Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the impact of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) on quality of life in obese diabetic patients compared to standard medical therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
We prospectively studied two matched obese populations with type 2 diabetes. Thirty patients underwent laparoscopic RYGB and 31 received standard medical therapy combined with a diabetes support and education program (DSE), consisting of educational sessions on diet and exercise. Groups were matched by age, gender, weight, glucostatic parameters, and use of glucose-lowering medications (oral agents and insulin therapy). Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) was assessed using the normalized SF-36 questionnaire, and data were collected at baseline and at 12-month follow-up.
Results
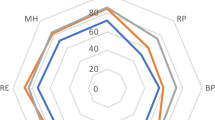
Diabetic patients who underwent RYGB experienced a statistically significant increase in their overall HRQOL. However, the role-physical and mental health domains increased but did not reach statistical significance. Diabetic patients in the medical therapy and DSE group did not show any significant increase in HRQOL. The between-group differences for the HRQOL changes from baseline were significant, other than for role-physical and mental health domains. Percentage changes in glucostatic parameters, discontinuation of glucose-lowering medications, and T2DM remission were not found to predict the percentage change in SF-36 scores at 12 months after RYGB.
Conclusions
For the first time, with a prospective matched control study, we demonstrate a significant improvement in HRQOL in obese diabetic patients who underwent RYGB, but not in those who were offered standard medical therapy and DSE.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J (2008) Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:1431–1437
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, Guidone C, Iaconelli A, Leccesi L, Nanni G, Pomp A, Castagneto M, Ghirlanda G, Rubino F (2012) Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 366:1577–1585
Hofso D, Jenssen T, Hager H, Roislien J, Hjelmesaeth J (2010) Fasting plasma glucose in the screening for type 2 diabetes in morbidly obese subjects. Obes Surg 20:302–307
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, Marks JS (2003) Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 289:76–79
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K, Schoelles K (2004) Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 292:1724–1737
Buchwald H, Estok R, Fahrbach K, Banel D, Jensen MD, Pories WJ, Bantle JP, Sledge I (2009) Weight and type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 122(248–256):e245
Colquitt JL, Picot J, Loveman E, Clegg AJ (2009) Surgery for obesity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 15(2):CD003641
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, Brethauer SA, Kirwan JP, Pothier CE, Thomas S, Abood B, Nissen SE, Bhatt DL (2012) Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 366:1567–1576
The WHOQOL group (1998) The World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL): development and general psychometric properties. Soc Sci Med 46(1982):1569–1585
Kral JG, Sjostrom LV, Sullivan MB (1992) Assessment of quality of life before and after surgery for severe obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 55:611s–614s
Ware JE, Kosinski M (2001) Interpreting SF-36 summary health measures: a response. Qual Life Res Int J Qual Life Asp Treat Care Rehabil 10:405–413 discussion 415–420
Weiner S, Neugehauer EA (2013) Quality of life of diabetic patients with medical or surgical treatment. Nutr Hosp 28(Suppl 2):66–77
Oldridge NB, Stump TE, Nothwehr FK, Clark DO (2001) Prevalence and outcomes of comorbid metabolic and cardiovascular conditions in middle- and older-age adults. J Clin Epidemiol 54:928–934
Torquati A, Lutfi RE, Richards WO (2007) Predictors of early quality-of-life improvement after laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery. Am J Surg 193:471–475
Dixon JB, Dixon ME, O’Brien PE (2001) Quality of life after lap-band placement: influence of time, weight loss, and comorbidities. Obes Res 9:713–721
Karlsson J, Sjostrom L, Sullivan M (1998) Swedish obese subjects (SOS)—an intervention study of obesity. Two-year follow-up of health-related quality of life (HRQL) and eating behavior after gastric surgery for severe obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab disord J Int Assoc Study Obes 22:113–126
