Abstract
Purpose
The sedative effects of pregabalin during perioperative period have not been sufficiently characterized. The aim of this study was to verify the sedative effects of premedication with pregabalin on intravenous sedation (IVS) using propofol and also to assess the influences of this agent on circulation, respiration, and postanesthetic complications.
Methods
Ten healthy young volunteers underwent 1 h of IVS using propofol, three times per subject, on separate days (first time, no pregabalin; second time, pregabalin 100 mg; third time, pregabalin 200 mg). The target blood concentration (C T) of propofol was increased in a stepwise fashion based on the bispectral index (BIS) value. Ramsay’s sedation score (RSS) was determined at each propofol C T. Propofol C T was analyzed at each sedation level. Circulation and respiration during IVS and complications were also verified.
Results
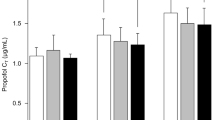
Propofol C T was reduced at BIS values of 60 and 70 in both premedicated groups (100 mg: p = 0.043 and 0.041; 200 mg: p = 0.004 and 0.016, respectively) and at a BIS value of 80 in the pregabalin 200 mg group (p < 0.001). Propofol C T was decreased at RSS 4–6 in the pregabalin 100 mg group (RSS 4: p = 0.047; RSS 5: p = 0.007; RSS 6: p = 0.014), and at RSS 3–6 in the pregabalin 200 mg group (RSS 3–5: p < 0.001; RSS 6: p = 0.002).
Conclusion
We conclude that oral premedication with pregabalin reduces the amount of propofol required to obtain an acceptable and adequate sedation level.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gajraj NM. Pregabalin for pain management. Pain Pract. 2005;5:95–102.
Moore RA, Straube S, Wiffen PJ, Derry S, McQuary HJ. Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;3:CD007076.
Yucel A, Ozturk E, Aydoan MS, Durmus M, Colak C, Ersoy MO. Effects of 2 different doses of pregabalin on morphine consumption and pain after abdominal hysterectomy: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2011;72:173–83.
Mathiesen O, Jørgensen DG, Hilsted KL, Trolle W, Stjernholm P, Christiansen H, Hjortsø NC, Dahl JB. Pregabalin and dexamethasone improves post-operative pain treatment after tonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55:297–305.
Peng PW, Li C, Farcas E, Haley A, Wong W, Bender J, Chung F. Use of low-dose pregabalin in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2010;105:155–61.
Bornemann-Cimenti H, Lederer AJ, Wejbora M, Michaeli K, Kern-Pirsch C, Archan S, Rumpold-Seitlinger G, Zigeuner R, Sandner-Kiesling A. Preoperative pregabalin administration significantly reduces postoperative opioid consumption and mechanical hyperalgesia after transperitoneal nephrectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:845–9.
Hill CM, Balkennohl M, Thomas DW, Walker R, Mathe H, Murray G. Pregabalin in patients with postoperative dental pain. Eur J Pain. 2001;5:119–24.
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K. A randomized controlled trial of perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain. 2008;134:106–12.
White PF, Tufanogullari B, Taylor J, Klein K. The effect of pregabalin on postoperative anxiety and sedation levels: a dose-ranging study. Anesth Analg. 2009;108:1140–5.
Ghai A, Gupta M, Rana N, Wadhera R. The effect of pregabalin and gabapentin on preoperative anxiety and sedation: a double blind study. Anaesth Pain Intensive Care. 2012;16:257–61.
Mishriky BM, Waldron NH, Habib AS. Impact of pregabalin on acute and persistent postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2014;114:10–31.
Moreau-Bussière F, Gaulin J, Gagnon V, Sansoucy Y, Médicis E. Preoperative pregabalin does not reduce propofol ED50: a randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2013;60:364–9.
Baidya DK, Agarwal A, Khanna P, Arora MK. Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011;27:307–14.
