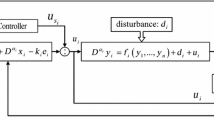
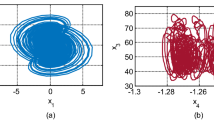
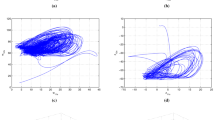
Abstract
This paper studies the Lorenz hyperchaos synchronization and its application to improve the security of communication systems. Two methods are proposed to synchronize the general forms of hyperchaotic systems, and their performance in secure communication application is verified. These methods use the radial basis function (RBF)-based neural controllers for this purpose. The first method uses a standard RBF neural controller. Particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is used to derive and optimize the parameters of the RBF controller. In the second method, with the aim of increasing the robustness of the RBF controller, an error integral term is added to the equations of RBF neural network. For this method, the coefficients of the error integral component and the parameters of RBF neural network are also derived and optimized via PSO algorithm. For better comparison, the proposed methods and an optimal PID controller optimized by PSO are applied to the Lorenz hyperchaotic system for secure communication. Simulation results show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed methods in both performance and robustness in comparison with the PID controller.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang T, Chua LO (1997) Impulsive stabilization for control and synchronization of chaotic systems: theory and application to secure communication. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 44:976–988
Chee CY, Xu D (2005) Secure digital communication using controlled projective synchronization of chaos. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:1063–1070
Bai EW, Lonngren KE, Uçar A (2005) Secure communication via multiple parameter modulation in a delayed chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:1071–1076
Li C, Liao X, Wong K (2005) Lag synchronization of hyperchaos with application to secure communications. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23:183–193
Hyun C-H, Kim J-H, Kim E, Park M (2006) Adaptive fuzzy observer based synchronization design and secure communications of chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 27:930–940
Chen HC, Chang JF, Yan JJ, Liao TL (2008) EP-based PID control design for chaotic synchronization with application in secure communication. Expert Syst Appl 34:1169–1177
Changchien S-K, Huang C-K, Nien H-H, Shieh H-W (2009) Synchronization of the chaotic secure communication system with output state delay. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39:1578–1587
Hyun C-H, Park C-W, Kim J-H, Park M (2009) Synchronization and secure communication of chaotic systems via robust adaptive high-gain fuzzy observer. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40:2200–2209
Chang W-D (2009) Digital secure communication via chaotic systems. Digit Signal Process 19:693–699
Wang XY, Wang M-J (2009) A chaotic secure communication scheme based on observer. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 14:1502–1508
Zhu F (2009) Observer-based synchronization of uncertain chaotic system and its application to secure communications. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40:2384–2391
Grzybowski JMV, Rafikov M, Balthazar JM (2009) Synchronization of the unified chaotic system and application in secure communication. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14:2793–2806
Lin J-S, Huang C-F, Liao T-L, Yan J-J (2010) Design and implementation of digital secure communication based on synchronized chaotic systems. Digit Signal Process 20:229–237
Wang F, Liu C (2007) Synchronization of unified chaotic system based on passive control. Physica D 225:55–60
Zhang H, Ma X (2004) Synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems with parameters perturbation via active control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 21:39–47
Lin J-S, Yan J-J (2009) Adaptive synchronization for two identical generalized Lorenz chaotic systems via a single controller. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 10:1151–1159
Salarieh H, Alasti A (2009) Adaptive synchronization of two chaotic systems with stochastic unknown parameters. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14:508–519
Yau H-T, Shieh C-S (2008) Chaos synchronization using fuzzy logic controller. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 9:1800–1810
Li S-Y, Ge Z-M (2011) Generalized synchronization of chaotic systems with different orders by fuzzy logic constant controller. Expert Syst Appl 38:2302–2310