Julia C, Ciangura C, Capuron L, Bouillot JL, Basdevant A, Poitou C, Oppert JM (2013) Quality of life after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and changes in body mass index and obesity-related comorbidities. Diabetes metab 39:148–154
Vincent HK, Ben-David K, Conrad BP, Lamb KM, Seay AN, Vincent KR (2012) Rapid changes in gait, musculoskeletal pain, and quality of life after bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis Off J Am Soc Bariatr Surg 8:346–354
American Diabetes Association (2013) Standards of medical care in diabetes–2013. Diabetes care 36(Suppl 1):S11–S66
Khoo CM, Chen J, Pamuklar Z, Torquati A (2014) Effects of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass or Diabetes Support and Education on Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion in Morbidly Obese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Ann Surg 259(3):494–501
Bergman RN, Finegood DT, Ader M (1985) Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo. Endocr Rev 6:45–86
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Sarwer DB, Wadden TA, Moore RH, Eisenberg MH, Raper SE, Williams NN (2010) Changes in quality of life and body image after gastric bypass surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis Off J Am Soc Bariatr Surg 6:608–614
Hill-Briggs F, Gary TL, Baptiste-Roberts K, Brancati FL (2005) Thirty-six-item short-form outcomes following a randomized controlled trial in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 28:443–444
Lobo CM, Frijling BD, Hulscher ME, Bernsen RM, Grol RP, Prins A, van der Wouden JC (2004) Effect of a comprehensive intervention program targeting general practice staff on quality of life in patients at high cardiovascular risk: a randomized controlled trial. Qual Life Res Int J Qual Life Asp Treat Care Rehabil 13:73–80
Klein S, Sheard NF, Pi-Sunyer X, Daly A, Wylie-Rosett J, Kulkarni K, Clark NG (2004) Weight management through lifestyle modification for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: rationale and strategies: a statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition. Diabetes Care 27:2067–2073
Bjorner JB, Lyng Wolden M, Gundgaard J, Miller KA (2013) Benchmarks for interpretation of score differences on the SF-36 health survey for patients with diabetes. Value Health J Int Soc Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 16:993–1000
Jacobson AM, de Groot M, Samson JA (1994) The evaluation of two measures of quality of life in patients with type I and type II diabetes. Diabetes Care 17:267–274
Chang CY, Huang CK, Chang YY, Tai CM, Lin JT, Wang JD (2010) Prospective study of health-related quality of life after Roux-en-Y bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Br J Surg 97:1541–1546
Kolotkin RL, Norquist JM, Crosby RD, Suryawanshi S, Teixeira PJ, Heymsfield SB, Erondu N, Nguyen AM (2009) One-year health-related quality of life outcomes in weight loss trial participants: comparison of three measures. Health Qual Life Outcomes 7:53
Donald M, Dower J, Coll JR, Baker P, Mukandi B, Doi SA (2013) Mental health issues decrease diabetes-specific quality of life independent of glycaemic control and complications: findings from Australia’s living with diabetes cohort study. Health Qual Life Outcomes 11:170
Klein BE, Klein R, Moss SE (1998) Self-rated health and diabetes of long duration. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 21:236–240
Rubin RR, Peyrot M (1999) Quality of life and diabetes. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev 15:205–218
Petterson T, Lee P, Hollis S, Young B, Newton P, Dornan T (1998) Well-being and treatment satisfaction in older people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 21:930–935
Glasgow RE, Ruggiero L, Eakin EG, Dryfoos J, Chobanian L (1997) Quality of life and associated characteristics in a large national sample of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 20:562–567
Acknowledgments
Research supported by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant No. K23 DK075907 from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD to Dr Alfonso Torquati.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Philip Omotosho, Alessandro Mor, Prapimporn Chattranukulchai Shantavasinkul, Leonor Corsino, and Alfonso Torquati have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Philip Omotosho and Alessandro Mor have contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omotosho, P., Mor, A., Shantavasinkul, P.C. et al. Gastric bypass significantly improves quality of life in morbidly obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Surg Endosc 30, 2857–2864 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4568-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4568-0