Abstract
Background
Although endoscopic resection (ER) may be sufficient treatment for early-stage esophageal cancer, additional treatment is recommended when there is a high risk of cancer recurrence. It is unclear whether delaying esophagectomy by performing and assessing the success of ER affects outcomes as compared with immediate esophagectomy without ER. Additionally, long-term survival after sequential ER and esophagectomy required further investigation.
Methods
Between 2011 and 2015, 48 patients with stage T1 esophageal cancer underwent esophagectomy after ER with curative intent at our institution. Two-to-one propensity score methods were used to identify 96 matched-control patients who were treated with esophagectomy only using baseline patient, tumor characteristics and surgical approach. Time from initial evaluation to esophagectomy, relapse-free survival, overall survival, and postoperative complications were compared between the propensity-matched groups.
Results
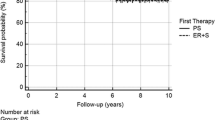
In the ER + esophagectomy group, the time from initial evaluation to esophagectomy was significantly longer than in the esophagectomy only group (114 vs. 8 days, p < 0.001). The incidence of dense adhesion (p = 0.347), operative time (p = 0.867), postoperative surgical complications (p = 0.966), and postoperative length of hospital stay (p = 0.125) were not significantly different between the groups. Moreover, recurrence-free survival and overall survival were also similar between the two groups (p = 0.411 and p = 0.817, respectively).
Conclusions
Treatment of stage T1 esophageal cancer with ER prior to esophagectomy did not increase the difficulty of performing esophagectomy or the incidence of postoperative complications and did not affect survival after esophagectomy. These results suggest that ER can be recommended for patients with stage T1 cancer even if esophagectomy is warranted eventually.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang GQ, Jiao GG, Chang FB, Fang WH, Song JX, Lu N, Lin DM, Xie YQ, Yang L (2004) Long-term results of operation for 420 patients with early squamous cell esophageal carcinoma discovered by screening. Ann Thorac Surg 77(5):1740–1744
Pech O, Bollschweiler E, Manner H, Leers J, Ell C, Holscher AH (2011) Comparison between endoscopic and surgical resection of mucosal esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus at two high-volume centers. Ann Surg 254(1):67–72
Kim DU, Lee JH, Min BH, Shim SG, Chang DK, Kim YH, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, Rhee JC, Kim KM, Shim YM (2008) Risk factors of lymph node metastasis in T1 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(4):619–625
Spechler SJ (2015) Dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus: limitations of current management strategies. Am J Gastroenterol 100(4):927–935
Pech O, May A, Gossner L, Rabenstein T, Manner H, Huijsmans J, Vieth M, Stolte M, Berres M, Ell C (2007) Curative endoscopic therapy in patients with early esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma or high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia. Endoscopy 39(1):30–35
Das A, Singh V, Fleischer DE, Sharma VK (2008) A comparison of endoscopic treatment and surgery in early esophageal cancer: an analysis of surveillance epidemiology and end results data. Am J Gastroenterol 103(6):1340–1345
Nealis TB, Washington K, Keswani RN (2011) Endoscopic therapy of esophageal premalignancy and early malignancy. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw: JNCCN 9(8):890–899
Choi JY, Park YS, Jung HY, Ahn JY, Kim MY, Lee JH, Choi KS, Kim do H, Choi KD, Song HJ, Lee GH, Cho KJ, Kim JH (2011) Feasibility of endoscopic resection in superficial esophageal squamous carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 73(5):881–889
Park JS, Youn YH, Park JJ, Kim JH, Park H (2016) Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous neoplasms. Clin Endosc 49(2):168–175
Qin X, He S, Zhang Y, Xue L, Lu N, Wang G (2014) Diagnosis and staging of superficial esophageal precursor based on pre-endoscopic resection system comparable to endoscopic resection. BMC Cancer 14:774
Merkow RP, Bilimoria KY, Keswani RN, Chung J, Sherman KL, Knab LM, Posner MC, Bentrem DJ (2014) Treatment trends, risk of lymph node metastasis, and outcomes for localized esophageal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(7):dju133
Davison JM, Landau MS, Luketich JD, McGrath KM, Foxwell TJ, Landsittel DP, Gibson MK, Nason KS et al (2016) A model based on pathologic features of superficial esophageal adenocarcinoma complements clinical node staging in determining risk of metastasis to lymph nodes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(3):369–377
