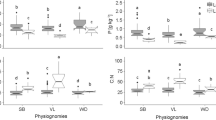
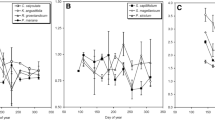
Abstract
A key question in savanna ecology is how trees and grasses coexist under N limitation. We used N stable isotopes and N content to study N source partitioning across seasons from trees and associated grasses in a semi-arid savanna. We also used 15N tracer additions to investigate possible redistribution of N by trees to grasses. Foliar stable N isotope ratio (δ15N) values were consistent with trees and grasses using mycorrhiza-supplied N in all seasons except in the wet season when they switched to microbially fixed N. The dependence of trees and grasses on mineralized soil N seemed highly unlikely based on seasonal variation in mineralization rates in the Kruger Park region. Remarkably, foliar δ15N values were similar for all three tree species differing in the potential for N fixation through nodulation. The tracer experiment showed that N was redistributed by trees to understory grasses in all seasons. Our results suggest that the redistribution of N from trees to grasses and uptake of N was independent of water redistribution. Although there is overlap of N sources between trees and grasses, dependence on biological sources of N coupled with redistribution of subsoil N by trees may contribute to the coexistence of trees and grasses in semi-arid savannas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbadie L, Mariotti A, Menaut J (1992) Independance of savanna grasses from soil organic matter for their nitrogen supply. Ecology 73:608–613
Aranibar JN, Anderson IC, Epstein HE, Feral CJW, Swap RJ, Ramontsho J, Macko SA (2008) Nitrogen isotope composition of soils, C3 and C4 plants along land use gradients in southern Africa. J Arid Environ 72:326–337. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.06.007
Archibald S, Scholes RJ (2007) Leaf green-up in a semi-arid African savanna—separating tree and grass responses to environmental cues. J Veg Sci 18:583–594. doi:10.1658/1100-9233(2007) (18 [583:LGIASA]2.0.CO;2)
Coetsee C, February EC, Bond WJ (2008) Nitrogen availability is not affected by frequent fire in a South African savanna. J Trop Ecol 24:647–654. doi:10.1017/S026646740800549X
Cole MM (1986) The Savannas: biogeography and geobotany. Academic Press, New York
Cooke JEK, Weih M (2005) Nitrogen storage and seasonal nitrogen cycling in populus: bridging molecular physiology and ecophysiology. New Phytol 167:19–30. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01451.x
Craine JM, Elmore AJ, Aidar MPM, Bustamante M, Dawson TE, Hobbie EA, Kahmen A, Mack MC, McLauchlan KK, Michelsen A, Nardoto GB, Pardo LH, Peñuelas J, Reich PB, Schuur EAG, Stock WD, Templer PH, Virginia RA, Welker JM, Wright IJ (2009a) Global patterns of foliar nitrogen isotopes and their relationships with climate, mycorrhizal fungi, foliar nutrient concentrations, and nitrogen availability. New Phytol 183:980–992. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02917.x
Craine JM, Ballantyne F, Peel M, Zambatis N, Morrow C, Stock WD (2009b) Grazing and landscape controls on nitrogen availability across 330 South African savanna sites. Austral Ecol 34:731–740. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.2009.01978.x
Danckwerts JE, Gordon AJ (1990) Partitioning, storage and remobilization of 14C assimilated by Themeda triandra Forssk. Afr J Range Forage Sci 7:97–105
Dybzinski R, Tilman D (2007) Resource use patterns predict long-term outcomes of plant competition for nutrients and light. Am Nat 170:305–318. doi:10.1086/519857
Eksteen J, Nkosi S (2009) Andover 2009 game count
Fargione J, Tilman D (2005) Niche differences in phenology and rooting depth promote coexistence with a dominant C4 bunchgrass. Oecologia 143:598–606. doi:10.1007/s00442-005-0010-y
February EC, Higgins SI (2010) The distribution of tree and grass roots in savannas in relation to soil nitrogen and water. S Afr J Bot 76:517–523. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2010.04.001
Frak E, Le Roux X, Millard P, Guillaumie S, Wendler R (2006) Nitrogen availability, local light regime and leaf rank effects on the amount and sources of N allocated within the foliage of young walnut (Juglans nigra × regia) trees. Tree Physiol 26:43–49
