Abstract
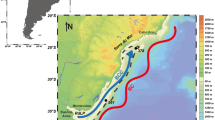
Four sediment cores were analysed in order to determine the sedimentary processes associated with the channel-ridge depositional system that characterise the George V Land continental margin on the Wilkes Land. The sedimentary record indicates that the WEGA channel was a dynamic turbiditic system up to M.I.S. 11. After this time, the channel became a lower-energy environment with sediments delivered to the channel through high-density bottom waters that we identify to be the high salinity shelf waters (HSSW) forming on the shelf area. The HSSW entrains the fine-grained sediments of the shelf area and deliver them to the continental rise. The biostratigraphy and facies of the sediments within the WEGA channel indicate that the HSSW down flow was active also during last glacial. The change from a turbiditic system to a low-energy bottom current system within the WEGA channel likely reflects a different ice-flow pattern, with ice-sheet reaching the continental shelf edge only within the ice trough (ice stream).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armand LK, Crosta X, Romero O, Pichon JJ (2005) The biogeography of major diatom taxa in Southern Ocean sediments: 1 Sea ice related species. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatl Paleoecol 223:93–126. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.02.015
Baines PG, Condie S (1998) Observations and modelling of Antarctic downslope flows: a review. Ocean, Ice and Atmosphere: interactions at the Antarctic Continental Margin. Antarct Res Ser 75:29–49
Barde MF (1981) Les Diatomées des sediments actuels et du Quaternaire supérieur de l’Atlantique nord-oriental. Interet hydrologique et climatique. Bull Inst Geologie Bassin Aquitaine 29:85–111
Barker PF, Camerlenghi A, Acton GD, Ramsay ATS (eds) (2002) In: Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, scientific results, 178 [CD-ROM]. Available from: Ocean Drilling Program, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77845–9547, USA
Bergamasco A, Defendi V, Del Negro P, Fonda Umani S (2003) Effects of the physical properties of water masses on microbial activity during an Ice Shelf Water overflow in the central Ross Sea. Antarct Sci 15(3):405–411. doi:10.1017/S0954102003001421
Berkman PA, Forman SL (1996) Pre-bomb radiocarbon and the reservoir correction for calcareous marine species in the Southern Ocean. Geophys Res Lett 23(4):363–366. doi:10.1029/96GL00151
Bianchi C, Gersonde R (2004) Climate evolution at the last deglaciation: the role of the Southern Ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 228(3–4):407–424. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.003
Bindoff NL, Rosenberg MA, Warner MJ (2000) On the circulation and water masses over the Antarctic continental slope and rise between 80 and 150°E. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 47:2299–2326. doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(00)00038-2
Bodén P (1991) Reproducibility in the random settling method for quantitative diatom analysis. Micropaleontology 37(3):313–319. doi:10.2307/1485893
Busetti M, Caburlotto A, Armand L, Damiani D, Giorgetti G, Lucchi RG, Quilty PG, Villa G (2003) Plio-Quaternary sedimentation on the Wilkes Land continental rise: preliminary results. In: Harris PT, Brancolini G, Bindoff N, De Santis L (eds) Recent investigations of the Mertz Polynya and George Vth Land Continental Margin, East Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research II, vol 50 (8–9), pp 1529–1562
Caburlotto A, De Santis L, Zanolla C, Camerlenghi A, Dix JK (2006) New insights into Quaternary glacial dynamic changes on the George V continental margin (East Antarctica). Quat Sci Rev 25:3029–3049. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.06.012
Cortese G, Gersonde R (2007) Morphometric variability in the diatom Fragilariopsis kerguelensis: Implications for Southern Ocean paleoceanography. Earth Planet Sci Lett 257(3–4):526–544. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.03.021
Cowan EA (2002) Identification of the glacial signal from the Antarctic Peninsula since 30 Ma at Site 1101 in a continental rise sediment drift. In: Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results CD-Rom
Crosta X, Pichon JJ, Labracherie M (1997) Distribution of Chaetoceros resting spores in modern peri-Antarctic sediments. Mar Micropaleontol 29:283–299. doi:10.1016/S0377-8398(96)00033-3
