Abstract
Background
The Alvarado score is a clinical scoring system used in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. This study aimed to compare the reliability of the Alvarado score and clinical judgment and to refine the score to make it easier to use.
Methods
In this prospective, randomized study, patients presenting at the authors’ outpatient department with suspected appendicitis during a 1-year period were assigned in weekly alternation to either group A or group B. The group A patients were treated on the basis of their Alvarado score, and the group B patients underwent treatment based on clinical judgment. The correctness of the methods was assessed by evaluation of the final histology. Statistical comparison of the data was performed using SPSS 20.
Results
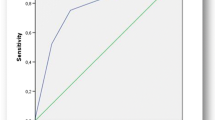
The study investigated 269 patients (131 in group A and 138 in group B). The groups were homogeneous in terms of mean age, gender, body mass index, and American Society of Anesthesiologists score. The number of negative appendectomies was 12 (9.16 %) in group A versus 5 (3.6 %) in group B (p = 0.063). The clinical judgment had better specificity and sensitivity than the Alvarado score. For that reason, the specificity of the Alvarado score was refined using statistical methods, with weighting of certain clinical data and inclusion of new ones (e.g., ultrasound investigation). Consequently, the area under the curve by receiver operating characteristic analysis gradually increased, and the Alvarado score became more accurate.
Conclusion
The study findings showed clinical judgment to be more reliable in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis than the Alvarado score, but the score is a useful diagnostic aid, especially for young colleagues. The use of the new scoring system has become easier. It includes fewer criteria as well as an important and sensitive predictor: the ultrasound investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JE, Bickler SW, Chang DC, Talamini MA (2012) Examining a common disease with unknown etiology: trends in epidemiology and surgical management of appendicitis in California 1995–2009. World J Surg 36:2787–2794
Gilmore OJ, Browett JP, Griffin PH, Ross IK, Brodribb AJ, Cooke TJ et al (1975) Appendicitis and mimicking conditions: a prospective study. Lancet 2:421–424
András A (2009) Változások az akut appendicitis epidemiológiájában, etiológiájában, diagnosztikájában és terápiájában (changes in epidemiology, etiology, diagnostics, and therapy of acute appendicitis). Orv Hetil 10:443–446
Raja AS, Wright C, Sodickson AD, Zane RD et al (2010) Negative appendectomy rate in the era of CT (an 18-year perspective). Radiology 256:460–465
Jaffrey RB, Laing FC, Lewis FR (1987) Acute appendicitis high resolution real-time ultrasound findings. Radiology 163:11–14
Collaborative SCOAP, Cuschieri J, Florence M et al (2008) Negative appendectomy and imaging accuracy in the Washington State Surgical Care and outcomes assessment programme. Ann Surg 248:557–563
Alvarado A (1986) A practical score for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ann Emerg Med 15:557–564
Al-Hashemy AM, Seleem MI (2004) Appraisal of the modified Alvarado score for acute appendicitis in adults. Saudi Med J 25:1229–1231
Impellizzeri P, Centonze A, Antonuccio P, Turiaco N, Cifalà S, Basile M et al (2002) Utility of a scoring system in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in pediatric age: a retrospective study. Minerva Chir 57:341–346
Chan MY, Tan C, Chiu MT, Ng YY (2003) Alvarado score: an admission criterion in patients with right iliac fossa pain. Surgeon 1:39–41
Pruekprasert P, Maipang T, Geater A, Apakupakul N, Ksuntigij P (2004) Accuracy in diagnosis of acute appendicitis by comparing serum C-reactive protein measurements, Alvarado score, and clinical impression of surgeons. J Med Assoc Thai 87:296–303
Denizbasi A, Unluer EE (2003) The role of emergency medicine resident using the Alvarado score in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis compared with the general surgery resident. Eur J Emerg Med 10:296–304
Jo YH, Kim K, Rhee JE, Kim TY, Lee JH, Kang SB et al (2010) The accuracy of emergency medicine and surgical residents in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Am J Emerg Med 28:766–770
Douglas CD, Macpherson NE, Davidson PM, Gani JS (2000) Randomised controlled trial of ultrasonography in diagnosis of acute appendicitis, incorporating the Alvarado score. BMJ 14:919–922
Lee SL, Ho HS (2003) Ultrasonography and computed tomography in suspected acute appendicitis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 24:69–73
Horton MD, Counter SF, Florence MG, Hart MJ (2000) A prospective trial of computed tomography and ultrasonography for diagnosing appendicitis in the atypical patient. Am J Surg 179:379–381
Parker L, Nazarian NL, Gingold EL, Palit CD, Hoey CL, Frangos AJ (2014) Cost and radiation savings of partial substitution of ultrasound for CT in appendicitis evaluation: a national projection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202:124–135
Sooriakumaran P, Lovell D, Brown R (2005) A comparison of clinical judgment vs the modified Alvarado score in acute appendicitis. Int J Surg 3:49–52
Kurane SB, Sangolli MS, Gogate AS (2008) A one-year prospective study to compare and evaluate diagnostic accuracy of modified Alvarado score and ultrasonography in acute appendicitis, in adults. Indian J Surg 70:125–129
Pouget-Baudry Y, Mucci S, Eyssartier E, Guesdon-Portes A, Lada P, Casa C et al (2010) The use of the Alvarado score in the management of right lower quadrant abdominal pain in the adult. J Visc Surg 147:e40–e44
Ohle R, O’Reilly F, O’Brien KK, Fahey T, Dimitrov BD (2011) The Alvarado score for predicting acute appendicitis: a systematic review. BMC Med 28:139
Owen TD, Williams H, Stiff G, Jenkinson LR, Rees BI (1992) Evaluation of the Alvarado score in acute appendicitis. J R Soc Med 85:87–88
Arain GM, Sohu KM, Ahmed E, Haider W, Naqi SA (2001) Role of Alvarado score in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Pak J Surg 17:41–46
Khan I, ur Rehman A (2005) Application of alvarado scoring system in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 17:41–44
Singh K, Gupta S, Pargal P (2008) Application of Alvarado scoring system in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. JK Sci 10:84–86
Al Qahtani HH, Muhammad AA (2004) Alvarado score as an admission criterion for suspected appendicitis in adults. Saudi J Gastroenterol 10:86–91
Abdeldaim Y, Mahmood S, McAvinchey D (2007) The Alvarado score as a tool for diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Ir Med J 100:342
Gwynn LK (2001) The diagnosis of acute appendicitis: clinical assessment versus computed tomography evaluation. J Emerg Med 21:119–123
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the European Union and cofunded by the European Social Fund under the project Telemedicine-Focused Research Activities on the Field of Mathematics, Informatics, and Medical Sciences, project number TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0073.
Disclosures
Eszter Mán, Zsolt Simonka, Ákos Varga, Ferenc Rárosi, and György Lázár have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mán, E., Simonka, Z., Varga, Á. et al. Impact of the alvarado score on the diagnosis of acute appendicitis: comparing clinical judgment, alvarado score, and a new modified score in suspected appendicitis: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Surg Endosc 28, 2398–2405 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3488-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3488-8