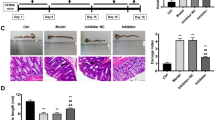
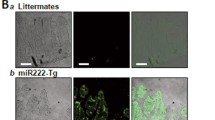
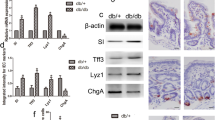
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterised by insulin deficiency/resistance and hyperglycaemia. We previously reported the presence of an impaired tight junction and decreased expression of occludin (Ocln) and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) in the intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) of type 1 DM mice, but the exact mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in impairing the tight junction in IECs of DM mice. Using an integrated comparative miRNA microarray, miR-429 was found to be up-regulated in IECs of type 1 DM mice. Then, miR-429 was confirmed to directly target the 3’-UTR of Ocln, although it did not target ZO-1. Moreover, miR-429 down-regulated the Ocln expression in IEC-6 cells in vitro. Finally, exogenous agomiRNA-429 was shown to down-regulate Ocln and induce intestinal barrier dysfunction in normal mice, while exogenous antagomiRNA-429 up-regulated Ocln in vivo and improved intestinal barrier function in DM mice. In conclusion, increased miR-429 could down-regulate the expression of Ocln by targeting the Ocln 3′-UTR, which impaired intestinal barrier function in DM mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 3’-UTR:
-
3’-untranslated region
- 4-kD FITC-dextran:
-
4-kD fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated dextran
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- DE:
-
Diabetic enteropathy
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- FSS:
-
Fluorescein sodium salt
- IEC:
-
Intestinal epithelial cell
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- miRNA/miR:
-
MicroRNAs
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- NC:
-
Negative control
- Ocln:
-
Occludin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- STZ:
-
Streptozocin
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- TJ:
-
Tight junction
- ZO-1:
-
Zonula occludens-1
References
Al-Sadi R, Khatib K, Guo S, Ye D, Youssef M, Ma T (2011) Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G1054–G1064
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
American DA (2010) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 33(Suppl 1):S62–S69
Arrieta MC, Bistritz L, Meddings JB (2006) Alterations in intestinal permeability. Gut 55:1512–1520
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bruewer M, Luegering A, Kucharzik T, Parkos CA, Madara JL, Hopkins AM, Nusrat A (2003) Proinflammatory cytokines disrupt epithelial barrier function by apoptosis-independent mechanisms. J Immunol 171:6164–6172
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T et al (2009) Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven improvement of gut permeability. Gut 58:1091–1103
Chatzigeorgiou A, Halapas A, Kalafatakis K, Kamper E (2009) The use of animal models in the study of diabetes mellitus. In Vivo 23:245–258
Clayburgh DR, Shen L, Turner JR (2004) A porous defense: the leaky epithelial barrier in intestinal disease. Lab Invest 84:282–291
De Block CE, De Leeuw IH, Pelckmans PA, Van Gaal LF (2006) Current concepts in gastric motility in diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev 2:113–130
de Ferranti SD, de Boer IH, Fonseca V et al (2014) Type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circulation 130:1110–1130
Du Y, Xu Y, Ding L, Yao H, Yu H, Zhou T, Si J (2009) Down-regulation of miR-141 in gastric cancer and its involvement in cell growth. J Gastroenterol 44:556–561
Furman BL (2015) Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 70:5.47.1–5.47.20
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Gao H, Liu C (2014) miR-429 represses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HBV-related HCC. Biomed Pharmacother 68:943–949
Gracz AD, Ramalingam S, Magness ST (2010) Sox9 expression marks a subset of CD24-expressing small intestine epithelial stem cells that form organoids in vitro. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G590–G600
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, Stoffel M (2005) Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with 'antagomirs'. Nature 438:685–689
Li A, Omura N, Hong SM, Vincent A, Walter K, Griffith M, Borges M, Goggins M (2010) Pancreatic cancers epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and miR-200b levels. Cancer Res 70:5226–5237
Li L, Tang J, Zhang B et al (2015) Epigenetic modification of MiR-429 promotes liver tumour-initiating cell properties by targeting Rb binding protein 4. Gut 64:156–167
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433:769–773
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Marcusson EG, Teruya-Feldstein J, Bell GW, Weinberg RA (2010) Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol 28:341–347
Marchiando AM, Shen L, Graham WV, Edelblum KL, Duckworth CA, Guan Y, Montrose MH, Turner JR, Watson AJ (2011) The epithelial barrier is maintained by in vivo tight junction expansion during pathologic intestinal epithelial shedding. Gastroenterology 140:1208–1218.e1-2
Martinez C, Lobo B, Pigrau M et al (2013) Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: an organic disorder with structural abnormalities in the jejunal epithelial barrier. Gut 62:1160–1168
McArthur K, Feng B, Wu Y, Chen S, Chakrabarti S (2011) MicroRNA-200b regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated alterations in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 60:1314–1323
