Yang CG, Wu YF, Xu ZR, Wang JH (2011) A radial microfluidic concentration gradient generator with high-density channels for cell apoptosis assay. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 11:3305–3312
Young EWK, Simmons CA (2010) Macro-and microscale fluid flow systems for endothelial cell biology. Lab Chip Miniatur Chem Biol 10:143–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tehranirokh, M., Kouzani, A.Z., Francis, P.S. et al. Generating different profiles of gradient concentrations inside a gel-filled chamber: design and simulation. Microsyst Technol 19, 623–628 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1673-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-012-1673-z