Abstract
Background and aims
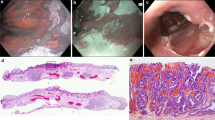
Piecemeal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is the standard treatment of nodular Barrett’s esophagus dysplasia and T1a cancer. Piecemeal resection may be incomplete and makes precise histologic assessment difficult. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is a technique that enables en-bloc resection but has not gained widespread acceptance due to its technical difficulty, risk and long procedure time.
Methods
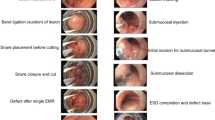
We developed a protocol consisting of a combination of a limited ESD with supplementary EMR in the same session if necessary, designed to increase en-bloc resection of the most worrisome neoplastic area while maximizing the rate of complete resection of dysplasia. Records of consecutive patients referred for treatment during a 2-year period were reviewed.
Results
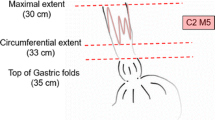
Eleven patients were treated: two with ESD and nine with combined ESD/EMR. Eight patients had mucosal lesions; three patients had submucosally invasive cancer and were referred to surgery. Five of the 8 mucosal lesions were removed en-bloc by ESD with dysplasia-free margins. Two patients with T1a cancer had low-grade dysplasia in the ESD margins and removal of all dysplasia on EMR. One patient with T1a cancer had high-grade dysplasia in the ESD margins and on EMR. He required a second endoscopy to remove residual neoplasia. There were no adverse events. The mean procedure time was 66.4 ± 15.1 min.
Conclusions
Combining a limited ESD with EMR in the same session enables efficient treatment of visible dysplastic lesions in Barrett’s esophagus.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMR:
-
Endoscopic mucosal resection
- ESD:
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- LGD:
-
Low-grade dysplasia
- HGD:
-
High-grade dysplasia
References
Kothari S, Kaul V (2015) Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection for endoscopic therapy of Barrett’s Esophagus-related neoplasia. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 44:317–335
Gaddam S, Wani S (2013) Endoscopic therapy of barrett esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 23:1–16
Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FG, Peters FP, Alvarez Herrero L, Ten Kate FJ et al (2011) Randomized trial on endoscopic resection-cap versus multiband mucosectomy for piecemeal endoscopic resection of early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc 74:35–43
Berry M (2014) Esophageal cancer: staging system and guidelines for staging and treatment. J Thorac Dis. 6(Suppl 3):S289–S297
Oka S, Tanaka S, Saito Y, Iishi H, Kudo SE et al (2015) Local recurrence after endoscopic resection for large colorectal neoplasia: a multicenter prospective study in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol 110:697–707
Min YW, Min BH, Lee JH, Kim JJ (2014) Endoscopic treatment for early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 20:4566–4573
Uedo N, Takeuchi Y, Ishihara R (2012) Endoscopic management of early gastric cancer: endoscopic mucosal resection or endoscopic submucosal dissection: data from a Japanese high-volume center and literature review. Ann Gastroenterol 25:281–290
Oyama T (2014) Esophageal ESD: technique and prevention of complications. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 24:201–212
Higuchi K, Tanabe S, Azuma M, Katada C, Sasaki T et al (2013) A phase II study of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal neoplasms (KDOG 0901). Gastrointest Endosc 78:704–710
Neuhaus H, Terheggen G, Rutz EM, Vieth M, Schumacher B (2012) Endoscopic submucosal dissection plus radiofrequency ablation of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus. Endoscopy 44:1105–1113
Hoteya S, Matsui A, Iizuka T, Kikuchi D, Yamada A et al (2013) Comparison of the clinicopathological characteristics and results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for esophagogastric junction and non-junctional cancers. Digestion 87:29–33
Probst A, Aust D, Märkl B, Anthuber M, Messmann H (2015) Early esophageal cancer in Europe: endoscopic treatment by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy 47:113–121
Chevaux JB, Piessevaux H, Jouret-Mourin A, Yeung R, Danse E, Deprez PH (2015) Clinical outcome in patients treated with endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial Barrett’s neoplasia. Endoscopy 47:103–112
Falk GW (2015) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for Barrett-associated neoplasia: is it ready for the endoscopist’s toolbox? Endoscopy 47:97–98
Toyonaga T, Man-I M, Morita Y, Azuma T (2014) Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) versus simplified/hybrid ESD. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 24:191–199
Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, Bergman JJ, Gossner L (2006) T he development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett’s esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology 131:1392–1399
Bae JH, Yang DH, Lee S, Soh JS, Lee S (2015) Optimized hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors: a randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc, in press
Young PE, Gentry AB, Acosta RD, Greenwald BD, Riddle M (2010) Endoscopic ultrasound does not accurately stage early adenocarcinoma or high-grade dysplasia of the esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:1037–1041
Muthusamy VR, Kim S, Wallace MB (2015) Advanced imaging in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 44:439–458
Bahin F, Jayanna M, Williams SJ, Lee EY, Bourke MJ (2015) Efficacy of viscous budesonide slurry for prevention of esophageal stricture formation after complete endoscopic mucosal resection of short-segment Barrett’s neoplasia. Endoscopy, in press
Pech O, May A, Manner H, Behrens A, Pohl J (2014) Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology 146:652–660
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Ian Holmes, Tressia Hing and Shai Friedland have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmes, I., Hing, T. & Friedland, S. Combining endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection to treat neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Endosc 30, 5330–5337 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4885-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4885-y