Crosta X, Romero O, Armand LK, Pichon JJ (2005) The biogeography of major diatom taxa in Southern Ocean sediments: 2 open ocean related species. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 223:66–92. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.03.028
De Santis L, Brancolini G, Donda F (2003) Seismo-stratigraphic analysis of the Wilkes Land continental margin (East Antartica): influence of glacially driver processes on the Cenozoic deposition. In: Harris PT, Brancolini G, Bindoff N, De Santis L (eds) Recent investigations of the Mertz polynya and George Vth Land Continental Margin, East Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research II, vol 50 (8–9), pp 1563–1594
Domack EW (1982) Sedimentology of glacial and glacial marine deposits on the George V-Adelie continental shelf East Antarctica. Boreas 11(1):79–97
Domack EW (1988) Biogenic facies in the Antarctic glacimarine environment: basis for a polar Glacimarine summary. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 63:357–372. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(88)90105-8
Donda F, Brancolini G, De Santis L, Trincardi F (2003) Seismic facies and sedimentary processes on the continental rise off Wilkes Land (East Antartica): evidence of bottom current activity. In: Harris PT, Brancolini G, Bindoff N, De Santis L (eds) Recent investigations of the Mertz Polynya and George Vth Land Continental Margin, East Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research II, vol 50 (8–9), pp 1509–1527
Dunbar R, Anderson JB, Domack EW, Jacobs SS (1985) Oceanographic influences on sedimentation along the Antarctic Continental Shelf. In: Jacobs SS, Stanley S (eds) Oceanology of the Antarctic Continental Shelf. Antarctic Research Series 43, pp 291–312
Eittreim SL, Smith GL (1987) Seismic sequences and their distribution on the Wilkes Land margin. In: Eittreim SL, Hampton MA (eds) The Antarctic continental margin: Geology and Geophysics of Offshore Wilkes Land. Circum Pacific Council for Energy and Mineral Resources. Earth Sciences Series 5A, pp 15–43
Eittreim SL, Gorgon AL, Ewing M, Thorndike EM, Bruchhausen PM (1971) The nepheloid layer and observed bottom currents in the Indian-Pacific Antarctic sea. In: Gordon AL (ed) Studies in physical oceanography: a tribute to George Wüst on his 80th birthday. Gordon and Breach, New York, pp 19–35
Eittreim SL, Cooper AK, Wannesson J (1995) Seismic stratigraphic evidence of icesheet advances on the Wilkes Land margin of Antarctica. Sediment Geol 96:131–156. doi:10.1016/0037-0738(94)00130-M
EPICA Community Members (2004) Eight glacials cycles from an Antarctic ice core. Nature 429:623–628
Escutia C, Eittreim SL, Cooper AK (1997) Cenozoic glaciomarine sequences on the Wilkes Land continental rise, Antarctica. In: Proceedings of international symposium on Antarctic earth sciences VIII, pp 791–795
Escutia C, Eittreim SL, Cooper AK, Nelson CH (2000) Morphology and acoustic character of the Antarctic Wilkes Land turbidite system: ice-sheet sourced versus river-sourced fans. J Sediment Res 70(1):84–93
Escutia C, Warnke D, Acton GD, Barcena A, Burckle L, Canals M, Frazee CS (2003) Sediment distribution and sedimentary processes across the Antarctic Wilkes Land margin during the Quaternary. In: Harris PT, Brancolini G, Bindoff N, De Santis L (eds) Recent investigations of the Mertz Polynya and George Vth Land Continental Margin, East Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research II, vol 50 (8–9), pp 1481–1508
Folk RL, Ward WC (1978) Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27:3–26
Fryxell GA, Prasad AKSK (1990) Eucampia antarctica var. recta (Mangin) stat. Nov. (Bacillariophyceae): life stages at the Weddell Sea ice edge. Phycologia 29(1):27–38
Gordon AL, Tchernia P (1972) Waters of the continental margin of the Adelie Coast, Antarctica. Antarctic Oceanology. II The Australian-New Zealand Sector. Antarct Res Ser 19:59–70
Grützner J, Rebesco M, Cooper AK, Forsberg CF, Kryc KA, Wefer G (2003) Evidence for orbitally controlled size variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet during the late Miocene. Geology 31(9):777–780
Guyodo Y, Valet J-P (1999) Global changes in intensity of the Earth’s magnetic field during the past 800 ky. Nature (Lond) 399:249–252