Morgül Ö, Akgül M (2002) A switching synchronization scheme for a class of chaotic systems. Phys Lett A 301:241–249
Jiang GP, Chen GR, Tang WK (2003) A new criterion for chaos synchronization using linear state feedback control. Int J Bifurc Chaos 13:2343–2351
Lin D, Wang X, Nian F, Zhang Y (2010) Dynamic fuzzy neural networks modeling and adaptive backstepping tracking control of uncertain chaotic systems. Neurocomputing 73:2873–2881
Wang H, Han ZZ, Xie QY, Zhang W (2009) Finite-time chaos control via nonsingular terminal sliding mode control. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 14:2728–2733
Mou C, Jiang C-S, Bin J, Wu Q-X (2009) Sliding mode synchronization controller design with neural network for uncertain chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39:1856–1863
Pourmahmood M, Khanmohammadi S, Alizadeh G (2011) Synchronization of two different uncertain chaotic systems with unknown parameters using a robust adaptive sliding mode controller. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 16:2853–2868
Lin T-C, Chen M-C, Roopaei M (2011) Synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems based on adaptive type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24:39–49
Zheng Y, Chen G (2009) Fuzzy impulsive control of chaotic systems based on TS fuzzy model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 39:2002–2011
Yin C, Zhong S-M, Chen W-F (2011) Design PD controller for master-slave synchronization of chaotic Lur’e systems with sector and slope restricted nonlinearities. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 16:1632–1639
Coelho LS, Bernert DLA (2009) PID control design for chaotic synchronization using a Tribes optimization approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42:634–640
Coelho LS, Grebogi RB (2010) Chaotic synchronization using PID control combined with population based incremental learning algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 37:5347–5352
Coelho LS, Bernert DLA (2010) A modified ant colony optimization algorithm based on differential evolution for chaotic synchronization. Expert Syst Appl 37:4198–4203
Ren H, Liu D (2007) Synchronization of chaos using radial basis functions neural networks. J Syst Eng Electron 18:83–88
Hsu C-F, Chung C-M, Lin C-M, Hsu C-Y (2009) Adaptive CMAC neural control of chaotic systems with a PI-type learning algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 36:11836–11843
Chen M, Chen W (2009) Robust adaptive neural network synchronization controller design for a class of time delay uncertain chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 41:2716–2724
Sheikhan M, Shahnazi R, Garoucy S (2011) Synchronization of general chaotic systems using neural controllers with application to secure communication. Neural Comput Appl (article in press). doi:10.1007/s00521-011-0697-0
Chen C-S, Chen H-H (2009) Robust adaptive neural-fuzzy-network control for the synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 10:1466–1479
Chen C-S (2009) Quadratic optimal neural fuzzy control for synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems. Expert Syst Appl 36:11827–11835
Lin D, Wang X (2011) Self-organizing adaptive fuzzy neural control for the synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems with random-varying parameters. Neurocomputing 74:2241–2249
Kolumbán G, Kennedy MP, Chua LO (1997) The role of synchronization in digital communication using chaos I. Fundamentals of digital communications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 44:927–936
Wu X-J, Wang H, Lu H-T (2011) Hyperchaotic secure communication via generalized function projective synchronization. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 12:1288–1299
Rössler OE (1976) An equation for continuous chaos. Phys Lett A 57:397–398
Kapitaniak T, Steeb WH (1991) Transition to hyperchaos in coupled generalized Van der Pol equations. Phys Lett A 152:33–36
Anishchenko VS, Kapitaniak T, Safonova MA, Sosnovzeva OV (1994) Birth of double–double scroll attractor in coupled Chua circuit. Phys Lett A 192:207–214
Kapitaniak T, Chua LO, Zhung GQ (1994) Experimental hyperchaos in coupled Chua’s circuits. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl 41:499–503
Hsieh JY, Hwang CC, Wang AP, Li WJ (1999) Controlling hyperchaos of the Rössler system. Int J Control 72:882–886
Laval L, M’Sirdi NK (2002) Controlling chaotic and hyperchaotic systems via energy regulation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 14:1015–1025
