Abstract
Purpose
This multi-center, randomized, phase III study was conducted to demonstrate the non-inferiority of DA-3031 compared with daily filgrastim in patients during the first cycle of chemotherapy for breast cancer in terms of the duration of severe neutropenia (DSN).
Methods
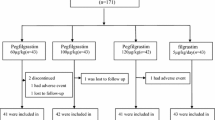
Seventy-four patients with breast cancer who were receiving combination chemotherapy with docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TAC) were enrolled. All participants were randomized to receive either daily subcutaneous injections of filgrastim 100 μg/m2/day for up to 10 days or a single subcutaneous injection of DA-3031 at fixed doses of 6 mg on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle.
Results
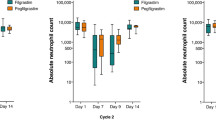
The mean duration of grade 4 (G4) neutropenia in cycle 1 was 2.08 ± 0.85 days for the filgrastim group and 2.28 ± 1.14 days for the DA-3031 group. The difference between groups was 0.2 ± 1.10 days (95 % confidence interval (CI) = −0.26, 0.66), which supported non-inferiority. No statistically significant differences were observed in nadir absolute neutrophil count (ANC) (154.34/mm3 and 161.75/mm3 for the filgrastim and DA-3031 groups, respectively; P = 0.8414) or in time to ANC recovery (10.03 ± 0.75 and 9.83 ± 1.56 days in the filgrastim and DA-3031 groups, respectively; P = 0.0611) during cycle 1. Serious AEs occurred in six (15.8 %) patients receiving filgrastim and in ten (27.8 %) patients receiving DA-3031; however, none was determined to be related to the study drug.
Conclusions
DA-3031 and daily filgrastim are similar in regard to DSN and safety in breast cancer patients receiving TAC chemotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budman DR, Berry DA, Cirrincione CT, Henderson IC, Wood WC, Weiss RB, Ferree CR, Muss HB, Green MR, Norton L, Frei E 3rd (1998) Dose and dose intensity as determinants of outcome in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. The Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(16):1205–1211
Wood WC, Budman DR, Korzun AH, Cooper MR, Younger J, Hart RD, Moore A, Ellerton JA, Norton L, Ferree CR et al (1994) Dose and dose intensity of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II, node-positive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 330(18):1253–1259. doi:10.1056/NEJM199405053301801
Kuderer NM, Dale DC, Crawford J, Cosler LE, Lyman GH (2006) Mortality, morbidity, and cost associated with febrile neutropenia in adult cancer patients. Cancer 106(10):2258–2266. doi:10.1002/cncr.21847
Citron ML, Berry DA, Cirrincione C, Hudis C, Winer EP, Gradishar WJ, Davidson NE, Martino S, Livingston R, Ingle JN, Perez EA, Carpenter J, Hurd D, Holland JF, Smith BL, Sartor CI, Leung EH, Abrams J, Schilsky RL, Muss HB, Norton L (2003) Randomized trial of dose-dense versus conventionally scheduled and sequential versus concurrent combination chemotherapy as postoperative adjuvant treatment of node-positive primary breast cancer: first report of intergroup trial C9741/Cancer and Leukemia Group B trial 9741. J Clin Oncol 21(8):1431–1439. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.09.081
Eiermann W, Pienkowski T, Crown J, Sadeghi S, Martin M, Chan A, Saleh M, Sehdev S, Provencher L, Semiglazov V, Press M, Sauter G, Lindsay MA, Riva A, Buyse M, Drevot P, Taupin H, Mackey JR (2011) Phase III study of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide with concomitant versus sequential docetaxel as adjuvant treatment in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-normal, node-positive breast cancer: BCIRG-005 trial. J Clin Oncol 29(29):3877–3884. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.5437
Smith TJ, Bohlke K, Lyman GH, Carson KR, Crawford J, Cross SJ, Goldberg JM, Khatcheressian JL, Leighl NB, Perkins CL, Somlo G, Wade JL, Wozniak AJ, Armitage JO, American Society of Clinical Oncology (2015) Recommendations for the use of WBC growth factors: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 33(28):3199–3212. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.62.3488
Aapro MS, Bohlius J, Cameron DA, Dal Lago L, Donnelly JP, Kearney N, Lyman GH, Pettengell R, Tjan-Heijnen VC, Walewski J, Weber DC, Zielinski C, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (2011) 2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 47(1):8–32. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.10.013
