Abstract
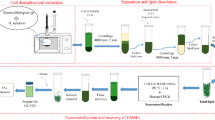
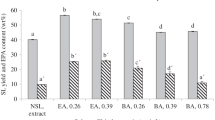
In this study, lipid extraction from Aurantiochytrium sp. was performed using a molten-salt/ionic-liquid mixture. The total fatty acid content of Aurantiochytrium sp. was 478.8 mg/g cell, from which 145 mg/g cell (30.3 % of total fatty acids) of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) was obtained. FeCl3·6H2O showed a high lipid extraction yield (207.9 mg/g cell), when compared with that of [Emim]OAc, which was only 118.1 mg/g cell; notably however, when FeCl3·6H2O was mixed with [Emim]OAc (5:1, w/w), the yield was increased to 478.6 mg/g cell. When lipid was extracted by the FeCl3·6H2O/[Emim]OAc mixture at a 5:1 (w/w) blending ratio under 90 °C, 30 min reaction conditions, the fatty acid content of the extracted lipid was a high purity 997.7 mg/g lipid, with most of the DHA having been extracted (30.2 % of total fatty acids). Overall, lipid extraction from Aurantiochytrium sp. was enhanced by the synergistic effects of the molten-salt/ionic-liquid mixture with different ions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid
- [Emim]OAc:
-
1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium acetate
References
Sanghvi A, Lo Y (2010) Present and potential industrial applications of macro-and microalgae. Recent Pat Food Nutr Agric 2(3):187–194
Doucha J, Straka F, Lívanský K (2005) Utilization of flue gas for cultivation of microalgae Chlorella sp. in an outdoor open thin-layer photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 17(5):403–412
Lee JY, Yoo C, Jun SY, Ahn CY, Oh HM (2010) Comparison of several methods for effective lipid extraction from microalgae. Bioresour Technol 101(1):S75–S77
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25(3):294–306
Miao X, Wu Q (2003) Exploitation of biomass renewable energy sources of microalgae. Renew Energy 3:13–16
Shin H, Park J, Jung W, Cho H, Kim S (2011) Development of biorefinery process using microalgae. J Korean Soc Precis Eng 28:154–167
Mendes RL, Nobre BP, Cardoso MT, Pereira AP, Palavra AF (2003) Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of compounds with pharmaceutical importance from microalgae. Inorg Chim Acta 356:328–334
Tang S, Qin C, Wang H, Li S, Tian S (2011) Study on supercritical extraction of lipids and enrichment of DHA from oil-rich microalgae. J Supercrit Fluids 57(1):44–49
Tapiero H, Ba GN, Couvreur P, Tew K (2002) Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and eicosanoids in human health and pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother 56(5):215–222
Innis SM (2008) Dietary omega 3 fatty acids and the developing brain. Brain Res 1237:35–43
Sijtsma L, Swaaf MD (2004) Biotechnological production and applications of the ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(2):146–153
Shimizu K, Tariq M, Rebelo LP, Lopes JNC (2010) Binary mixtures of ionic liquids with a common ion revisited: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Mol Liq 153(1):52–56
Olivier-Bourbigou H, Magna L, Morvan D (2010) Ionic liquids and catalysis: recent progress from knowledge to applications. Appl Catal A Gen 373(1):1–56
Castejón HJ, Lashock RJ (2012) Mixtures of ionic liquids with similar molar volumes form regular solutions and obey the cross-square rules for electrolyte mixtures. J Mol Liq 167:1–4
EL-Mahdy GA, Abdeltawab AA, Al-Othman ZA, Al-Lohedan HA (2013) Influence of ionic liquid pre-immersion on the corrodibility of zinc in chloride containing environment. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:6829–6838
Khupse ND, Kurolikar SR, Kumar A (2010) Temperature dependent viscosity of mixtures of ionic liquids at different compositions. Indian J Chem 49(5):727