Hampton MA, Eittreim SL, Richmond BM (1987) Geology of sediment cores from the George V continental margin. In: Eittreim SL, Hampton MA (eds) The Antarctic continental margin: Geology and Geophysics of offshore Wilkes Land. Circum Pacific Council for Energy and Mineral Resources Earth Sciences Series 5A, pp 75–88
Harris PT, O’Brien P (1998) Bottom currents, sedimentation and ice-sheet retreat facies succession on the Mac Robertson shelf, East Antarctica. Mar Geol 151:47–72
Harris PT, Brancolini G, Armand L, Busetti M, Beaman RJ, Giorgetti G, Presti M, Trincardi F (2001) Continental shelf drift deposit indicates non-steady state Antarctic bottom water production in the Holocene. Mar Geol 179:1–8
Hayes DE, Frakes LA et al (1975) Initial reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project 28. US Government Printing Office
Imbrie J, Hays JD, McIntyre A, Mix AC, Morley JJ, Pisias NG, Prell WL, Shackleton NJ (1984) The orbital theory of Pleistocene climate: support from a revised chronology of the marine d18O record. In: Berger A, Imbrie J, Hays J, Kukla GJ, Saltzman E (eds) Milankovitch and cmate. Reidel, Boston, pp 269–305
Ivanov VV, Shapiro GI, Huthnance JM, Aleynik DL, Golovin PN (2003) Cascades of dense water around the World Ocean. Prog Oceanogr 60(1):47–98
Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Cattani O, Dreyfus G, Falourd S, Hoffmann G, Minster B, Nouet J, Barnola JM, Chappellaz J, Fischer H, Gallet JC, Johnsen S, Leuenberger M, Loulergue L, Luethi D, Oerter H, Parrenin F, Raisbeck G, Raynaud D, Schilt A, Schwander J, Selmo E, Souchez R, Spahni R, Stauffer B, Steffensen JP, Stenni B, Stocker TF, Tison JL, Werner M, Wolff EW (2007) Orbital and Millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800,000 years. Science 317:793–796
Kuvaas B, Leitchenkov G (1992) Glaciomarine turbidite and current controlled deposits Prydz Bay, Antarctica. Mar Geol 108:365–381
Lambert F, Delmonte B, Petit JR, Bigler M, Kaufmann PR, Ruth U, Hutterli M, Steffensen JP, Maggi V (2007) New insights on Antarctic Quaternary climate from high-resolution aeolian dust data from the EPICA—Dome C ice core. Geophysical Research Abstracts, vol 9, 07464
Leventer A, Domack EW, Ishman SE, Brachfeld S, McClennen CE, Manley P (1996) Productivity cycles of 200–300 years in the Antarctic Peninsula region: understanding linkages among the sun, atmosphere, oceans, sea ice and biota. GSA Bull 108(12):1626–1644
Lucchi RG, Rebesco M (2007) Glacial contourites on the Antarctic Peninsula margin: insight for paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic conditions. In: Viana AR, Rebesco M (eds) Economic and paleoceanographic significance of contourite deposits, vol 276. Geological Society, London, pp 111–127 (special publications)
Lucchi RG, Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A, Busetti M, Tomadin L, Villa G, Persico D, Morigi C, Bonci MC, Giorgetti G (2002) Mid-late Pleistocene glacimarine sedimentary processes of a high latitude, deep-sea sediment drift (Antarctic Peninsula Pacific margin). Mar Geol 189:343–370
Macrì P, Sagnotti L, Dinares-Turrel J, Caburlotto A (2005) A composite record of Late Pleistocene relative geomagnetic paleointensity from the Wilkes Land Basin (Antarctica) Physics of the Earth and Planetary interiors, vol 151, pp 223–242
Macrì P, Sagnotti L, Lucchi R, Rebesco M (2006) A stacked record of relative geomagnetic paleointensity for the last 270 ka from sedimentary sequences on the western continental rise of the Antarctic Peninsula. Earth Planet Sci Lett 252:162–179
McGinnis JP, Hayes DE (1995) The roles of down-slope and along-slope depositional processes: southern Antarctic Peninsula margin. In: Cooper AK, Barker PG, Brancolini G (eds) Geology and seismic stratigraphy of the Antarctic margin. Antarctic Research Series 68, pp 141–156
McGinnis JP, Hayes DE, Driscoll NW (1997) Sedimentary processes across the continental rise of the southern Antarctic Peninsula. Mar Geol 141:91–109
Michels KH, Rogenhagen J, Kuhn G (2001) Recognition of contour-current influence in mixed contourite-turbidite sequences of the western Weddell Sea, Antartica. Mar Geophys Res 22:465–485
Michels KH, kuhn G, Hillenbrand CD, Diekmann B, Futterer DK, Grobe H, Uenzelmann-Neben G (2002) The southern Weddell sea: combined contourite-turbidite sedimentation at the southeastern margin of the Weddell Gyre. In: Stow DAV, Pudsey CJ, Howe JA, Faugeres J-C, Viana AR (eds) Deep-water contourite systems: modern drifts and ancient series, Seismic and sedimentary characteristics, vol 22. Geological Society, London, pp 305–325
