Abstract
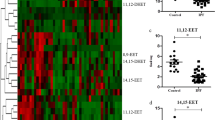
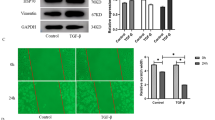
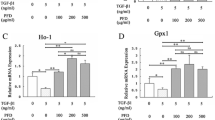
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), the metabolites of arachidonic acid derived from the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) epoxygenases, are mainly metabolized by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to their corresponding diols. EETs but not their diols, have anti-inflammatory properties and inhibition of sEH might provide protective effects against inflammatory fibrosis. We test the effects of a selected sEH inhibitor, 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea (TPPU), on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (PF) in mice. A mouse model of PF was established by intratracheal injection of bleomycin and TPPU was administered for 21 days after bleomycin injection. We found TPPU treatment improved the body weight loss and survival rate of bleomycin-stimulated mice. Histological examination showed that TPPU treatment alleviated bleomycin-induced inflammation and maintained the alveolar structure of the pulmonary tissues. TPPU also decreased the bleomycin-induced deposition of collagen and the expression of procollagen I mRNA in lung tissues of mice. TPPU decreased the transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6 levels in the serum of bleomycin-stimulated mice. Furthermore, TPPU inhibited the proliferation and collagen synthesis of mouse fibroblasts and partially reversed TGF-β1-induced α-smooth muscle actin expression. Our results indicate that the inhibition of sEH attenuates bleomycin-induced inflammation and collagen deposition and therefore prevents bleomycin-induced PF in a mouse model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaudhuri N, Duck A, Frank R, Holme J, Leonard C (2014) Real world experiences: pirfenidone is well tolerated in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med 108:224–226
Chen G, Wang P, Zhao G, Xu G, Gruzdev A, Zeldin DC, Wang DW (2011) Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase CYP2J2 attenuates nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat 96:63–71
Chen W, Yang S, Ping W, Fu X, Xu Q, Wang J (2015) CYP2J2 and EETs protect against lung ischemia/reperfusion injury via anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:2043–2054
Della Latta V, Cecchettini A, Del Ry S, Morales MA (2015) Bleomycin in the setting of lung fibrosis induction: from biological mechanisms to counteractions. Pharmacol Res 97:122–130
Feng W, Xu X, Zhao G, Li G, Liu T, Zhao J, Dong R, Wang DW, Tu L (2013) EETs and CYP2J2 inhibit TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in pulmonary artery endothelial cells and TGF-beta1-induced migration in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Int J Mol Med 32:685–693
Kim J, Imig JD, Yang J, Hammock BD, Padanilam BJ (2014) Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents renal interstitial fibrosis and inflammation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 307:F971–F980
Kim J, Yoon SP, Toews ML, Imig JD, Hwang SH, Hammock BD, Padanilam BJ (2015) Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents renal interstitial fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 308:F131–F139
Kiss L, Schutte H, Padberg W, Weissmann N, Mayer K, Gessler T, Voswinckel R, Seeger W, Grimminger F (2010) Epoxyeicosatrienoates are the dominant eicosanoids in human lungs upon microbial challenge. Eur Respir J 36:1088–1098
Lee AR, Pechenino AS, Dong H, Hammock BD, Knowlton AA (2013) Aging, estrogen loss and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). PLoS One 8:e70719
Liu JY, Lin YP, Qiu H, Morisseau C, Rose TE, Hwang SH, Chiamvimonvat N, Hammock BD (2013) Substituted phenyl groups improve the pharmacokinetic profile and anti-inflammatory effect of urea-based soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in murine models. Eur J Pharm Sci 48:619–627
Liu W, Wan J, Han JZ, Li C, Feng DD, Yue SJ, Huang YH, Chen Y, Cheng QM, Li Y, Luo ZQ (2013) Antiflammin-1 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Respir Res 14:101
Loot AE, Fleming I (2011) Cytochrome P450-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and pulmonary hypertension: central role of transient receptor potential C6 channels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 57:140–147
Murakami S, Nagaya N, Itoh T, Fujii T, Iwase T, Hamada K, Kimura H, Kangawa K (2004) C-type natriuretic peptide attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L1172–L1177
Norton SK, Wijesinghe DS, Dellinger A, Sturgill J, Zhou Z, Barbour S, Chalfant C, Conrad DH, Kepley CL (2012) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids are involved in the C(70) fullerene derivative-induced control of allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 130:761–769.e2
Raghu G, Weycker D, Edelsberg J, Bradford WZ, Oster G (2006) Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:810–816
Revermann M, Barbosa-Sicard E, Dony E, Schermuly RT, Morisseau C, Geisslinger G, Fleming I, Hammock BD, Brandes RP (2009) Inhibition of the soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. J Hypertens 27:322–331
Scotton CJ, Chambers RC (2007) Molecular targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus. Chest 132:1311–1321
Senouvo FY, Tabet Y, Morin C, Albadine R, Sirois C, Rousseau E (2011) Improved bioavailability of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids reduces TP-receptor agonist-induced tension in human bronchi. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 301:L675–682
Sheppard D (2006) Transforming growth factor beta: a central modulator of pulmonary and airway inflammation and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:413–417
Sirish P, Li N, Liu JY, Lee KS, Hwang SH, Qiu H, Zhao C, Ma SM, Lopez JE, Hammock BD, Chiamvimonvat N (2013) Unique mechanistic insights into the beneficial effects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in the prevention of cardiac fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:5618–5623
Spector AA, Fang X, Snyder GD, Weintraub NL (2004) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): metabolism and biochemical function. Prog Lipid Res 43:55–90
Ulu A, Appt S, Morisseau C, Hwang SH, Jones PD, Rose TE, Dong H, Lango J, Yang J, Tsai HJ, Miyabe C, Fortenbach C, Adams MR, Hammock BD (2012) Pharmacokinetics and in vivo potency of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in cynomolgus monkeys. Br J Pharmacol 165:1401–1412
Wynn TA (2011) Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med 208:1339–1350
Xu X, Zhang XA, Wang DW (2011) The roles of CYP450 epoxygenases and metabolites, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, in cardiovascular and malignant diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:597–609
Yang J, Schmelzer K, Georgi K, Hammock BD (2009) Quantitative profiling method for oxylipin metabolome by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:8085–8093
Yang J, Bratt J, Franzi L, Liu JY, Zhang G, Zeki AA, Vogel CF, Williams K, Dong H, Lin Y, Hwang SH, Kenyon NJ, Hammock BD (2015) Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor attenuates inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 52:46–55
Yu G, Zeng X, Wang H, Hou Q, Tan C, Xu Q (2015) 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid suppresses cigarette smoke extract-induced apoptosis in lung epithelial cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:474–486
Zhao G, Tu L, Li X, Yang S, Chen C, Xu X, Wang P, Wang DW (2012) Delivery of AAV2-CYP2J2 protects remnant kidney in the 5/6-nephrectomized rat via inhibition of apoptosis and fibrosis. Hum Gene Ther 23:688–699
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Special Funds for Major State Basic Research Projects (2012CB518104), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81170059), Project supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20130162110052) and was partially funded by the NIEHS grant ES02710 and American Asthma Foundation #09-0269.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Sun, GY., Liu, T. et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3- (1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Cell Tissue Res 363, 399–409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2262-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2262-0