Pech O, May A, Manner H, Behrens A, Pohl J, Weferling M, Hartmann U, Manner N, Huijsmans J, Gossner L, Rabenstein T, Vieth M, Stolte M, Ell C et al (2014) Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology 146(3):652–660
Gertler R, Stein HJ, Schuster T, Rondak IC, Höfler H, Feith M et al (2014) Prevalence and topography of lymph node metastases in early esophageal and gastric cancer. Ann Surg 259(1):96–101
Participants in the Paris Workshop (2003) The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc 58 (6 Suppl): S3–S43
Van Westreenen HL, Westerterp M, Bossuyt PM, Pruim J, Sloof GW, van Lanschot JJ, Groen H, Plukker JT (2004) Systematic review of the staging performance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(18):3805–3812
Lightdale CJ, Kulkarni KG (2005) Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the staging and follow-up of esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(20):4483–4489
Eguchi T, Nakanishi Y, Shimoda T, Iwasaki M, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Kato H, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Umemura S (2006) Histopathological criteria for additional treatment after endoscopic mucosal resection for esophageal cancer: analysis of 464 surgically resected cases. Modern Pathol 19(3):475–480
Ciocirlan M, Lapalus MG, Hervieu V, Souquet JC, Napoleon B, Scoazec JY, Lefort C, Saurin JC, Ponchon T (2007) Endoscopic mucosal resection for squamous premalignant and early malignant lesions of the esophagus. Endoscopy 39(1):24–29
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers. http://www.nccn.org. Version 1.2017. Updated March 21, 2017. Accessed 1 June 2017
Tomita N, Matsumoto T, Hayashi T, Arakawa A, Sonoue H, Kajiyama Y, Tsurumaru M (2008) Lymphatic invasion according to D2-40 immunostaining is a strong predictor of nodal metastasis in superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: algorithm for risk of nodal metastasis based on lymphatic invasion. Pathol Int 58(5):282–287
Sgourakis G, Gockel I, Lang H (2013) Endoscopic and surgical resection of T1a/T1b esophageal neoplasms: a systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 19(9):1424–1437
Holscher AH (2007) Endoscopic mucosal resection for early squamous-cell cancer of the esophagus–a dangerous game or standard treatment? Endoscopy 39(1):77–79
Badreddine RJ, Prasad GA, Lewis JT, Lutzke LS, Borkenhagen LS, Dunagan KT, Wang KK (2010) Depth of submucosal invasion does not predict lymph node metastasis and survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(3):248–253
Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K, Goto O, Kodashima S, Yamamichi N, Omata M (2009) Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc 70(5):860–866
Takahashi H, Arimura Y, Masao H, Okahara S, Tanuma T, Kodaira J, Kagaya H, Shimizu Y, Hokari K, Tsukagoshi H, Shinomura Y, Fujita M (2010) Endoscopic submucosal dissection is superior to conventional endoscopic resection as a curative treatment for early squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 72(2):255–264
Okada K, Tsuchida T, Ishiyama A, Taniguchi T, Suzuki S, Horiuchi Y, Matsuo Y, Yoshizawa N, Suganuma T, Omae M, Kubota M, Hirasawa T, Yamamoto Y, Inamori M, Yamamoto N, Nakajima A (2012) Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection for en bloc resection of superficial pharyngeal carcinomas. Endoscopy 44(6):556–564
Tang B, Bai JY, Zhao XY, Fan CQ, Yang X, Deng L, Yang SM, Yu J (2015) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal cancer with near-circumferential lesions: our experience with 40 patients. Surg Endosc 29(8):2141–2148
Acknowledgements
This work is supported, in part, by Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Foundation key project (14JC140140), Grant from Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 15411951602; No. 16401970704), Trans-Century Training Programme Foundation for the Talents by the State Education Commission (NCET-13-0148), Grant from Health and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. XYQ2011025; No. 2013ZYJB0301). We thank Shannon Wyszomierski, Ph.D. for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Shengfei Wang, Yangle Huang, Juntao Xie, Lingdun Zhuge, Longlong Shao, Jiaqing Xiang, Yawei Zhang, Yihua Sun, Hong Hu, Sufeng Chen, Toni Lerut, James Luketich, Jie Zhang, and Haiquan Chen have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Shengfei Wang, Yangle Huang, and Juntao Xie contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Huang, Y., Xie, J. et al. Does delayed esophagectomy after endoscopic resection affect outcomes in patients with stage T1 esophageal cancer? A propensity score-based analysis. Surg Endosc 32, 1441–1448 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5830-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5830-4