Gathumbi SM, Cadisch G, Buresh RJ, Giller KE (2003) Subsoil nitrogen capture in mixed legume stands as assessed by deep nitrogen-15 placement. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:573–582
Gaye CB, Edmunds WM (1996) Groundwater recharge estimation using chloride, stable isotopes and tritium profiles in the sands of northwestern Senegal. Environ Geol 27:246–251
Gebauer RLE, Ehleringer JR (2000) Water and nitrogen uptake patterns following moisture pulses in a cold desert community. Ecology 81:1415–1424. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2000) (081 [1415:WANUPF]2.0.CO;2)
Glass AD (2005) Homeostatic processes for the optimization of nutrient absorption: Physiology and molecular ecology. In: Bassirirad H (ed) Nutrient acquisition by plants. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 117–145
Handley LL, Raven JA (1992) The use of natural abundance of nitrogen isotopes in plant physiology and ecology. Plant Cell Environ 15:965–985. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1992.tb01650.x
Hartnett DC, Potgieter AF, Wilson GWT (2004) Fire effects on mycorrhizal symbiosis and root system architecture in southern African savanna grasses. Afr J Ecol 42:328–337. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2028.2004.00533.x
Hawkins H-J, Hettasch H, West AG, Cramer MD (2009) Hydraulic redistribution by Protea “Sylvia” (Proteaceae) facilitates soil water replenishment and water acquisition by an understorey grass and shrub. Funct Plant Biol 36:752–760. doi:10.1071/FP09046
Hesla BI, Tieszen HL, Boutton TW (1985) Seasonal water relations of savanna shrubs and grasses in Kenya, East Africa. J Arid Environ 8:15–31
Hobbie EA, Macko SA, Shugart HH (1999) Interpretation of nitrogen isotope signatures using the NIFTE model. Oecologia 120:405–415. doi:10.1007/s004420050873
Hogberg P (1990) 15N natural abundance as a possible marker of the ectomycorrhizal habit of trees in mixed African woodlands. New Phytol 115:483–486. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00474.x
Hogberg P (1997) 15N natural abundance in soil-plant systems. New Phytol 137:179–203
Hogberg P, Alexander IJ (1995) Roles of root symbioses in African woodland and forest: evidence from 15N abundance and foliar analysis. J Ecol 83:217–224
Hogberg P, Piearce GD (1986) Mycorrhizas in Zambian trees in relation to host taxonomy, vegetation type and successional patterns. J Ecol 74:775–785
Jacobs SM, Pettit NE, Naiman RJ (2007) Nitrogen fixation by the savanna tree Philenoptera violacea (Klotzsch) Schrire (apple leaf) of different ages in a semi-arid riparian landscape. S Afr J Bot 73:163–167. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2006.09.001
Knoop WT, Walker BH (1985) Interactions of woody and herbaceous vegetation in a southern African savanna. J Ecol 73:235–253
Kulmatiski A, Beard KH, Verweij RJT, February EC (2010) A depth-controlled tracer technique measures vertical, horizontal and temporal patterns of water use by trees and grasses in a subtropical savanna. New Phytol 188:199–209. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03338.x
Lehmann J, Muraoka T, Zech W (2001) Root activity patterns in an Amazonian agroforest with fruit trees determined by 32P, 33P and 15N applications. Agrofor Syst 52:185–197
Littell RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW, Wolfinger RD, Schabenberger O (2006) SAS for mixed models. SAS Institute, Cary
Ludwig F, Dawson TE, Prins HHT, Berendse F, Kroon H (2004) Below-ground competition between trees and grasses may overwhelm the facilitative effects of hydraulic lift. Ecol Lett 7:623–631. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00615.x
Masclaux-Daubresse C, Daniel-Vedele F, Dechorgnat J, Chardon F, Gaufichon L, Suzuki A (2010) Nitrogen uptake, assimilation and remobilization in plants: challenges for sustainable and productive agriculture. Ann Bot 105:1141–1157. doi:10.1093/aob/mcq028
McKane RB, Johnson LC, Shaver GR, Nadelhoffer KJ, Rastetter EB, Fry B, Giblin AE, Kielland K, Kwiatkowski BL, Laundre JA, Murray G (2002) Resource-based niches provide a basis for plant species diversity and dominance in arctic tundra. Nature 415:68–71. doi:10.1038/415068a
