Abstract
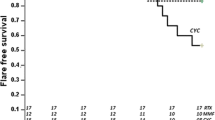
Although immunosuppressive regimens of corticosteroids combined with high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide (IVCY) have been reported to suppress the activity of lupus nephritis, there is controversy regarding its application for children and adolescents, because of its potential toxicity including gonadal dysfunction. On the basis of the recent finding that a low-dose IVCY regimen for induction therapy in adult lupus nephritis effectively achieves renal remission comparable with that achieved with a conventional high-dose IVCY regimen, we treated two children with severe lupus nephritis by low-dose (fixed dose of 500 mg m−2, cumulative dose 3 g m−2, approximately one-fourth of the conventional high-dose IVCY regimen) IVCY and oral mizoribine (5 mg kg−1 day−1) and steroids (3 methylprednisolone pulse followed by oral prednisolone). They responded well to this regimen, showing remarkable improvement in both histological and clinical manifestations in a short period of time. From these findings we suggest that the new low-dose IVCY regimen may be as effective as the conventional high-dose IVCY regimen, without significant adverse effect, for induction therapy in children with severe lupus nephritis (class III or IV).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niaudet P (2000) Treatment of lupus nephritis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 14:158–166
Bartosh SM, Fine RN, Sullivan EK (2001) Outcome after transplantation of young patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a report of the North America pediatric renal transplant cooperative study. Transplantation 72:973–978
Sonda K, Takahashi K, Fchinoue S, Hayasaka Y, Kawaguchi H, Teraoka S, Toma H, Oka K (1996) Clinical pharmacokinetic study of mizoribine in renal transplantation patients. Transplant Proc 28:3643–3648
Yoshioka K, Ohashi Y, Sakai T, Ito H, Yoshikawa N, Nakamura H, Tanizawa T, Wada H, Maki S (2000) A multicenter trial mizoribine compared with placebo in children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 58:317–324
Kaneko K, Nagaoka R, Ohtomo Y, Yamashiro Y (1999) Mizoribine for childhood IgA nephropathy. Nephron 83:376–377
Nagaoka R, Kaneko K, Ohtomo Y, Yamashiro Y (2002) Mizoribine treatment for childhood nephropathy. Pediatr Int 44:217–223
Tanaka H, Tsugawa K, Tsuruga K, Nakahata T, Ito E, Waga S (2004) Mizoribine for the treatment of lupus nephritis in children and adolescents. Clin Nephrol 62:412–417
Yoshidome K, Takei S, Imanaka H, Maeno N, Ohkawa T, Kawano Y (2004) Efficacy of mizoribine in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus in children. Pediatr Int 46:444–449
Weening JJ, Agati DD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijin JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennete JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65:521–530
Austin HA 3rd, Kipple JH, Balow JE, le Riche NG, Steinberg AD, Plotz PH (1986) Therapy of lupus nephritis: control trial of predonisone and cytotoxic drugs. N Eng J Med 314:614–619
Boumpas DT, Austin HA 3rd, Vaughan EM, Kipple JH, Steinberg AD, Yarboro CH (1992) Controlled trial of pulse methylpredonisolone versus two regimens of pulse cyclophosphamide in severe lupus nephritis. Lancet 340:741–745
Gourley MF, Austin HA 3rd, Scott D, Yarboro CH, Vaughan EM, Muir J (1996) Methylpredonisolone and cyclophosphamide, alone or in combination, in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med 125:549–557
Illei GG, Austin HA, Crane M, Collinins L, Gourley MF, Yarboro CH (2001) Combination therapy with pulse cyclophosphamide plus pulse methylpredonisolone improves long-term renal outcome without adding toxicity in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med 135:248–257
Lehman TJ, Sherry DD, Wagner L, McCurdy DK, Emery H, Magilavy DB (1989) Intermittent intravenous cyclophosphamide therapy for lupus nephritis. J Pediatr 114:1055–1060
Lehman TJ, Onel K (2000) Intermittent intravenous cyclophosphamide arrests progression of the renal chronicity index in childhood systemic lupus erythematousus. J Pediatr 136:243–247
Houssiau FA, Vasconcelos C, D’Cruz D, Sebastiani GD, Garrido ER, Danieli MG (2002) Immunosupressive therapy in lupus nephritis: the Euro-lupus nephritis trial. A randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 46:2121–2131
Kusaba R, Otubo O, Sugimoto H, Takahashi I, Yamada Y, Yamauchi J, Akiyama N, Inou T (1981) Immunosuppressive effect of bredinin in the management of patients with renal transplantation. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc 18:420–425
Yokota S (2002) Mizoribine: mode of action and effects in clinical use. Pediatr Int 44:196–198
Chan TM, Li FK, Tang CSO, Wong RWS, Fang GX, Ji YL, Lau CS, Wong AKM, Tong MKL, Chan KW, Lai KN (2000) Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. N Eng J Med 343:1156–1162
Tucker LB, Menon S, Schaller JG, Isenberg DA (1995) Adult- and childhood-onset systemic lupus erytematosus: a comparison of onset, clinical features, serology, and outcome. Br J Rheumatol. 34:866–872
Contreras G, Pardo V, Leclercq B, Lenz O Tozman E, O’Nan P, Roth D (2004) Sequential therapy for proliferative lupus nephritis. N Eng J Med 350:971–980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujinaga, S., Kaneko, K., Ohtomo, Y. et al. Induction therapy with low-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide, oral mizoribine, and steroids for severe lupus nephritis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1500–1503 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1983-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1983-9