Jang MJ, Chen CL, Chen CK (2002) Sliding mode control of hyperchaos in Rössler systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 14:1465–1476
Yau HT, Yan JJ (2007) Robust controlling hyperchaos of the Rössler system subject to input nonlinearities by using sliding mode control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 33:1767–1776
Wang H, Han ZZ, Mo Z (2010) Synchronization of hyperchaotic systems via linear control. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 15:1910–1920
Zheng S, Dong G, Bi Q (2010) Adaptive modified function projective synchronization of hyperchaotic systems with unknown parameters. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 15:3547–3556
An H-L, Chen Y (2009) The function cascade synchronization scheme for discrete-time hyperchaotic systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 14:1494–1501
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: The proceedings of the international conference on neural networks, pp 1942–1948
Wang F, Liu C (2006) A new criterion and hyperchaos synchronization using linear feedback control. Phys Lett A 360:274–278
Wang F, Liu C (2007) Passive control of hyperchaotic Lorenz system and circuit experimental on EWB. Int J Modern Phys B 21:3053–3064
Wu X, Guan Z-H, Wu Z (2008) Adaptive synchronization between two different hyperchaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal 68:1346–1351
Xu J, Cai G, Zheng S (2009) Adaptive synchronization for an uncertain new hyperchaotic Lorenz system. Int J Nonlinear Sci 8:117–123
Li C (2011) Tracking control and generalized projective synchronization of a class of hyperchaotic system with unknown parameter and disturbance. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat (article in press). doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.05.017
Smaoui N, Karouma A, Zribi M (2011) Secure communications based on the synchronization of the hyperchaotic Chen and the unified chaotic systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 16:3279–3293
Li Y, Tang WKS, Chen G (2005) Generating hyperchaos via state feedback control. Int J Bifur Chaos 15:3367–3375
Chen A, Lu J, Lü J, Yu S (2006) Generating hyperchaos Lü attractor via state feedback control. Phys A 364:103–110
Jia Z, Lu J, Deng G (2007) Nonlinearity state feedback and adaptive synchronization of hyperchaotic Lü systems. Syst Eng Electron 29:598–600
Wang F-Q, Liu C-X (2006) Hyperchaos evolved from the Liu chaotic system. Chin Phys 15:963–968
Liu C, Liu T, Liu L, Liu K (2004) A new chaotic attractor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22:1031–1038
Jia Q (2007) Hyperchaos generated from the Lorenz chaotic system and its control. Phys Lett A 366:217–222
Khadra A, Liu ZX, Shen X (2005) Impulsively synchronizing chaotic systems with delay and applications to secure communication. Automatica 41:1491–1502
Grassi G (2009) Observer-based hyperchaos synchronization in cascaded discrete-time systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40:1029–1039
Hu M, Xu Z, Zhang R (2008) Full state hybrid projective synchronization in continuous-time chaotic (hyperchaotic) systems. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 13:456–464
Zhu C (2010) Control and synchronize a novel hyperchaotic system. Appl Math Comput 216:274–284
Shi Y, Eberhart RC (1998) Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization. In: The proceedings of the international conference on evolutionary programming, pp 591–600
Chen S, Billings SA, Cowan CFN, Grant PW (1990) Practical identification of Narmax models using radial basis functions. Int J Control 52:1327–1350
Holcomb T, Moran M (1991) Local training for radial basis function networks: towards solving the hidden unit problem. In: The proceedings of the American control conference, pp 2331–2336
Lee S, Rhce MK (1991) A Gaussian potential function network with hierarchically self-organizing learning. Neural Netw 4:207–224
Musavi MT, Ahmed W, Chan KH, Faris KB, Hummels DM (1992) On the training of radial basis function classifiers. Neural Netw 5:595–603
Lan Y, Soh YC, Huang G-B (2010) Constructive hidden nodes selection of extreme learning machine for regression. Neurocomputing 73:3191–3199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhan, M., Shahnazi, R. & Garoucy, S. Hyperchaos synchronization using PSO-optimized RBF-based controllers to improve security of communication systems. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 835–846 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0774-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0774-4