Zamboni WC (2003) Pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim. Pharmacotherapy 23(8 Pt 2):9S–14S
Aapro M, Crawford J, Kamioner D (2010) Prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia with granulocyte colony-stimulating factors: where are we now? Support Care Cancer 18(5):529–541. doi:10.1007/s00520-010-0816-y
Park KH, Sohn JH, Lee S, Park JH, Kang SY, Kim HY, Park IH, Park YH, Im YH, Lee HJ, Hong DS, Park S, Shin SH, Kwon HC, Seo JH (2013) A randomized, multi-center, open-label, phase II study of once-per-cycle DA-3031, a biosimilar pegylated G-CSF, compared with daily filgrastim in patients receiving TAC chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer. Investig New Drugs 31(5):1300–1306. doi:10.1007/s10637-013-9973-4
Martin M, Pienkowski T, Mackey J, Pawlicki M, Guastalla JP, Weaver C, Tomiak E, Al-Tweigeri T, Chap L, Juhos E, Guevin R, Howell A, Fornander T, Hainsworth J, Coleman R, Vinholes J, Modiano M, Pinter T, Tang SC, Colwell B, Prady C, Provencher L, Walde D, Rodriguez-Lescure A, Hugh J, Loret C, Rupin M, Blitz S, Jacobs P, Murawsky M, Riva A, Vogel C, Breast Cancer International Research Group 001 Investigators (2005) Adjuvant docetaxel for node-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 352(22):2302–2313. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043681
Martín M, Lluch A, Seguí MA, Ruiz A, Ramos M, Adrover E, Rodríguez-Lescure A, Grosse R, Calvo L, Fernandez-Chacón C, Roset M, Antón A, Isla D, del Prado PM, Iglesias L, Zaluski J, Arcusa A, López-Vega JM, Muñoz M, Mel JR (2006) Toxicity and health-related quality of life in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant docetaxel, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide (TAC) or 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (FAC): impact of adding primary prophylactic granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to the TAC regimen. Ann Oncol 17(8):1205–1212. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl135
Aapro M, Schwenkglenks M, Lyman GH, Lopez Pousa A, Lawrinson S, Skacel T, Bacon P, von Minckwitz G (2010) Pegfilgrastim primary prophylaxis vs. current practice neutropenia management in elderly breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 74(3):203–210. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.06.004
Lee KH, Kim JY, Lee MH, Han HS, Lim JH, Park KU, Park IH, Cho EK, Yoon SY, Kim JH, Choi IS, Park JH, Choi YJ, Kim HJ, Jung KH, Kim SY, Oh DY, Im SA (2016) A randomized, multicenter, phase II/III study to determine the optimal dose and to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pegteograstim (GCPGC) on chemotherapy-induced neutropenia compared to pegfilgrastim in breast cancer patients: KCSG PC10-09. Support Care Cancer 24(4):1709–1717. doi:10.1007/s00520-015-2963-7
Blackwell K, Semiglazov V, Krasnozhon D, Davidenko I, Nelyubina L, Nakov R, Stiegler G, Singh P, Schwebig A, Kramer S, Harbeck N (2015) Comparison of EP2006, a filgrastim biosimilar, to the reference: a phase III, randomized, double-blind clinical study in the prevention of severe neutropenia in patients with breast cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 26(9):1948–1953. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv281
Yano R, Konno A, Watanabe K, Tsukamoto H, Kayano Y, Ohnaka H, Goto N, Nakamura T, Masada M (2013) Pharmacoethnicity of docetaxel-induced severe neutropenia: integrated analysis of published phase II and III trials. Int J Clin Oncol 18(1):96–104. doi:10.1007/s10147-011-0349-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of each participating center and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. All patients gave written informed consent before any study-related procedure was performed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, K.H., Lee, S., Park, J.H. et al. A randomized, multi-center, open-label, phase III study of once-per-cycle DA-3031, a pegylated G-CSF, in comparison with daily filgrastim in patients receiving TAC chemotherapy for breast cancer. Support Care Cancer 25, 505–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3429-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3429-2