Abstract
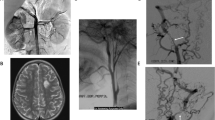
Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita (CMTC) is a congenital localized or generalized vascular anomaly, usually sporadic in occurrence. It can be associated with other cutaneous or systemic manifestations. About 300 cases have been reported. The molecular etiology remains largely unknown. The main purpose of this study is to delineate the molecular basis for a syndromic CMTC phenotype in a consanguineous Saudi family. Clinical phenotyping including detailed neurological imaging, followed by autozygosity mapping and trio whole exome sequencing (WES) are also studied. We have identified a homozygous truncating mutation in ARL6IP6 as the likely cause of a syndromic form of CMTC associated with major dysmorphism, developmental delay, transient ischemic attacks and cerebral vascular malformations. This gene was previously implicated by genome wide association study (GWAS) as a susceptibility locus to ischemic stroke in young adults. We identify ARL6IP6 as a novel candidate gene for a syndromic form of CMTC. This suggests that ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIA) may represent, at least in some cases, the mild end of a phenotypic spectrum that has at its severe end autosomal recessive CMTC. This finding contributes to a growing appreciation of the continuum of Mendelian and common complex diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkuraya FS (2010) Autozygome decoded. Genetics in Medicine. 12(12):765–771
Alkuraya FS (2012) Discovery of rare homozygous mutations from studies of consanguineous pedigrees. Curr Protoc Hum Genet 6.12. 1–6:3
Alkuraya FS (2013) The application of next-generation sequencing in the autozygosity mapping of human recessive diseases. Hum Genet 132(11):1197–1211
Alkuraya FS (2015) Human knockout research: new horizons and opportunities. Trends Genet 31(2):108–115
Amitai DB, Fichman S, Merlob P, Morad Y, Lapidoth M, Metzker A (2000) Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita: clinical findings in 85 patients. Pediatr Dermatol 17(2):100
Cheng Y-C, O’Connell JR, Cole JW et al (2011) Genome-wide association analysis of ischemic stroke in young adults. G3: genes, Genomes. Genetics 1(6):505–514
Gerritsen M, Steijlen P, Brunner H, Rieu P (2000) Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita: report of 18 cases. Br J Dermatol 142(2):366–369
Gruppo MDRA, DeGrauw MDTJ, Palasis MDS, Kalinyak MDKA, Bofinger MDMK (1998) Strokes, cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita, and factor V Leiden. Pediatr Neurol 18(4):342–345
Hinek A, Jain S, Taylor G, Nykanen D, Chitayat D (2008) High copper levels and increased elastolysis in a patient with cutis marmorata teleangiectasia congenita. Am J Med Genet A 146A(19):2520–2527. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32474
Kienast A, Hoeger P (2009) Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita: a prospective study of 27 cases and review of the literature with proposal of diagnostic criteria. Clin Exp Dermatol 34(3):319–323
Mirzaa GM, Conway RL, Gripp KW, Lerman-Sagie T, Siegel DH, deVries LS, Lev D, Kramer N, Hopkins E, Graham JM Jr, Dobyns WB (2012) Megalencephaly-capillary malformation (MCAP) and megalencephaly–polydactyly–polymicrogyria–hydrocephalus (MPPH) syndromes: two closely related disorders of brain overgrowth and abnormal brain and body morphogenesis. Am J Med Genet A 158A(2):269–291
Torrelo A, Zambrano A, Happle R (2003) Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita and extensive mongolian spots: type 5 phacomatosis pigmentovascularis. Br J Dermatol 148(2):342–345
Torrelo A, Zambrano A, Happle R (2006) Large aberrant Mongolian spots coexisting with Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita (phacomatosis pigmentovascularis type V or phacomatosis cesiomarmorata). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20(3):308–310
Tsuruta D, Fukai K, Seto M et al (1999) Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis type IIIb associated with moyamoya disease. Pediatr Dermatol 16(1):35–38
Van Lohuizen C (1922) Über eine seltene angeborene Hautanomalie (cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita). Acta Derm Venereol 3(202):11
Van Schaik SM, Reneman L, Engelen M, Roos YB, Poll-The BT (2015) Strokelike episodes and cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita. J Child Neurol 30(1):129–132
Acknowledgments
We thank the family for their enthusiastic participation. We also thank the Genotyping and Sequencing Core Facilities at KFSHRC for their technical help. This study was supported by KACST Grant 13-BIO1113-20 (FSA) and King Salman Center for Disability Research grant (FSA).
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
I. S. Abumansour and H. Hijazi have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abumansour, I.S., Hijazi, H., Alazmi, A. et al. ARL6IP6, a susceptibility locus for ischemic stroke, is mutated in a patient with syndromic Cutis Marmorata Telangiectatica Congenita. Hum Genet 134, 815–822 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1561-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1561-6