Bauer CS, Nieto-Rostro M, Rahman W, Tran-Van-Minh A, Ferron L, Douglas L, Kadurin I, Sri Ranjan Y, Fernandez-Alacid L, Millar NS, Dickenson AH, Lujan R, Dolphin AC. The increased trafficking of the calcium channel subunit α2δ-1 to presynaptic terminals in neuropathic pain is inhibited by the α2δ ligand pregabalin. J Neurosci. 2009;29:4076–88.
Fink K, Dooley DJ, Meder WP, Suman-Chauhan N, Duffy S, Clusmann H, Göthert M. Inhibition of neuronal Ca2+ influx by gabapentin and pregabalin in the human neocortex. Neuropharmacology. 2002;42:229–36.
Tanabe M, Takasu K, Takeuchi Y, Ono H. Pain relief by gabapentin and pregabalin via supraspinal mechanism after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86:3258–64.
Bee LA, Dickenson AH. Descending facilitation from the brainstem determines behavioural and neuronal hypersensitivity following nerve injury and efficacy of pregabalin. Pain. 2008;140:209–23.
Sills GJ. The mechanism of action of gabapentin and pregabalin. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006;6:108–13.
Ramsay MAE, Savege TM, Simpson BRJ, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J. 1974;2:656–9.
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML, MacKenzie TD, Ogedegbe O, Smith SC Jr, Svetkey LP, Taler SJ, Townsend RR, Wright JT Jr, Narva AS, Ortiz E. Evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311:507–20.
Taffe P, Sicard N, Pittet V, Pichard S, Burnand B. The occurrence of intra-operative hypotension varies between hospitals: observational analysis of more than 147,000 anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009;53:995–1005.
Ito S, Sugiyama H, Kitahara S, Ikemoto Y, Yokoyama T. Effects of propofol and pentobarbital on calcium concentration in presynaptic boutons on a rat hippocampal neuron. J Anesth. 2011;25:727–33.
Ito S, Karube N, Sugiyama H, Hirokawa J, Kitahara S, Yokoyama T. Effects of propofol on glutamate-induced calcium mobilization in presynaptic boutons of rat hippocampal neurons. Open J Anesthesiol. 2016;6:27–36.
Herring BE, McMillan K, Pike CM, Marks J, Fox AP, Xie Z. Etomidate and propofol inhibit the neurotransmitter release machinery at different sites. J Physiol. 2011;589:1103–15.
Xie Z, McMillan K, Pike CM, Cahill AL, Herring BE, Wang Q, Fox AP. Interaction of anesthetics with neurotransmitter release machinery proteins. J Neurophysiol. 2013;109:758–67.
Wakita M, Kotani N, Nonaka K, Shin M, Akaike N. Effects of propofol on GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in isolated hippocampal single nerve-synapse preparations. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718:63–73.
Bhawna R, Gupta K, Gupta PK, Agarwal S, Jain M, Chauhan H. Oral pregabalin premedication for attenuation of haemodynamic pressor response of airway instrumentation during general anaesthesia: a dose response study. Indian J Anaesth. 2012;56:49–54.
Gupta K, Bansal P, Gupta PK, Singh YP. Pregabalin premedication—a new treatment option for hemodynamic stability during general anesthesia: a prospective study. Anesth Essays Res. 2011;5:57–62.
Eipe N, Penning J. Postoperative depression associated with pregabalin: a case series and a preoperative decision algorithm. Pain Res Manag. 2011;16:353–6.
Panousis P, Heller AR, Burghardt M, Bley MJ, Koch T. The effects of electromyographic activity on the accuracy of the Narcotrend® monitor compared with the Bispectral Index during combined anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2007;62:868–74.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (24593058) and the Academic Enrichment Fund allotted to the Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Faculty of Dental Science, Kyushu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Karube, N., Ito, S., Sako, S. et al. Sedative effects of oral pregabalin premedication on intravenous sedation using propofol target-controlled infusion. J Anesth 31, 586–592 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2366-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2366-7