Marsh K, Boxall J, Lichtenthaler R (2004) Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures-a review. Fluid Phase Equilib 219(1):93–98
Fujita K, Kobayashi D, Nakamura N, Ohno H (2013) Direct dissolution of wet and saliferous marine microalgae by polar ionic liquids without heating. Enzyme Microb Technol 52(3):199–202
Lovejoy KS, Davis LE, McClellan LM, Lillo AM, Welsh JD, Schmidt EN, Sanders CK, Lou AJ, Fox DT, Koppisch AT (2013) Evaluation of ionic liquids on phototrophic microbes and their use in biofuel extraction and isolation. J Appl Psychol 25(4):973–981
Heinze T, Koschella A (2005) Solvents applied in the field of cellulose chemistry. a mini review. Polimeros 15(2):84–90
Fischer S, Thümmler K, Pfeiffer K, Liebert T, Heinze T (2002) Evaluation of molten inorganic salt hydrates as reaction medium for the derivatization of cellulose. Cellulose 9(3):293–300
Fischer S, Leipner H, Thümmler K, Brendler E, Peters J (2003) Inorganic molten salts as solvents for cellulose. Cellulose 10(3):227–236
Choi SA, Lee JS, Oh YK, Jeong MJ, Kim SW, Park JY (2014) Lipid extraction from Chlorella vulgaris by molten-salt/ionic-liquid mixtures. Algal Res 3:44–48
Lepage G, Roy C (1986) Direct transesterification of all classes of lipids in a one-step reaction. J Lipid Res 27(1):114–120
Choi SA, Oh YK, Jeong MJ, Kim SW, Lee JS, Park JY (2014) Effects of ionic liquid mixtures on lipid extraction from Chlorella vulgaris. Renew Energy 65:169–174
Hong WK, Yu A, Oh BR, Park JM, Kim CH, Sohn JH, Kondo A, Seo JW (2013) Large-scale production of microalgal lipids containing high levels of docosahexaenoic acid upon fermentation of Aurantiochytrium sp. KRS101. Food Nutr Sci 4:1–5
Çetinkol ÖP, Dibble DC, Cheng G, Kent MS, Knierim B, Auer M, Wemmer DE, Pelton JG, Melnichenko YB, Ralph J (2010) Understanding the impact of ionic liquid pretreatment on eucalyptus. Biofuels 1(1):33–46
Li C, Knierim B, Manisseri C, Arora R, Scheller HV, Auer M, Vogel KP, Simmons BA, Singh S (2010) Comparison of dilute acid and ionic liquid pretreatment of switchgrass: biomass recalcitrance, delignification and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 101(13):4900–4906
Samayam IP, Schall CA (2010) Saccharification of ionic liquid pretreated biomass with commercial enzyme mixtures. Bioresour Technol 101(10):3561–3566
Annat G, Forsyth M, MacFarlane DR (2012) Ionic liquid mixtures variations in physical properties and their origins in molecular structure. J Phys Chem B 116(28):8251–8258
Niedermeyer H, Hallett JP, Villar-Garcia IJ, Hunt PA, Welton T (2012) Mixtures of ionic liquids. Chem Soc Rev 41(23):7780–7802
Mäki-Arvela P, Anugwom I, Virtanen P, Sjöholm R, Mikkola JP (2010) Dissolution of lignocellulosic materials and its constituents using ionic liquids—a review. Ind Crops Prod 32(3):175–201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the New & Renewable Energy Technology Development Program of the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government Ministry of Knowledge Economy (No. 20123010090010) and by the Advanced Biomass R&D Center (ABC) of Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (ABC-2012-053880).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
S.-A. Choi, J.-Y. Jung contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, SA., Jung, JY., Kim, K. et al. Effects of molten-salt/ionic-liquid mixture on extraction of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-rich lipids from Aurantiochytrium sp. KRS101. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 2199–2204 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1197-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-014-1197-2