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H, Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD, Patel T (2006) Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 130:2113–2129
Min XH, Yu T, Qing Q, Yuan YH, Zhong W, Chen GC, Zhao LN, Deng N, Zhang LF, Chen QK (2014) Abnormal differentiation of intestinal epithelium and intestinal barrier dysfunction in diabetic mice associated with depressed Notch/NICD transduction in Notch/Hes1 signal pathway. Cell Biol Int 38:1194–1204
Mruk DD, Yan CC (2015) The mammalian blood-testis barrier: its biology and regulation. Endocr Rev er20141101
Nikaido H (2003) Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:593–656
Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM (2013) Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med 19:1584–1596
Ogbonnaya KI, Arem R (1990) Diabetic diarrhea. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med 150:262–267
Ordog T, Hayashi Y, Gibbons SJ (2009) Cellular pathogenesis of diabetic gastroenteropathy. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 55:315–343
Parlesak A, Schafer C, Schutz T, Bode JC, Bode C (2000) Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. J Hepatol 32:742–747
Qu HQ, Jiang ZD (2014) Clostridium difficile infection in diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 105:285–294
Reddy MA, Jin W, Villeneuve L, Wang M, Lanting L, Todorov I, Kato M, Natarajan R (2012) Pro-inflammatory role of microrna-200 in vascular smooth muscle cells from diabetic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:721–729
Saitou M, Fujimoto K, Doi Y, Itoh M, Fujimoto T, Furuse M, Takano H, Noda T, Tsukita S (1998) Occludin-deficient embryonic stem cells can differentiate into polarized epithelial cells bearing tight junctions. J Cell Biol 141:397–408
Sapone A, de Magistris L, Pietzak M et al (2006) Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 55:1443–1449
Schulzke JD, Gitter AH, Mankertz J, Spiegel S, Seidler U, Amasheh S, Saitou M, Tsukita S, Fromm M (2005) Epithelial transport and barrier function in occludin-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669:34–42
Sharma A, Ng H, Kumar A, Teli K, Randhawa J, Record J, Maroules M (2014) Colorectal cancer: Histopathologic differences in tumor characteristics between patients with and without diabetes. Clin Colorectal Cancer 13:54–61
Steed E, Balda MS, Matter K (2010) Dynamics and functions of tight junctions. Trends Cell Biol 20:142–149
Tang Y, Banan A, Forsyth CB, Fields JZ, Lau CK, Zhang LJ, Keshavarzian A (2008) Effect of alcohol on miR-212 expression in intestinal epithelial cells and its potential role in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:355–364
Turner JR (2009) Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:799–809
Wallberg M, Cooke A (2013) Immune mechanisms in type 1 diabetes. Trends Immunol 34:583–591
Wong V, Gumbiner BM (1997) A synthetic peptide corresponding to the extracellular domain of occludin perturbs the tight junction permeability barrier. J Cell Biol 136:399–409
Yang Y, Ma Y, Shi C et al (2013) Overexpression of miR-21 in patients with ulcerative colitis impairs intestinal epithelial barrier function through targeting the Rho GTPase RhoB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 434:746–752
Ye D, Guo S, Al-Sadi R, Ma TY (2011) MicroRNA regulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. Gastroenterology 141:1323–1333
Ye D, Ma TY (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms that mediate basal and tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced regulation of myosin light chain kinase gene activity. J Cell Mol Med 12:1331–1346
Yu D, Marchiando AM, Weber CR, Raleigh DR, Wang Y, Shen L, Turner JR (2010) MLCK-dependent exchange and actin binding region-dependent anchoring of ZO-1 regulate tight junction barrier function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8237–8241
Zhong XY, Yu T, Zhong W, Li JY, Xia ZS, Yuan YH, Yu Z, Chen QK (2015) Lgr5 positive stem cells sorted from small intestines of diabetic mice differentiate into higher proportion of absorptive cells and Paneth cells in vitro. Dev Growth Differ 57:453–465
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270442 and No. 81370475).
Contribution statement
Tao Yu and Xi-Ji Lu carried out the molecular biology studies, participated in the sequence alignment and drafted the manuscript. Ti-Dong Shan and Can-Ze Huang carried out the immunofluorescence assays. Hui Ouyang and Ji-Hao Xu participated in the induction of the diabetes model. Jie-Yao Li and Hong-Sheng Yang conducted the statistical analysis. Wa Zhong and Zhong-Sheng Xia participated in the design of the study and participated in the sequence alignment. Qi-Kui Chen conceived the study, participated in its design and coordination, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Tao Yu and Xi-Ji Lu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 19.8 kb)
Figure 6
MiR-429 did not affect the expressions of ZO-1, Claudin-2, and Claudin-3 in IEC-6. (a-c) The mRNA and protein expressions of ZO-1, Claudin-2, and Claudin-3 in IEC-6 cells (48 hours after transfection) were assessed by qRTPCR (a) and Western blot (b) in the three groups. The integrated intensities of bands (c) were calculated using β-actin as an endogenous control. (JPG 112 kb)
ESM 3
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, T., Lu, XJ., Li, JY. et al. Overexpression of miR-429 impairs intestinal barrier function in diabetic mice by down-regulating occludin expression. Cell Tissue Res 366, 341–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2435-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2435-5