Millard P, Grelet G-A (2010) Nitrogen storage and remobilization by trees: ecophysiological relevance in a changing world. Tree Physiol 30:1083–1095. doi:10.1093/treephys/tpq042
Nadelhoffer KJ, Fry B (1994) Nitrogen isotope studies in forest ecosystems. In: Lajtha K, Michener RH (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp 22–44
Robinson D (2001) δ15N as an integrator of the nitrogen cycle. Trends Ecol Evol 16:153–162. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(00)02098-X
Sala OE, Golluscio RA, Lauenroth WK, Soriano A (1989) Resource partitioning between shrubs and grasses in the Patagonian steppe. Oecologia 81:501–505. doi:10.1007/BF00378959
Sankaran M, Hanan NP, Scholes RJ, Ratnam J, Augustine DJ, Cade BS, Gignoux J, Higgins SI, Le Roux X, Ludwig F, Ardo J, Banyikwa F, Bronn A, Bucini G, Caylor KK, Coughenour MB, Diouf A, Ekaya W, Feral CJ, February EC, Frost PGH, Hiernaux P, Hrabar H, Metzger KL, Prins HHT, Ringrose S, Sea W, Tews J, Worden J, Zambatis N (2005) Determinants of woody cover in African savannas. Nature 438:846–849. doi:10.1038/nature04070
Schoener TW (1974) Resource partitioning in ecological communities. Science 185(4145):27–39
Scholes MC, Scholes RJ, Otter LB, Woghiren AJ (2003) Biogeochemisty: the cycling of elements. In: Du Toit JT, Rogers KH, Biggs HC (eds) The Kruger experience: ecology and management of savanna heterogeneity. Island Press, Washington, pp 130–148
Shearer G, Kohl DH (1986) N2-fixation in field settings : estimations based on natural 15N abundance. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:699–756
Sternberg LDSL, Bucci S, Franco A, Goldstein G, Hoffman WA, Meinzer FC, Moreira MZ, Scholz F (2005) Long range lateral root activity by Neotropical savanna trees. Plant Soil 270:169–178. doi:10.1007/s11104-004-1334-9
Stroosnijder L (1991) The soils of Sahel and the experimental fields. In: De Vries FWTP, Mjiteye MA (eds) The productivity of Sahelian rangelands, a study of soils, vegetation and exploitation of this natural resource. Wageningen University, Wageningen, pp 52–71
Swap RJ, Aranibar JN, Dowty PR, Gilhooly WP III, Macko SA (2004) Natural abundance of 13C and 15N in C3 and C4 vegetation of southern Africa: patterns and implications. Glob Chang Biol 10:350–358. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.00702.x
Tagliavini M, Millard P (2005) Fluxes of nitrogen within deciduous fruit trees. Acta Sci Pol Hort Cult 4:21–30
Vitousek PM, Shearer G, Kohl DH (1989) Foliar 15N natural abundance in Hawaiian rainforest: patterns and possible mechanism. Oecologia 78:383–388
Walter H (1971) Ecology of tropical and subtropical vegetation. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh
Wang L, Macko SA (2011) Constrained preferences in nitrogen uptake across plant species and environments. Plant Cell Environ 34:525–534. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02260.x
Zencich SJ, Froend RH, Turner JV, Gailitis V (2002) Influence of groundwater depth on the seasonal sources of water accessed by Banksia tree species on a shallow, sandy coastal aquifer. Oecologia 131:8–19. doi:10.1007/s00442-001-0855-7
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Shell Research Foundation and the Resource Ecology Group at Wageningen University. The Mpumalanga Tourism and Parks Agency kindly granted us permission to carry out this study at the AGR and we thank the management and staff of AGR for their cooperation. The management and staff of Wits Rural Facility of the University of Witwatersrand are thanked for providing work space and assistance in the field. We thank Phanuel Manzini and Floyd Manzini for their assistance in the field and laboratory in South Africa. Grant Hall is thanked for his help in the stable isotope laboratory. K. Yoganand helped in fieldwork and provided comments on earlier versions of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Allan Green.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priyadarshini, K.V.R., Prins, H.H.T., de Bie, S. et al. Overlap in nitrogen sources and redistribution of nitrogen between trees and grasses in a semi-arid savanna. Oecologia 174, 1107–1116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2848-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2848-8