O’Brien PE, Cooper AK, Florindo F, Handwerger DA, Lavelle M, Passchier JJ, Pospichal PG, Quilty PG, Richter C, Theissen KM, Whitehead JM (2004) Prydz Channel fan and the History of Extreme Ice Advances in Prydz Bay. In: Cooper AK, O’Brien PE, Richter C (eds) Proceeding ODP, scientific results, 188, [CD-ROM]. Available from: Ocean Drilling Program, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77845–9547, USA
Payne RR, Conolly JR (1972) Turbidite sedimentation off the Antarctic continent. Antarct Res Ser 19:349–364
Presti M, De Santis L, Busetti M, Harris PT (2003) Late Pleistocene and Holocene sedimentation on the Gorge V Continental Shelf, East Antarctica. In: Harris PT, Brancolini G, Bindoff N, De Santis L (eds) Recent investigations of the Mertz Polynya and George Vth Land Continental Margin, East Antarctica. Deep-Sea Research II 50 (8–9), pp 1441–1461
Presti M, De Santis L, Brancolini G, Harris PT (2005) Continental shelf record of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet evolution: seismo-stratigraphic evidence from the George V Basin. Quat Sci Rev 24(10–11):1223–1241
Pudsey CJ (2000a) Neogene record of Antarctic Peninsula glaciations in continental rise sediments: ODP leg 178, site 1095. In: Barker PF, Camerlenghi A, Acton GD, Ramsay ATS (eds) Proceedings of ODP, science results, vol 178, pp 1–25
Pudsey CJ (2000b) Sedimentation on the continental rise west of the Antarctic Peninsula over the last three glacial cycles. Mar Geol 167:313–338
Rebesco M, Larter RD, Camerlenghi A, Barker PF (1996) Giant sediment drifts on the Continental Rise West of the Antarctic Peninsula. Geol Mar Lett 16:65–75
Rebesco M, Larter RD, Barker PF, Camerlenghi A, Vanneste LE (1997) History of Sedimentation on the Continental Rise West of the Antarctic Peninsula. In: Cooper AK and Barker PF (eds) Geology and seismic stratigraphy of the Antarctic Margin, Part 2 AGU. Antarctic Research Series 71, pp 29–49
Rintoul SR (1998) On the origin and influence of Adelie Land bottom water. Ocean, Ice and Atmosphere: Interactions at the Antarctic Continental Margin. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., pp 151–171
Rivaro P, Frache R, Bergamasco A, Hohmann R (2003) Dissolved oxygen, NO and PO as tracers for Ross Sea Ice Shelf Water overflow. Antarct Sci 15(3):399–404
Schrader HJ, Gersonde R (1978) Diatoms and Silicoflagellates. In: Zachariasse WJ et al (eds) Micropaleontological counting methods and techniques-an exercise on an eight meters section of the Lower Pliocene of Capo Rossello, Sicily, vol 17. Micropaleontological Bulletins, Utrecht, pp 129–176
Shapiro GI, Huthnance JM, Ivanov VV (2003) Dense water cascading off the continental shelf. J Geophys Res Oceans 108 (C12): art. no. 3390
Swan ARH, Sandilands M (1995) Introduction to geological data analysis. Blackwell, London, 446 p
Tanahashi M, Eittreim SL, Wannesson J (1994) Seismic stratigraphic sequences of the Wilkes Land margin. Terra Antarct 1(2):391–393
Zielinski U, Bianchi C, Gersonde R, Kunz-Pirrung M (2002) Last occurrence datums of the diatoms Rouxia leventerae and Rouxia constricta: indicators for marine isotope stages 6 and 8 in Southern Ocean sediments. Mar Micropaleontol 46:127–137
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Captain and crew of the R.V. Tangaroa for their skilful support during the WEGA 2000 cruise. We thank G. Kuhn, M. Weber and R. Stein for detailed review that greatly improved the manuscript. This work was funded by the Programma Nazionale delle Ricerche in Antartide (PNRA) under the WEGA Project. The first author benefits from an OGS doctoral fellowship in Polar Science at the University of Siena (Italy). The grain size analysis has been made at the “Laboratorio Antartide” at the Department of Geological, environmental and Marine Sciences of the University of Trieste (Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caburlotto, A., Lucchi, R.G., De Santis, L. et al. Sedimentary processes on the Wilkes Land continental rise reflect changes in glacial dynamic and bottom water flow. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 99, 909–926 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-009-0422-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-009-0422-8