Abstract
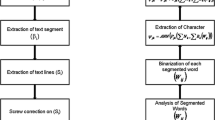
In the Indian subcontinent, a number of languages are in use, and an automatic recognition of printed and handwritten scripts facilitates number of applications such as image document sorting and penetrating online libraries of image documents. This framework proposed a bilingual (English and Hindi) character-spotting framework based on feedforward neural network which works on corpus of bilingual handwritten offline documents. The proposed Pixel Plot and Trace and Re-plot and Re-trace (PPTRPRT) framework traced the actual text region of the offline handwritten bilingual scripts and lead the process of line segmentation along with skew and de-skew operations. The findings of the iterations were adopted in pixel-space-based word segmentation, which were further used in character segmentation. Moreover, PPTRPRT performs normalization operation to incorporate all pen-breadth deviations and inscription slant. The proposed framework was state of the art, reflected clearly from the findings of the framework. The proposed framework is proficient to character segmentation and provides accuracy up to 99.78 %.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pal U, Roy RK, Roy K, Kimura F (2009) Indian multi-script full pin-code string recognition for postal automation. In: 10th International conference on document analysis and recognition, 2009, ICDAR ‘09, pp 456–460, 26–29 July 2009. ISSN 1520-5363. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2009.171
Pal U, Roy RK, Roy K, Kimura F (2012) Multi-lingual city name recognition for Indian postal automation. In: 2012 International conference on frontiers in handwriting recognition (ICFHR), pp 169–173, 18–20 Sep 2012. ISBN: 978-1-4673-2262-1. doi:10.1109/ICFHR.2012.238
Pal S, Alireza A, Pal U, Blumenstein M (2012) Multi-script off-line signature identification. In: 12th International conference on hybrid intelligent systems (HIS), pp 236–240, 4–7 Dec 2012. ISBN 978-1-4673-5114-0. doi:10.1109/HIS.2012.6421340
Wshah S, Kumar G, Govindaraju V (2012) Multilingual word spotting in offline handwritten documents. In: 21st International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 310–313, 11–15 Nov 2012. INSPEC Accession Number: 13324552, ISSN 1051-4651
Chaudhuri BB, Bera S (2009). Handwritten text line identification in Indian scripts. In: 10th International conference on document analysis and recognition. ICDAR ‘09, pp 636–640, 26–29 July 2009. ISSN 1520-5363. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2009.69
Wshah S, Kumar G, Govindaraju V (2012) Script independent word spotting in offline handwritten documents based on hidden Markov models. In: International conference on frontiers in handwriting recognition (ICFHR), pp 14–19, 18–20 Sep 2012. ISSN 978-1-4673-2262-1. doi:10.1109/ICFHR.2012.264
Natarajan P, Shirin S, Prasad R, MacRostie E, Subramanian K (2006) Multi-lingual offline handwriting recognition using hidden Markov models: a script-independent approach. In: Book title Arabic and Chinese handwriting recognition, pp 231–250, 27–28, Sep 2006. ISBN 978-3-540-78198-1. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-78199-8_14
Rajput GG, Anita HB (2012) Handwritten script recognition using DCT, Gabor filter and wavelet features at line level. In: Book title: soft computing techniques in vision science, pp 33–43. ISBN 978-3-642-25506-9. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-25507-6_4
Pal U, Sharma N, Wakabayashi T, Kimura F (2007). Handwritten numeral recognition of six popular Indian scripts. In: Ninth international conference on document analysis and recognition, 2007. ICDAR 2007, pp 749–753, 23–26 Sept 2007. ISBN 978-0-7695-2822-9. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2007.4377015
Pal U, Chaudhuri BB (1997) Automatic separation of words in multi-lingual multi-script Indian documents. In: Proceedings of the fourth international conference on document analysis and recognition, pp 576–579, 18–20 Aug 1997. ISBN 0-8186-7898-4. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.1997.620567
Chaudhuri BB, Bera S (2009). Handwritten text line identification in Indian scripts. In: 10th International conference on document analysis and recognition, 2009. ICDAR ‘09, pp 636–640, 26–29 July 2009. ISBN 978-1-4244-4500-4. INSPEC Accession Number: 10904634
Jayadevan R, Pal U, Kimura F (2010) Recognition of words from legal amounts of Indian bank cheques. In: International conference on frontiers in handwriting recognition (ICFHR), pp 166–171, 16–18 Nov 2010. ISBN 978-1-4244-8353-2. doi:10.1109/ICFHR.2010.33
Pal U, Roy RK, Kimura F (2010) Bangla and english city name recognition for Indian postal automation. In: 20th International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 1985–1988, 23–26 Aug 2010. ISBN 978-1-4244-7542-1. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.489
Stamatopoulos N, Gatos B, Louloudis G, Pal U (2013) ICDAR 2013 handwriting segmentation contest. In: 12th International conference on document analysis and recognition (ICDAR), pp 1402–1406, 25–28 Aug 2013. ISSN 1520-5363. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2013.283
Wu X, Tang Y, Bu W (2014) Offline text-independent writer identification based on scale invariant feature transform. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics and Secur 526–536. ISSN 1556-6013. doi:10.1109/TIFS.2014.2301274
Pal S, Pal U, Blumenstein M (2012) Off-line english and Chinese signature identification using foreground and background features. In: The 2012 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN), pp 1–7, 10–15 June 2012. ISBN 978-1-4673-1488-6. doi:10.1109/IJCNN.2012.6252613
Ryu J, Koo HI, Cho NI (2015) Word segmentation method for handwritten documents based on structured learning. IEEE Trans Signal Process Lett 22(8):1161–1165
Dhaka VP, Sharma MK (2015) An efficient segmentation technique for Devanagari offline handwritten scripts using the feedforward neural network. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-1844-9
Dhaka VP, Sharma MK (2015) Classification of image using a genetic general neural decision tree. Int J Appl Pattern Recognit 2(1):76–95
Ryu J, Koo HI, Cho NI (2015) “Word segmentation method for handwritten documents based on structured learning”. IEEE Trans Signal Process Lett 1161–1165. doi:10.1109/LSP.2015.2389852
Li Y, Zheng Y, Doermann D (2008) “Script-independent text line segmentation in freestyle handwritten documents” l2(3) 1313–1329. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70792
Nagar R, Mitra SK (2015) Feature extraction based on stroke orientation estimation technique for handwritten numeral. Eighth Int Conf Adv Pattern Recognit (ICAPR) 2(3):1–6. doi:10.1109/ICAPR.2015.7050654
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M.K., Dhaka, V.P. Pixel plot and trace based segmentation method for bilingual handwritten scripts using feedforward neural network. Neural Comput & Applic 27, 1817–1829 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1972-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-1972-2