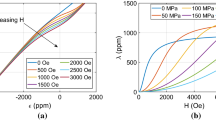
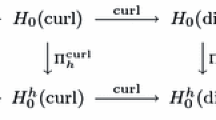
Abstract
The first objective of this contribution is the formulation of nonlinear problems in magneto-elasticity involving finite geometry of the surrounding free space. More specifically for the magnetic part of the problem, the surrounding free space is described by means of a boundary integral equation for which boundary elements are used that are appropriately coupled with the finite element discretization used inside the material. The second objective is to develop a numerical strategy to solve the strongly coupled magneto-mechanics problem at hand. Herein we provide a staggered scheme consisting of a magnetostatic resolution employing the above coupled BEM-FEM procedure at fixed deformation, followed by a mechanical resolution at fixed magnetic fields. This decoupled method renders the whole solution strategy very appealing since, among others, the first BEM-FEM resolution is linear for some prototype models, and the remaining mechanical resolution is analogous to nowadays classical nonlinear elastostatic problems in the finite strain range. Some nonlinear boundary-value problems are simulated to demonstrate the applicability of the proposed framework.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brebbia CA, Dominguez J (1998) Boundary elements. An introductory course, 2nd edn. WIT Press, Boston
Brebbia CA, Telles JCF, Wrobel LC (1984) Boundary element techniques. Theory and applications in engineering. Springer, Berlin
Brigadnov IA, Dorfmann A (2003) Mathematical modeling of magneto-sensitive elastomers. Int J Solids Struct 40:4659–4674
Brown WF (1966) Magnetoelastic interactions. Springer, Berlin
Bustamante R, Dorfmann A, Ogden RW (2006) Universal relations in isotropic nonlinear magnetoelasticity. Q J Mech Appl Math 59:435–450
Bustamante R, Dorfmann A, Ogden RW (2008) On variational formulations in nonlinear magnetoelastostatics. Math Mech Solids 13:725–745
Bustamante R, Dorfmann A, Ogden RW (2011) Numerical solution of finite geometry boundary-value problems in nonlinear magnetoelasticity. Int J Solids Struct 48:874–883
Dorfmann A, Ogden RW (2003) Magnetoelastic modelling of elastomers. Eur J Mech A Solids 22:497–507
Dorfmann A, Ogden RW (2004) Nonlinear magnetoelastic deformations. Q J Mech Appl Mech 57:599–622
Ericksen JL (2006) A modified theory of magnetic effects in elastic materials. Math Mech Solids 11:23–47
Ethiraj G, Miehe C (2016) Multiplicative magneto-elasticity of magnetosensitive polymers incorporating micromecanically-based network kernels. Int J Eng Sci 102:93–119
Ginder JM, Clark SM, Schlotter WF, Nichols ME (2002) Magnetostrictive phenomena in magnetorheological elastomers. Int J Mod Phys B 16:2412–2418
Holzapfel GA (2000) Nonlinear solid mechanics. A continuum approach for engineering. Wiley, Chichester
Jackson JD (1999) Classical electrodynamics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Jolly MR, Carlson JD, Muñoz BC (1996) A model of the behavior of magnetorheological materials. Smart Mater Struct 5:607–614
Nedjar B (2014) On finite strain poroplasticity with reversible and irreversible porosity laws. Formulation and computational aspects. Mech Mater 68:237–252
Nedjar B (2015) A theory of finite strain magneto-poromechanics. J Mech Phys Solids 84:293–312
Nedjar B (2016) A finite strain modeling of electro-viscoelastic materials. Int J Solids Struct 97–98:312–321
Nedjar B (2016) On constitutive models of finite elasticity with possible zero apparent Poisson’s ratio. Int J Solids Struct 91:72–77
Ogden RW (2011) Magnetostatics: from basic principles to nonlinear interactions in deformable media. In: Ogden RW, Steigmann DJ (eds) Mechanics and elastodynamics of magneto- and electro-elastic materials, CISM Courses And Lectures; No 527. Springer, Wien, pp 107–152
Pao YH (1978) Electromechanic forces in deformable continua. In: Nemat-Nasser S (ed) Mechanics today, vol 4. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 209–305
Simo JC (1998) Numerical analysis and simulation of plasticity. In: Ciarlet PG, Lions JL (eds) Handbook of numerical analysis, vol VI. Elsevier Science BV, North-Holland, pp 183–499
Simo JC, Hughes TJR (1998) Computational inelasticity. Springer, New York
Spencer AJM(1984) Constitutive theory for strongly anisotropic solids. In: Spencer AJM (ed) Continuum theory of the mechanics of fibre-reinforced composites, CISM Cources and Lectures No. 282. Springer, Wien
Steigmann DJ (2004) Equilibrium theory for magnetic elastomers and magnetoelastic membranes. Int J Non-linear Mech 39:1193–1216
Steinmann P(2011) Computational nonlinear electro-elasticity -getting started. In: Ogden RW , Steigmann DJ (eds) Mechanics and elastodynamics of magneto- and electro-elastic materials, CISM Courses and Lectures No. 527. Springer, Wien, pp 181–230
Varga Z, Filipcsei G, Zrínyi M (2006) Magnetic field sensitive functional elastomers with tunable elastic modulus. Polymer 47:227–233
Vu DK, Steinmann P (2007) Nonlinear electro- and magneto-elastostatics: material and spatial settings. Int J Solids Struct 44:7891–7901
Vu DK, Steinmann P (2010) A 2-d coupled BEM-FEM simulation of electro-elastostatics at large strain. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:1124–1133
Vu DK, Steinmann P (2012) On 3-d coupled BEM-FEM simulation of nonlinear electro-elastostatics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 201–204:82–90
Wriggers P (2008) Nonlinear finite element methods. Springer, Berlin
Wrobel LC (2002) The boundary element method, volume 1, applications in thermo-fluids and acoustics. Wiley, Chichester
Zhao X, Kim J, Cezar CA, Huebsch N, Lee K, Bouhadir K, Mooney DJ (2011) Active scaffolds for on-demand drug and cell delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci (PNAS) 108(1):67–72
Zrínyi M, Barsi L, Büki A (1996) Deformation of ferrogels induced by nonuniform magnetic fields. J. Chem. Phys. 104(21):8750–8756
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nedjar, B. A coupled BEM-FEM method for finite strain magneto-elastic boundary-value problems. Comput Mech 59, 795–807 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-016-1370-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-016-1370-3